1. Understanding the Mercedes-Benz ESP System
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in Mercedes-Benz vehicles is a sophisticated system designed to enhance driving safety by preventing skidding and loss of control. By understanding its components and how it functions, you can better diagnose and ad...
1. Understanding the Mercedes-Benz ESP System
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in Mercedes-Benz vehicles is a sophisticated system designed to enhance driving safety by preventing skidding and loss of control. By understanding its components and how it functions, you can better diagnose and address potential ESP malfunctions.
1.1. What is ESP and How Does it Work?
ESP stands for Electronic Stability Program. According to Mercedes-Benz, it is designed to detect and reduce skidding. ESP monitors wheel speed, steering angle, and lateral acceleration. If it detects a loss of control, it selectively applies brakes to individual wheels and adjusts engine power to help the driver maintain control. The system helps prevent oversteer (where the rear of the car slides out) and understeer (where the front of the car plows straight ahead).
- Sensors: ESP uses various sensors to monitor the vehicle’s behavior.
- Control Unit: The control unit analyzes the data from the sensors and determines if intervention is necessary.
- Hydraulic Unit: The hydraulic unit applies brakes to individual wheels as needed.
1.2. Key Components of the ESP System
The ESP system comprises several critical components that work together to ensure vehicle stability:
| Component |
Function |
| Wheel Speed Sensors |
Monitor the speed of each wheel to detect differences indicating a skid. |
| Steering Angle Sensor |
Measures the angle of the steering wheel to determine the driver’s intent. |
| Yaw Rate Sensor |
Detects the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis. |
| Lateral Acceleration Sensor |
Measures the sideways force acting on the vehicle. |
| ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) |
Prevents wheel lockup during braking, working in conjunction with ESP. |
1.3. Integration with Other Vehicle Systems
ESP integrates with other vehicle systems to provide a comprehensive safety net. For instance, it works with the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) to prevent wheel lockup during braking and the Traction Control System (TCS) to limit wheel spin during acceleration. It may also interface with the engine management system to reduce engine power when necessary.
- ABS (Anti-lock Braking System): Prevents wheel lockup during braking, improving steering control.
- TCS (Traction Control System): Limits wheel spin during acceleration, enhancing grip.
- Engine Management System: Reduces engine power to prevent wheel spin and maintain stability.
2. Identifying an ESP Malfunction
Recognizing the symptoms of an ESP malfunction is crucial for timely diagnosis and repair. The warning lights, changes in handling, and diagnostic codes can provide valuable clues.
2.1. Common Symptoms of ESP Issues
Several symptoms may indicate an ESP malfunction. These include:
- ESP Warning Light: The ESP warning light on the dashboard illuminates or flashes.
- Reduced Traction: Noticeable loss of traction, especially in slippery conditions.
- Erratic Handling: The vehicle feels unstable or difficult to control during turns or maneuvers.
- ABS Issues: Problems with the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS), as it is closely linked to ESP.
- Difficulty Starting: In some cases, an ESP malfunction can affect the vehicle’s ability to start.
- Stalling: The engine may stall unexpectedly.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to have your vehicle inspected by a qualified technician.
2.2. Interpreting ESP Warning Lights
The ESP warning light can display different messages, each indicating a specific issue:
- Solid Light: A solid ESP warning light typically indicates that the system is disabled or malfunctioning.
- Flashing Light: A flashing ESP warning light usually means that the system is actively engaged to correct a loss of traction.
- BAS/ESP Light: This indicates an issue with both the Brake Assist System (BAS) and ESP, suggesting a more complex problem.
Pay attention to the specific pattern of the warning light, as it can help narrow down the potential causes of the malfunction.
Diagnostic tools can retrieve error codes from the vehicle’s computer system, providing more detailed information about the ESP malfunction. Common codes include:
| Code |
Description |
Possible Cause |
| C1000 |
Control Unit Fault |
Faulty ESP control unit, wiring issues, or software problems. |
| C1101 |
ABS System Fault |
Problems with the ABS module, wheel speed sensors, or hydraulic unit. |
| C1200 |
Wheel Speed Sensor Malfunction |
Defective wheel speed sensor, damaged wiring, or sensor contamination. |
| C1401 |
Steering Angle Sensor Fault |
Malfunctioning steering angle sensor or wiring issues. |
| C1500 |
Yaw Rate Sensor Fault |
Faulty yaw rate sensor or wiring problems. |
| C1601 |
Lateral Acceleration Sensor Fault |
Defective lateral acceleration sensor or wiring issues. |
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we offer a range of diagnostic tools to help you accurately identify and resolve ESP malfunctions. Consider our advanced diagnostic tools for professional-grade insights, streamlining the repair process and reducing downtime. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for immediate assistance and expert advice.
3. Common Causes of ESP Malfunctions in Mercedes-Benz
Several factors can contribute to ESP malfunctions in Mercedes-Benz vehicles, ranging from sensor issues to electrical problems. Identifying the root cause is essential for effective repair.
3.1. Sensor Issues
Faulty sensors are a common cause of ESP malfunctions. The wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor, yaw rate sensor, and lateral acceleration sensor all play critical roles in the system’s operation.
- Wheel Speed Sensors: These sensors can fail due to physical damage, contamination, or electrical issues.
- Steering Angle Sensor: Misalignment, wear, or electrical faults can cause the steering angle sensor to malfunction.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: This sensor can be affected by vibration, physical damage, or electrical problems.
- Lateral Acceleration Sensor: Similarly, the lateral acceleration sensor can fail due to damage or electrical issues.
3.2. Electrical Problems
Electrical issues, such as wiring problems, loose connections, and voltage fluctuations, can also lead to ESP malfunctions. These problems can disrupt the communication between the sensors, control unit, and hydraulic unit, causing the system to fail.
3.3. ABS System Issues
Since ESP and ABS are closely linked, problems with the ABS system can also affect ESP. Issues such as a faulty ABS module, wheel speed sensor problems, or hydraulic unit malfunctions can trigger the ESP warning light.
3.4. Software and Control Unit Problems
Software glitches or a faulty ESP control unit can also cause ESP malfunctions. Software updates or reprogramming may be necessary to resolve these issues. In some cases, the control unit itself may need to be replaced.
3.5. Mechanical Issues
Mechanical problems, such as worn suspension components, misaligned wheels, or tire issues, can also contribute to ESP malfunctions. These issues can affect the vehicle’s stability and trigger the ESP system to activate unnecessarily.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing ESP Malfunctions
Diagnosing ESP malfunctions requires a systematic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you identify the root cause of the problem.
4.1. Preliminary Checks
Before diving into more complex diagnostics, start with these preliminary checks:
- Check the ESP Button: Ensure that the ESP system has not been accidentally turned off.
- Inspect Tires: Check the tire pressure and condition of all tires. Uneven tire wear or incorrect pressure can affect ESP performance.
- Visual Inspection: Look for any visible damage to sensors, wiring, or other components.
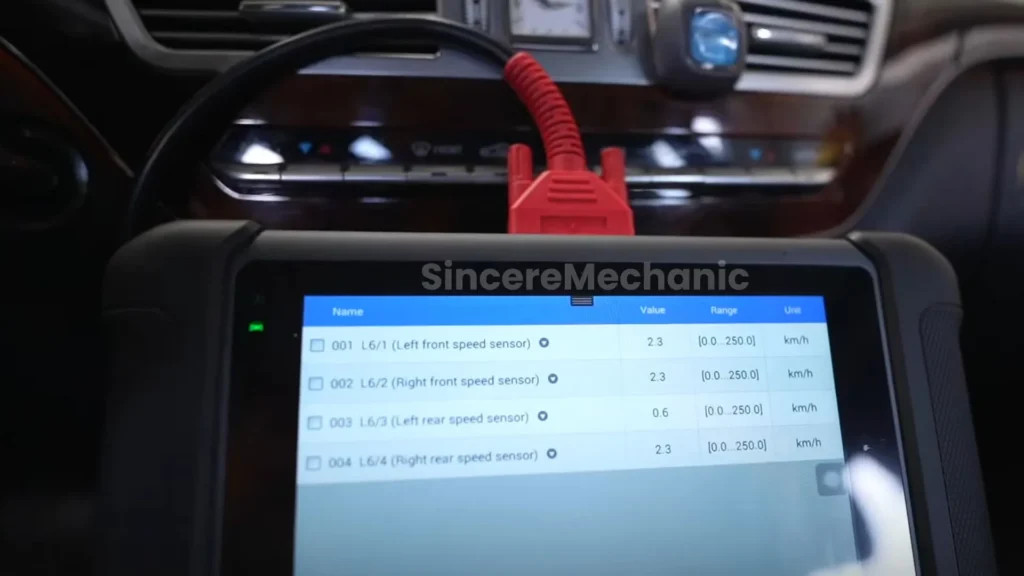
4.2. Using an OBD-II Scanner
An OBD-II scanner can retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from the vehicle’s computer system. Follow these steps:
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD-II scanner into the diagnostic port, typically located under the dashboard.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “on” position without starting the engine.
- Read the Codes: Follow the scanner’s instructions to read the stored DTCs.
- Interpret the Codes: Use a code lookup tool or consult a repair manual to interpret the codes and identify the potential causes of the ESP malfunction.
4.3. Testing Individual Components
If the DTCs point to a specific component, such as a wheel speed sensor, you can test the component using a multimeter or oscilloscope. Follow these steps:
- Locate the Component: Identify the location of the component you want to test.
- Disconnect the Connector: Disconnect the electrical connector from the component.
- Test for Continuity: Use a multimeter to test for continuity between the terminals of the component.
- Check Resistance: Measure the resistance of the component and compare it to the manufacturer’s specifications.
4.4. Checking Wiring and Connections
Inspect the wiring and connections associated with the ESP system for any signs of damage or corrosion. Follow these steps:
- Visual Inspection: Look for frayed wires, cracked insulation, or corroded connectors.
- Test for Voltage: Use a multimeter to check for proper voltage at the connectors.
- Check for Continuity: Test the continuity of the wiring harness to ensure there are no breaks or shorts.
For more complex issues, consider using advanced diagnostic tools such as:
- Oscilloscope: An oscilloscope can display the electrical signals from sensors and other components, allowing you to identify intermittent problems or signal distortions.
- Scan Tool with Live Data: A scan tool that can display live data from the ESP system can help you monitor the performance of individual components in real-time.
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we offer a comprehensive range of diagnostic tools to help you accurately diagnose and resolve ESP malfunctions. We provide solutions that enhance efficiency, reduce repair times, and improve overall customer satisfaction.
5. Solutions and Repairs for ESP Malfunctions
Once you’ve diagnosed the cause of the ESP malfunction, you can proceed with the necessary repairs. Common solutions include sensor replacement, wiring repairs, and control unit reprogramming.
5.1. Replacing Faulty Sensors
If a sensor is found to be defective, it will need to be replaced. Follow these steps:
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical shorts.
- Remove the Old Sensor: Remove the old sensor from its mounting location.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor and tighten the mounting hardware to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Reconnect the Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the sensor.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
5.2. Repairing Wiring Issues
Repairing wiring issues involves fixing damaged wires, replacing corroded connectors, and ensuring proper connections. Follow these steps:
- Identify the Damaged Wire: Locate the damaged wire or corroded connector.
- Repair the Wire: Repair the wire by splicing in a new section of wire or using heat-shrink tubing to insulate the damaged area.
- Replace the Connector: Replace the corroded connector with a new one.
- Ensure Proper Connections: Ensure that all connections are clean and secure.
5.3. Addressing ABS System Problems
Addressing ABS system problems may involve replacing the ABS module, repairing wheel speed sensor issues, or fixing hydraulic unit malfunctions. Follow these steps:
- Diagnose the ABS Issue: Use an OBD-II scanner to identify the specific ABS issue.
- Replace the ABS Module: If the ABS module is faulty, replace it with a new or remanufactured unit.
- Repair Wheel Speed Sensor Issues: Replace or repair any faulty wheel speed sensors.
- Fix Hydraulic Unit Malfunctions: Repair or replace the hydraulic unit if it is malfunctioning.
5.4. Reprogramming or Replacing the Control Unit
If the ESP control unit is found to be faulty or requires reprogramming, follow these steps:
- Check for Software Updates: Check with the manufacturer for any available software updates for the ESP control unit.
- Reprogram the Control Unit: Use a scan tool or programming tool to reprogram the control unit with the latest software.
- Replace the Control Unit: If reprogramming does not resolve the issue, replace the control unit with a new or remanufactured unit.
5.5. Mechanical Repairs
If mechanical issues are contributing to the ESP malfunction, address these issues by:
- Replacing Worn Suspension Components: Replace any worn ball joints, tie rod ends, or control arm bushings.
- Aligning the Wheels: Have the wheels aligned to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Addressing Tire Issues: Replace any worn or damaged tires and ensure proper tire pressure.
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we offer a wide range of tools and equipment to assist with these repairs, enhancing your ability to quickly and accurately address ESP malfunctions. Consider exploring our selection of automotive tools, designed to make repairs easier and more efficient.
6. Preventing Future ESP Malfunctions
Preventing future ESP malfunctions involves regular maintenance, proper driving habits, and timely repairs. Here are some tips to help you keep your ESP system in good working order.
6.1. Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for preventing ESP malfunctions. Follow these tips:
- Check Tire Pressure Regularly: Ensure that your tires are properly inflated to the recommended pressure.
- Inspect Tires for Wear: Regularly inspect your tires for signs of wear or damage.
- Check Wheel Alignment: Have your wheels aligned periodically to ensure proper handling and stability.
- Inspect Suspension Components: Inspect your suspension components for wear or damage.
6.2. Proper Driving Habits
Proper driving habits can also help prevent ESP malfunctions. Follow these tips:
- Avoid Aggressive Driving: Avoid aggressive acceleration, braking, and turning.
- Drive Safely in Slippery Conditions: Drive cautiously in wet, icy, or snowy conditions.
- Avoid Overloading the Vehicle: Avoid overloading the vehicle, as this can affect its stability.
6.3. Timely Repairs
Addressing any issues with your vehicle promptly can also help prevent ESP malfunctions. Follow these tips:
- Address Warning Lights Immediately: If the ESP warning light illuminates, have your vehicle inspected by a qualified technician as soon as possible.
- Repair Any Mechanical Issues: Repair any mechanical issues, such as worn suspension components or misaligned wheels, promptly.
- Keep Up with Scheduled Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for your vehicle.
7. The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET in ESP Diagnostics and Repairs
CARDIAGTECH.NET is your trusted partner for diagnosing and repairing ESP malfunctions. We offer a wide range of diagnostic tools, equipment, and expert advice to help you get your vehicle back on the road safely.
We offer a comprehensive selection of high-quality diagnostic tools to help you accurately identify and resolve ESP malfunctions. Our tools include:
- OBD-II Scanners: For reading and interpreting diagnostic trouble codes.
- Multimeters: For testing electrical components.
- Oscilloscopes: For analyzing electrical signals.
- Scan Tools with Live Data: For monitoring the performance of individual components in real-time.
Our diagnostic tools are designed to provide accurate and reliable results, helping you quickly identify the root cause of the ESP malfunction.
7.2. Expert Advice and Support
Our team of experienced technicians is available to provide expert advice and support to help you diagnose and repair ESP malfunctions. We can assist you with:
- Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes: We can help you understand the meaning of diagnostic trouble codes and identify the potential causes of the ESP malfunction.
- Testing Individual Components: We can provide guidance on how to test individual components using a multimeter or oscilloscope.
- Repairing Wiring Issues: We can offer advice on how to repair damaged wires or replace corroded connectors.
- Reprogramming or Replacing the Control Unit: We can provide guidance on how to reprogram or replace the ESP control unit.
In addition to diagnostic tools, we also offer a wide range of automotive tools and equipment to assist with ESP repairs. Our products include:
- Sensor Replacement Tools: For removing and installing sensors.
- Wiring Repair Kits: For repairing damaged wires and connectors.
- Suspension Repair Tools: For repairing or replacing suspension components.
- Wheel Alignment Equipment: For aligning the wheels to the manufacturer’s specifications.
Our tools and equipment are designed to make ESP repairs easier and more efficient.
For expert advice and support, contact CARDIAGTECH.NET at:
- Address: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CARDIAGTECH.NET
8. Case Studies: Real-World ESP Malfunction Scenarios
Examining real-world scenarios can provide valuable insights into ESP malfunctions and their resolutions. Here are a few case studies to illustrate common issues and their solutions.
8.1. Case Study 1: Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
Vehicle: 2016 Mercedes-Benz C300
Symptoms: ESP warning light illuminated, ABS warning light illuminated, reduced traction.
Diagnosis: Using an OBD-II scanner, the technician retrieved a code indicating a faulty wheel speed sensor on the front left wheel. The technician then tested the sensor using a multimeter and confirmed that it was not functioning properly.
Solution: The technician replaced the faulty wheel speed sensor with a new one. After clearing the diagnostic trouble codes, the ESP and ABS warning lights turned off, and the vehicle’s traction control system returned to normal operation.
8.2. Case Study 2: Steering Angle Sensor Misalignment
Vehicle: 2018 Mercedes-Benz E300
Symptoms: ESP warning light illuminated, erratic handling during turns.
Diagnosis: The technician used an OBD-II scanner to retrieve a code indicating a steering angle sensor misalignment. The technician then used a scan tool with live data to monitor the steering angle sensor and confirmed that it was not providing accurate readings.
Solution: The technician realigned the steering angle sensor using a scan tool. After clearing the diagnostic trouble codes, the ESP warning light turned off, and the vehicle’s handling returned to normal.
8.3. Case Study 3: Wiring Issue
Vehicle: 2017 Mercedes-Benz GLC300
Symptoms: ESP warning light illuminated, intermittent ABS issues.
Diagnosis: The technician used an OBD-II scanner to retrieve a code indicating an electrical issue in the ABS system. The technician then performed a visual inspection of the wiring harness and found a damaged wire near the ABS module.
Solution: The technician repaired the damaged wire by splicing in a new section of wire and insulating the connection with heat-shrink tubing. After clearing the diagnostic trouble codes, the ESP warning light turned off, and the ABS system returned to normal operation.
9. The Economic Impact of ESP Malfunctions
ESP malfunctions can have significant economic consequences for vehicle owners. Understanding these costs can help you make informed decisions about maintenance and repairs.
9.1. Cost of Diagnosis
The cost of diagnosing an ESP malfunction can vary depending on the complexity of the issue and the diagnostic tools used. On average, you can expect to pay between $75 and $150 for a diagnostic scan.
9.2. Cost of Repairs
The cost of repairing an ESP malfunction can also vary depending on the specific issue. Common repairs and their estimated costs include:
| Repair |
Estimated Cost |
| Wheel Speed Sensor Replacement |
$150 – $300 |
| Steering Angle Sensor Replacement |
$200 – $400 |
| Yaw Rate Sensor Replacement |
$250 – $500 |
| ABS Module Replacement |
$500 – $1,000 |
| Wiring Repair |
$100 – $300 |
| Control Unit Reprogramming |
$100 – $300 |
| Wheel Alignment |
$75 – $150 |
9.3. Potential for Further Damage
If an ESP malfunction is not addressed promptly, it can lead to further damage to other vehicle systems. For example, a faulty wheel speed sensor can cause the ABS system to malfunction, which can lead to brake damage and increased risk of accidents.
9.4. Decreased Resale Value
An ESP malfunction can also decrease the resale value of your vehicle. Potential buyers may be hesitant to purchase a vehicle with known safety issues, which can reduce the price you can command.
9.5. Increased Insurance Premiums
In some cases, an ESP malfunction can lead to increased insurance premiums. If the malfunction results in an accident, your insurance company may raise your rates due to the increased risk.