Sensor Esp Mercedes is a critical component for vehicle safety and stability. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we provide in-depth knowledge and solutions related to Mercedes ESP systems, helping you understand, troubleshoot, and maintain your vehicle’s stability control. This guide covers everything from understanding the system to diagnosing issues, offering expert insights and practical advice to ensure your Mercedes-Benz delivers optimal performance. Find the ideal diagnostic tools to keep your Mercedes running smoothly.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the ESP System in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 1.1. What is ESP?
- 1.2. How Does ESP Work?
- 1.3. Key Components of the ESP System
- 1.4. ESP vs. Other Stability Systems
- 1.5. Benefits of Having a Functional ESP System
- 2. Identifying Issues with the Sensor ESP Mercedes
- 2.1. Common Symptoms of ESP Problems
- 2.2. Understanding the ESP Warning Lights
- 2.3. Diagnosing the ESP System
- 2.4. Using Diagnostic Tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET
- 2.5. Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3. Causes of ESP System Malfunctions
- 3.1. Sensor Failures
- 3.2. Wiring and Electrical Issues
- 3.3. Hydraulic Unit Problems
- 3.4. Control Unit Failures
- 3.5. Wheel Alignment and Tire Issues
- 4. How to Fix Sensor ESP Mercedes Issues
- 4.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing a Faulty Sensor
- 4.2. Addressing Wiring Problems
- 4.3. Repairing or Replacing the Hydraulic Unit
- 4.4. Fixing Control Unit Issues
- 4.5. Ensuring Proper Wheel Alignment and Tire Condition
- 5. Preventing Future ESP System Problems
- 5.1. Regular Maintenance Tips
- 5.2. Best Practices for Driving in Adverse Conditions
- 5.3. The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET in Maintaining Your ESP System
- 6. Real-World Scenarios and Solutions
- 6.1. Case Study 1: Wheel Speed Sensor Failure
- 6.2. Case Study 2: Wiring Issue
- 6.3. Case Study 3: Hydraulic Unit Problem
- 7. The Future of ESP Technology in Mercedes-Benz
- 7.1. Advancements in ESP Systems
- 7.2. Integration with Autonomous Driving Systems
- 7.3. CARDIAGTECH.NET’s Commitment to Innovation
- 8. ESP System Maintenance Checklist
- 8.1. Monthly Checks
- 8.2. Bi-Annual Checks
- 8.3. Annual Checks
- 9. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET for Expert Assistance
- 9.1. How to Reach Us
- 9.2. Schedule a Consultation
- 9.3. Order Diagnostic Tools and Parts
- 10.1. What does the ESP warning light mean on my Mercedes-Benz?
- 10.2. Can I drive my Mercedes-Benz with the ESP warning light on?
- 10.3. How do I reset the ESP system on my Mercedes-Benz?
- 10.4. What are the common causes of ESP system malfunctions?
- 10.5. How can I diagnose ESP system problems?
- 10.6. Can I replace an ESP sensor myself?
- 10.7. What diagnostic tools does CARDIAGTECH.NET recommend for Mercedes-Benz ESP systems?
- 10.8. How often should I have my ESP system checked?
- 10.9. What are the benefits of having a functional ESP system?
- 10.10. How can CARDIAGTECH.NET help me maintain my ESP system?
1. Understanding the ESP System in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
1.1. What is ESP?
Electronic Stability Program (ESP), is a vital safety feature in Mercedes-Benz vehicles. It is designed to prevent skidding and loss of control, especially in challenging driving conditions. This system actively monitors the vehicle’s direction and compares it to the driver’s intended path. When a discrepancy is detected, ESP intervenes by applying brakes to individual wheels and adjusting engine power to help the driver maintain control.
1.2. How Does ESP Work?
ESP integrates several sensors to monitor various parameters:
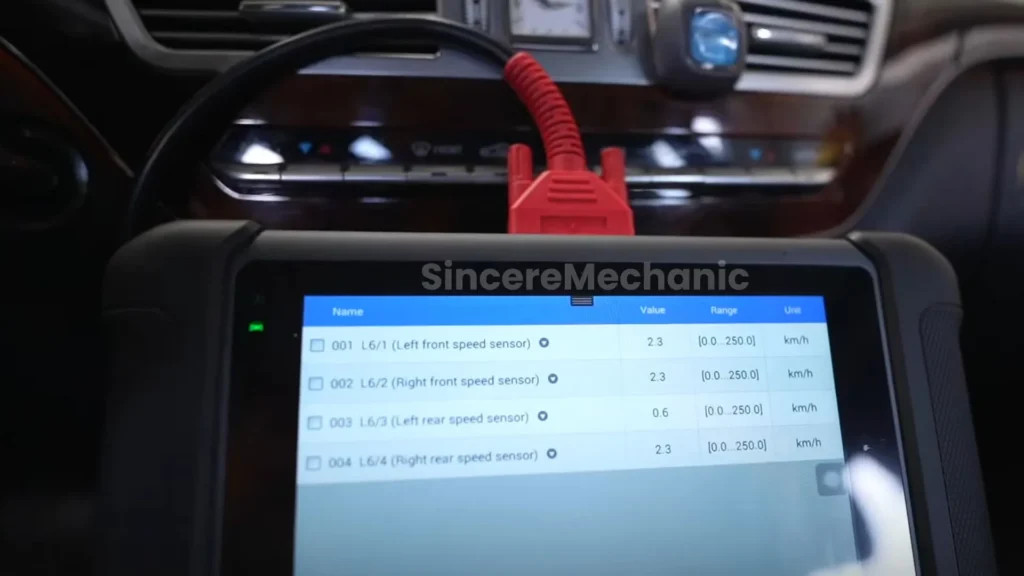
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Determine if any wheel is spinning faster or slower than others.
- Steering Angle Sensor: Measures the angle of the steering wheel, indicating the driver’s intended direction.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: Measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis, detecting if the car is turning more or less than intended.
- Lateral Acceleration Sensor: Measures the sideways force acting on the vehicle, indicating potential skidding.
When these sensors detect a potential loss of control, the ESP system rapidly calculates the necessary corrective actions. It can apply braking force to one or more wheels independently, reducing engine torque to help the vehicle regain stability. This intervention happens within milliseconds, often before the driver even realizes there’s a problem.
1.3. Key Components of the ESP System
The ESP system comprises several critical components:
- Control Unit: The brain of the ESP system, processing sensor data and determining the necessary corrective actions.
- Hydraulic Unit: Contains valves and pumps that control the brake pressure to individual wheels.
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Located at each wheel, these sensors provide data on wheel rotation speed.
- Steering Angle Sensor: Mounted on the steering column, this sensor measures the angle of the steering wheel.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: Usually located under the seat, this sensor measures the vehicle’s rotation.
- Lateral Acceleration Sensor: Also typically under the seat, this sensor measures sideways force.
1.4. ESP vs. Other Stability Systems
While many modern vehicles have stability control systems, Mercedes-Benz ESP stands out due to its integration and sophistication. Some other systems include:
- Traction Control System (TCS): Primarily focuses on preventing wheelspin during acceleration.
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): Prevents wheels from locking up during braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control.
- Electronic Brake-force Distribution (EBD): Optimizes brake force distribution between the front and rear wheels.
ESP combines the functions of TCS, ABS, and EBD, enhancing them with yaw control to provide a more comprehensive safety net.
1.5. Benefits of Having a Functional ESP System
A properly functioning ESP system offers numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Safety: Reduces the risk of accidents by helping drivers maintain control in critical situations.
- Improved Handling: Provides better stability and control, especially in adverse weather conditions.
- Reduced Skidding: Minimizes the likelihood of skidding on slippery surfaces.
- Increased Confidence: Gives drivers greater confidence behind the wheel, knowing the vehicle has an added layer of protection.
2. Identifying Issues with the Sensor ESP Mercedes
2.1. Common Symptoms of ESP Problems
Several symptoms can indicate issues with the ESP system:
- ESP Warning Light On: The most obvious sign is the ESP warning light illuminating on the dashboard.
- Reduced Stability: Vehicle feels less stable than usual, especially when cornering or driving on uneven surfaces.
- Erratic Braking: Unusual braking behavior, such as unexpected activation of the ABS or uneven brake force.
- Loss of Traction: Difficulty maintaining traction, especially during acceleration or on slippery surfaces.
- Steering Issues: Difficulty steering or a feeling of looseness in the steering wheel.
2.2. Understanding the ESP Warning Lights
The ESP warning light can appear in different ways, each indicating a specific condition:
- Solid Light: A solid ESP warning light typically indicates that the ESP system is disabled or has detected a fault.
- Flashing Light: A flashing ESP warning light usually means that the ESP system is actively intervening to stabilize the vehicle.
- ESP and ABS Lights On: If both the ESP and ABS warning lights are illuminated, it suggests a more significant issue affecting both systems.
- BAS ESP Light: This light indicates an issue with the Brake Assist System (BAS), which works in conjunction with ESP.
2.3. Diagnosing the ESP System
Diagnosing ESP issues requires a systematic approach:
- Visual Inspection: Check for any visible damage to the ESP components, such as sensors or wiring.
- Diagnostic Scan: Use an OBD-II scanner to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the ESP control unit.
- Sensor Testing: Test individual sensors to ensure they are functioning correctly. This can involve checking resistance, voltage, or signal output.
- Component Testing: Test other components, such as the hydraulic unit and control unit, to rule out any malfunctions.
2.4. Using Diagnostic Tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. These tools can help you accurately diagnose ESP issues and perform necessary repairs. Some of the recommended tools include:
| Tool | Description | Features | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| iCarsoft MB V3.0 | A professional diagnostic tool for Mercedes-Benz, covering all systems including ESP. | Reads and clears DTCs, live data streaming, actuation tests, special functions. | $220.00 |
| Autel MaxiCOM MK808S | An advanced diagnostic scanner with comprehensive coverage for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. | Full system diagnostics, bi-directional control, key coding, oil reset, EPB, BMS, SAS, DPF regeneration. | $549.00 |
| Launch X431 V+ | A high-end diagnostic tool with extensive functionality for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. | Full system diagnostics, ECU coding, programming, bi-directional control, guided functions. | $1,499.00 |
| Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnostic C4 | The official diagnostic system used by Mercedes-Benz dealerships. | Full system diagnostics, ECU programming, coding, SCN coding, guided diagnostics. | $2,500.00+ |
| Foxwell NT530 | A cost-effective diagnostic tool specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. | Reads and clears DTCs, live data streaming, actuation tests, special functions. | $189.00 |
These tools provide accurate and reliable diagnostics, helping you identify and resolve ESP issues efficiently.
2.5. Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
DTCs provide valuable information about the nature of the ESP problem. Here are some common DTCs related to ESP systems in Mercedes-Benz vehicles:
- C1000: Control unit fault.
- C1100: Wheel speed sensor fault.
- C1200: Steering angle sensor fault.
- C1300: Yaw rate sensor fault.
- C1400: Lateral acceleration sensor fault.
Each DTC has a specific meaning, and understanding these codes can help you pinpoint the exact source of the problem. Always refer to the Mercedes-Benz service manual for detailed descriptions and troubleshooting procedures for each code.
3. Causes of ESP System Malfunctions
3.1. Sensor Failures
Sensor failures are a common cause of ESP problems. Wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, yaw rate sensors, and lateral acceleration sensors can all fail due to wear, damage, or electrical issues. Symptoms of sensor failure include:
- Erratic ESP behavior: The ESP system may activate unnecessarily or fail to activate when needed.
- Inaccurate readings: Diagnostic tools may show incorrect or inconsistent readings from the sensors.
- Complete failure: The sensor may stop working altogether, triggering the ESP warning light.
3.2. Wiring and Electrical Issues
Wiring and electrical problems can also cause ESP malfunctions. Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring can disrupt the communication between the sensors, control unit, and other components. Common electrical issues include:
- Open circuits: A break in the wiring can prevent signals from reaching their destination.
- Short circuits: A short can cause signals to be misdirected or lost.
- Poor connections: Loose or corroded connectors can create resistance, disrupting signal flow.
3.3. Hydraulic Unit Problems
The hydraulic unit controls the brake pressure to individual wheels. Problems with the hydraulic unit can cause a variety of ESP issues, including:
- Valve malfunctions: Valves may become stuck, preventing proper brake pressure control.
- Pump failures: The pump may fail to generate sufficient pressure, affecting the ESP system’s ability to intervene.
- Leaks: Hydraulic fluid leaks can reduce the system’s effectiveness.
3.4. Control Unit Failures
The ESP control unit is responsible for processing sensor data and determining the necessary corrective actions. If the control unit fails, the ESP system will not function correctly. Common control unit issues include:
- Software glitches: Software errors can cause the control unit to malfunction.
- Hardware failures: Internal components may fail due to age, heat, or electrical damage.
- Corrosion: Moisture and corrosion can damage the control unit’s internal circuitry.
3.5. Wheel Alignment and Tire Issues
Incorrect wheel alignment or uneven tire wear can also affect the ESP system. These issues can cause inaccurate sensor readings, leading to unnecessary or ineffective ESP interventions. Ensure that your vehicle’s wheels are properly aligned and that your tires are in good condition.
4. How to Fix Sensor ESP Mercedes Issues
4.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing a Faulty Sensor
Replacing a faulty sensor involves the following steps:
- Identify the Faulty Sensor: Use a diagnostic tool to pinpoint the specific sensor that is causing the problem.
- Gather Tools and Parts: Collect the necessary tools, including wrenches, sockets, screwdrivers, and a new sensor.
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical accidents.
- Remove the Old Sensor: Carefully remove the old sensor, taking note of its orientation and any associated wiring.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor, ensuring it is properly aligned and securely connected.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Clear DTCs: Use a diagnostic tool to clear any DTCs related to the ESP system.
- Test the System: Test the ESP system by performing a short test drive to ensure it is functioning correctly.
4.2. Addressing Wiring Problems
Addressing wiring problems requires careful inspection and repair. Follow these steps:
- Inspect the Wiring: Visually inspect the wiring for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Test the Wiring: Use a multimeter to test the continuity and voltage of the wiring.
- Repair or Replace the Wiring: Repair any damaged wiring by splicing, soldering, or replacing sections as needed.
- Secure Connections: Ensure that all connections are clean, tight, and properly insulated.
4.3. Repairing or Replacing the Hydraulic Unit
Repairing or replacing the hydraulic unit is a more complex task that may require specialized tools and expertise. Consider the following steps:
- Diagnose the Problem: Use a diagnostic tool to confirm that the hydraulic unit is the source of the problem.
- Gather Tools and Parts: Collect the necessary tools, including wrenches, sockets, screwdrivers, and a new or rebuilt hydraulic unit.
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical accidents.
- Remove the Old Hydraulic Unit: Carefully remove the old hydraulic unit, taking note of its orientation and any associated wiring and hydraulic lines.
- Install the New Hydraulic Unit: Install the new or rebuilt hydraulic unit, ensuring it is properly aligned and securely connected.
- Bleed the Brakes: Bleed the brakes to remove any air from the hydraulic system.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Clear DTCs: Use a diagnostic tool to clear any DTCs related to the ESP system.
- Test the System: Test the ESP system by performing a short test drive to ensure it is functioning correctly.
4.4. Fixing Control Unit Issues
Fixing control unit issues can range from simple software updates to complete replacement.
- Check for Software Updates: Use a diagnostic tool to check for any available software updates for the ESP control unit.
- Perform a Software Update: Follow the instructions provided by the diagnostic tool to perform a software update.
- Replace the Control Unit: If a software update does not resolve the problem, you may need to replace the control unit. This requires programming the new control unit to match your vehicle’s specifications.
4.5. Ensuring Proper Wheel Alignment and Tire Condition
Proper wheel alignment and tire condition are essential for the ESP system to function correctly. Follow these steps:
- Check Wheel Alignment: Have your vehicle’s wheel alignment checked by a qualified technician.
- Adjust Wheel Alignment: If the wheel alignment is out of specification, have it adjusted to the correct settings.
- Inspect Tires: Inspect your tires for any signs of wear, damage, or uneven tread.
- Replace Tires: Replace any tires that are worn, damaged, or have uneven tread.
- Maintain Tire Pressure: Ensure that your tires are inflated to the correct pressure specifications.
5. Preventing Future ESP System Problems
5.1. Regular Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance can help prevent ESP system problems:
- Inspect Sensors: Regularly inspect the ESP sensors for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Check Wiring: Periodically check the wiring for any signs of wear, damage, or loose connections.
- Maintain Brake Fluid: Ensure that the brake fluid is clean and at the correct level.
- Check Wheel Alignment: Have your vehicle’s wheel alignment checked regularly.
- Inspect Tires: Regularly inspect your tires for any signs of wear, damage, or uneven tread.
5.2. Best Practices for Driving in Adverse Conditions
Driving in adverse conditions requires extra caution and awareness:
- Reduce Speed: Reduce your speed to maintain better control.
- Increase Following Distance: Increase your following distance to allow more time to react.
- Avoid Sudden Movements: Avoid sudden steering, braking, or acceleration.
- Use Winter Tires: Consider using winter tires for better traction in snow and ice.
- Engage ESP: Ensure that the ESP system is engaged to provide maximum stability.
5.3. The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET in Maintaining Your ESP System
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides a wealth of resources to help you maintain your ESP system, including:
- Diagnostic Tools: A wide range of diagnostic tools specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Technical Support: Expert technical support to help you diagnose and resolve ESP issues.
- Parts and Components: High-quality replacement parts and components for the ESP system.
- Educational Resources: Articles, guides, and videos to help you understand and maintain your ESP system.
6. Real-World Scenarios and Solutions
6.1. Case Study 1: Wheel Speed Sensor Failure
Scenario: A Mercedes-Benz C-Class owner notices the ESP warning light is illuminated on the dashboard. A diagnostic scan reveals a fault code indicating a problem with the right front wheel speed sensor.
Solution:
- The technician inspects the right front wheel speed sensor and finds that it is damaged.
- The technician replaces the faulty wheel speed sensor with a new one from CARDIAGTECH.NET.
- The technician clears the DTCs and performs a short test drive to ensure the ESP system is functioning correctly.
6.2. Case Study 2: Wiring Issue
Scenario: A Mercedes-Benz E-Class owner experiences erratic ESP behavior, with the system activating unnecessarily. A diagnostic scan reveals no specific fault codes.
Solution:
- The technician inspects the wiring harness and finds a corroded connector.
- The technician cleans and repairs the corroded connector.
- The technician tests the ESP system to ensure it is functioning correctly.
6.3. Case Study 3: Hydraulic Unit Problem
Scenario: A Mercedes-Benz S-Class owner notices the ESP and ABS warning lights are illuminated on the dashboard. A diagnostic scan reveals a fault code indicating a problem with the hydraulic unit.
Solution:
- The technician diagnoses the problem and determines that the hydraulic unit needs to be replaced.
- The technician replaces the faulty hydraulic unit with a rebuilt unit from CARDIAGTECH.NET.
- The technician bleeds the brakes, clears the DTCs, and performs a short test drive to ensure the ESP system is functioning correctly.
7. The Future of ESP Technology in Mercedes-Benz
7.1. Advancements in ESP Systems
ESP technology continues to evolve, with new features and capabilities being introduced in Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Some of the latest advancements include:
- Predictive ESP: Uses data from navigation systems and sensors to anticipate potential loss of control and proactively intervene.
- Crosswind Assist: Helps stabilize the vehicle in strong crosswinds.
- Torque Vectoring: Distributes torque between the rear wheels to improve cornering performance.
7.2. Integration with Autonomous Driving Systems
ESP is becoming increasingly integrated with autonomous driving systems, playing a crucial role in ensuring safety and stability in self-driving vehicles. As autonomous technology advances, ESP will continue to evolve to meet the demands of these new systems.
7.3. CARDIAGTECH.NET’s Commitment to Innovation
CARDIAGTECH.NET is committed to staying at the forefront of ESP technology, offering the latest diagnostic tools, parts, and resources to help you maintain your Mercedes-Benz ESP system. We continuously update our product offerings and technical knowledge to ensure that you have access to the best solutions for your vehicle.
8. ESP System Maintenance Checklist
8.1. Monthly Checks
- Inspect tires for wear and pressure.
- Check brake fluid level.
- Ensure no warning lights are illuminated on the dashboard.
8.2. Bi-Annual Checks
- Inspect ESP sensors for damage or corrosion.
- Check wiring connections for tightness and corrosion.
- Test brake system functionality.
8.3. Annual Checks
- Have wheel alignment checked and adjusted if necessary.
- Inspect brake pads and rotors.
- Perform a diagnostic scan to check for any stored DTCs.
9. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET for Expert Assistance
9.1. How to Reach Us
If you have any questions or need assistance with your Mercedes-Benz ESP system, please contact us:
- Address: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CARDIAGTECH.NET
9.2. Schedule a Consultation
Schedule a consultation with our expert technicians to discuss your ESP system needs and find the best solutions for your vehicle.
9.3. Order Diagnostic Tools and Parts
Order high-quality diagnostic tools and replacement parts from CARDIAGTECH.NET to keep your Mercedes-Benz ESP system in top condition.
10.1. What does the ESP warning light mean on my Mercedes-Benz?
The ESP warning light indicates that the Electronic Stability Program is either actively working to stabilize the vehicle (flashing) or is disabled due to a malfunction (solid).
10.2. Can I drive my Mercedes-Benz with the ESP warning light on?
Driving with a flashing ESP light is generally safe, as it indicates the system is working. However, driving with a solid ESP light is not recommended, as it means the system is disabled, reducing vehicle stability.
10.3. How do I reset the ESP system on my Mercedes-Benz?
Try turning the steering wheel lock to lock (full left, then full right) while parked. If the light persists, a diagnostic scan is needed to identify and clear any fault codes.
10.4. What are the common causes of ESP system malfunctions?
Common causes include sensor failures, wiring issues, hydraulic unit problems, and control unit failures.
10.5. How can I diagnose ESP system problems?
Use a diagnostic tool to read DTCs, inspect sensors and wiring, and test system components.
10.6. Can I replace an ESP sensor myself?
Replacing an ESP sensor is possible with the right tools and knowledge. However, it is recommended to have a professional technician perform the replacement.
10.7. What diagnostic tools does CARDIAGTECH.NET recommend for Mercedes-Benz ESP systems?
CARDIAGTECH.NET recommends the iCarsoft MB V3.0, Autel MaxiCOM MK808S, Launch X431 V+, Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnostic C4, and Foxwell NT530.
10.8. How often should I have my ESP system checked?
It is recommended to have your ESP system checked annually as part of your regular maintenance schedule.
10.9. What are the benefits of having a functional ESP system?
A functional ESP system enhances safety, improves handling, reduces skidding, and increases driver confidence.
10.10. How can CARDIAGTECH.NET help me maintain my ESP system?
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides diagnostic tools, technical support, replacement parts, and educational resources to help you maintain your ESP system.
Don’t wait until a small issue becomes a major problem. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today and let our experts help you keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly and safely. Our team is ready to provide you with the best diagnostic tools and expert advice to ensure your vehicle’s ESP system is always in top condition. Reach out to us now and experience the CARDIAGTECH.NET difference. Your safety and satisfaction are our top priorities.
Ensure your Mercedes-Benz delivers optimal performance and safety with our comprehensive support. Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit CARDIAGTECH.NET for immediate assistance.