Is your Mercedes W204 displaying an “ESP Inoperative” warning? This can be a concerning issue, but at CARDIAGTECH.NET, we’re here to help you understand the problem and find the right solutions. This guide will cover the common causes of ESP malfunctions, diagnostic steps, and how the right tools can get you back on the road safely. Discover how to address stability control system problems and ensure optimal vehicle performance.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Mercedes W204 ESP System
- 1.1 What is ESP and Why is it Important?
- 1.2 Symptoms of a Malfunctioning ESP System
- 2. Common Causes of “ESP Inoperative” on Mercedes W204
- 2.1 Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
- 2.2 Steering Angle Sensor Issues
- 2.3 Yaw Rate Sensor Malfunction
- 2.4 Brake System Problems
- 2.5 Low Battery Voltage
- 2.6 Damaged Wiring or Connectors
- 2.7 Software or Calibration Errors
- 2.8 Faulty Hydraulic Unit
- 2.9 Aftermarket Modifications
- 3. Diagnosing the “ESP Inoperative” Warning
- 3.1 Using a Diagnostic Scanner
- 3.2 Visual Inspection of Sensors and Wiring
- 3.3 Testing Sensor Functionality
- 3.4 Checking the Brake System
- 3.5 Verifying Battery Voltage and Connections
- 4. Repairing the ESP System
- 4.1 Replacing Faulty Sensors
- 4.2 Repairing Damaged Wiring
- 4.3 Addressing Brake System Issues
- 4.4 Software Updates and Recalibration
- 4.5 Checking Hydraulic Unit
- 5. Maintaining Your Mercedes W204 ESP System
- 5.1 Regular Inspections
- 5.2 Keeping Sensors Clean
- 5.3 Maintaining Proper Tire Pressure
- 5.4 Addressing Issues Promptly
- 5.5 Routine Diagnostic Scans
- 5.6 Proper Battery Maintenance
- 6. The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET
- 6.1 Diagnostic Tools
- 6.2 Sensors and Components
- 6.3 Expert Advice
- 6.4 Commitment to Quality
- 7. Real-World Scenarios and Case Studies
- 7.1 Case Study 1: Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
- 7.2 Case Study 2: Steering Angle Sensor Calibration
- 7.3 Case Study 3: Low Battery Voltage
- 7.4 Case Study 4: ABS Module Failure
- 8. Addressing Customer Concerns
- 8.1 “Is it Safe to Drive with the ESP Warning Light On?”
- 8.2 “How Much Will it Cost to Repair the ESP System?”
- 8.3 “Can I Repair the ESP System Myself?”
- 8.4 “How Often Should I Have My ESP System Checked?”
- 8.5 “What Diagnostic Tools Do I Need to Diagnose ESP Problems?”
- 8.6 “Can Aftermarket Modifications Affect My ESP System?”
- 9. Call to Action: Get Your ESP System Checked Today!
- Why Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET?
- Benefits of a Properly Functioning ESP System
- Act Now and Protect Yourself
1. Understanding the Mercedes W204 ESP System
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is a vital safety feature in your Mercedes W204, designed to prevent skidding and maintain control during challenging driving conditions. It works by monitoring various sensors and selectively applying brakes to individual wheels to correct oversteer or understeer. When the “ESP Inoperative” warning appears, it signifies that this system isn’t functioning correctly, potentially compromising your vehicle’s stability and handling. To grasp the urgency, imagine navigating a sharp turn in wet conditions – the ESP is what keeps you safely on course.
1.1 What is ESP and Why is it Important?
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is an essential safety feature in modern vehicles, including the Mercedes W204. Its primary function is to help drivers maintain control of their vehicles during challenging driving conditions, such as slippery roads or sudden maneuvers. ESP works by monitoring various sensors throughout the vehicle, including wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, and yaw rate sensors. These sensors provide real-time data to the ESP control unit, which then determines if the vehicle is deviating from its intended path.
If the ESP system detects that the vehicle is beginning to skid or lose traction, it can intervene by selectively applying brakes to individual wheels and/or reducing engine power. This helps to correct the vehicle’s trajectory and prevent loss of control. For example, if the system detects oversteer (where the rear of the vehicle is sliding out), it may apply the brakes to the outer front wheel to help bring the vehicle back into line.
ESP is particularly important in situations where drivers may lose control, such as during emergency braking or when encountering unexpected obstacles. By helping to maintain stability and control, ESP can significantly reduce the risk of accidents. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), ESP can reduce single-vehicle crashes by as much as 35%.
The Mercedes ESP system uses various sensors to maintain vehicle stability and control, helping to prevent skidding and loss of control.
1.2 Symptoms of a Malfunctioning ESP System
Recognizing the symptoms of a malfunctioning ESP system is crucial for timely diagnosis and repair. Here are some common signs that your Mercedes W204 ESP system may not be working correctly:
- Warning Light On: The most obvious symptom is the illumination of the ESP warning light on the dashboard. This light is usually an icon of a car with skid marks behind it.
- Reduced Traction: You may notice a decrease in traction, especially on slippery surfaces. The vehicle may feel less stable and more prone to skidding.
- Difficulty Controlling the Vehicle: In extreme cases, you may experience difficulty controlling the vehicle, particularly during sudden maneuvers or when driving on uneven surfaces.
- ABS Light On: In some instances, a malfunctioning ESP system can also trigger the ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) warning light. This is because the ESP system relies on the ABS system to function properly.
- Error Messages: The vehicle’s computer system may display error messages related to the ESP system, such as “ESP Inoperative” or “ESP Malfunction.”
- Unusual Braking Behavior: You may notice unusual braking behavior, such as the brakes engaging erratically or the vehicle pulling to one side when braking.
- Steering Issues: Difficulties with steering, like a stiff or unresponsive steering wheel, can also indicate ESP problems.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to have your Mercedes W204 inspected by a qualified technician as soon as possible. Ignoring these warning signs can compromise your safety and lead to more extensive damage to your vehicle. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the importance of addressing ESP issues promptly and offer a range of diagnostic tools to help you identify and resolve these problems efficiently. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for assistance.
2. Common Causes of “ESP Inoperative” on Mercedes W204
Several factors can trigger the “ESP Inoperative” warning on your Mercedes W204. Identifying the root cause is the first step towards resolving the issue. From sensor malfunctions to electrical problems, each potential cause requires a specific diagnostic approach. Here’s a breakdown of the most common culprits:
2.1 Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
Wheel speed sensors are crucial components of the ESP system, as they provide data on the rotational speed of each wheel. This information is used by the ESP control unit to determine if the vehicle is skidding or losing traction.
- Function: These sensors monitor the speed of each wheel, providing essential data to the ESP module.
- Symptoms: Inaccurate readings can disable the ESP system, leading to the warning light and compromised stability.
- Causes: Wheel speed sensors can fail due to various reasons, including:
- Physical damage from road debris
- Corrosion or contamination
- Electrical issues, such as short circuits or open circuits
- Troubleshooting:
- Use a diagnostic scanner to check for fault codes related to the wheel speed sensors.
- Visually inspect the sensors and wiring for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Use a multimeter to test the sensor’s resistance and signal output.
If a wheel speed sensor is found to be faulty, it should be replaced with a new one. It’s also essential to clean the sensor mounting area to ensure proper installation and accurate readings.
2.2 Steering Angle Sensor Issues
The steering angle sensor measures the position of the steering wheel and provides this information to the ESP control unit. This data is used to determine the driver’s intended direction and to adjust the ESP system accordingly.
- Function: Monitors the steering wheel’s position to help the ESP system determine the driver’s intended direction.
- Symptoms: Faults can result in the ESP system failing, causing instability and reduced control.
- Causes: Steering angle sensor issues can arise from:
- Misalignment after a wheel alignment or suspension work
- Electrical problems, such as short circuits or open circuits
- Internal sensor failure due to wear and tear
- Troubleshooting:
- Use a diagnostic scanner to check for fault codes related to the steering angle sensor.
- Perform a steering angle sensor calibration using a diagnostic tool.
- Visually inspect the sensor and wiring for any signs of damage or corrosion.
If the steering angle sensor is found to be faulty, it should be replaced with a new one. It’s also essential to perform a steering angle sensor calibration after replacement to ensure proper function.
2.3 Yaw Rate Sensor Malfunction
The yaw rate sensor measures the vehicle’s rotational speed around its vertical axis. This information is used by the ESP control unit to determine if the vehicle is rotating excessively, which can indicate a skid or loss of control.
- Function: Measures the vehicle’s lateral movement to help the ESP system detect skidding or loss of control.
- Symptoms: An error can disrupt ESP functionality, leading to compromised stability and handling.
- Causes: Yaw rate sensor malfunctions can be caused by:
- Physical damage from impacts or vibrations
- Electrical problems, such as short circuits or open circuits
- Internal sensor failure due to wear and tear
- Troubleshooting:
- Use a diagnostic scanner to check for fault codes related to the yaw rate sensor.
- Visually inspect the sensor and wiring for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Use a multimeter to test the sensor’s power supply and signal output.
If the yaw rate sensor is found to be faulty, it should be replaced with a new one. It’s also essential to ensure that the sensor is properly mounted and aligned.
2.4 Brake System Problems
The ESP system relies on the brake system to function properly. Therefore, any issues with the brake system can also trigger the “ESP Inoperative” warning.
- Function: Faulty brake components, such as pressure sensors or the ABS module, can interfere with ESP operations.
- Symptoms: This can lead to a range of issues, from reduced braking performance to complete ESP failure.
- Causes: Brake system problems that can affect ESP include:
- Faulty brake pressure sensors
- Malfunctioning ABS module
- Low brake fluid level
- Air in the brake lines
- Troubleshooting:
- Check the brake fluid level and top up if necessary.
- Bleed the brake lines to remove any air.
- Use a diagnostic scanner to check for fault codes related to the brake system.
- Visually inspect the brake components for any signs of damage or leaks.
If any brake system problems are found, they should be addressed promptly to ensure both braking performance and ESP functionality.
2.5 Low Battery Voltage
A weak or failing battery can cause a variety of electrical problems in your Mercedes W204, including issues with the ESP system.
- Function: A weak or failing battery can cause multiple electronic systems, including ESP, to malfunction.
- Symptoms: This can lead to intermittent ESP failures and other electrical issues.
- Causes: Low battery voltage can be caused by:
- An old or worn-out battery
- A faulty alternator
- Excessive electrical drain
- Troubleshooting:
- Check the battery voltage using a multimeter.
- Have the battery load tested to determine its condition.
- Check the alternator output to ensure it’s charging the battery properly.
If the battery is found to be weak or failing, it should be replaced with a new one. It’s also essential to address any underlying issues that may be causing excessive electrical drain.
2.6 Damaged Wiring or Connectors
Corroded or damaged electrical connections can lead to intermittent communication between the ESP components, triggering the “ESP Inoperative” warning.
- Function: Corroded or damaged electrical connections can lead to intermittent communication between the ESP components.
- Symptoms: This can cause the ESP system to malfunction and display the warning light.
- Causes: Damaged wiring or connectors can be caused by:
- Exposure to moisture or road salt
- Physical damage from impacts or vibrations
- Rodent damage
- Troubleshooting:
- Visually inspect the wiring and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Use a multimeter to check for continuity and voltage at the connectors.
- Clean or replace any corroded connectors.
If any damaged wiring or connectors are found, they should be repaired or replaced to ensure proper communication between the ESP components.
2.7 Software or Calibration Errors
Sometimes, the ESP system may require a software update or recalibration to restore functionality.
- Function: Sometimes, a software update or recalibration may be required to restore ESP functionality.
- Symptoms: This can be necessary after replacing certain components or if the system is displaying error messages.
- Causes: Software or calibration errors can be caused by:
- Software glitches
- Data corruption
- Incorrect calibration after component replacement
- Troubleshooting:
- Use a diagnostic scanner to check for software updates or calibration procedures.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to perform any necessary updates or calibrations.
If software or calibration errors are suspected, it’s essential to use a compatible diagnostic tool and follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
2.8 Faulty Hydraulic Unit
The hydraulic unit controls the brake pressure to individual wheels as directed by the ESP system. Issues with this unit can trigger the “ESP Inoperative” warning.
- Function: Issues with the hydraulic control unit that operates the brakes can trigger the warning.
- Symptoms: This can lead to erratic braking behavior and ESP malfunctions.
- Causes: A faulty hydraulic unit can result from:
- Internal mechanical failure
- Electrical issues
- Contamination of the hydraulic fluid
- Troubleshooting:
- Use a diagnostic scanner to check for fault codes related to the hydraulic unit.
- Visually inspect the hydraulic unit for any signs of leaks or damage.
- Check the hydraulic fluid level and condition.
If the hydraulic unit is found to be faulty, it may need to be replaced or rebuilt.
2.9 Aftermarket Modifications
Installing non-compatible wheels, tires, or suspension components can interfere with ESP functionality.
- Function: Installing non-compatible wheels, tires, or suspension components can interfere with ESP.
- Symptoms: This can cause the ESP system to malfunction and display the warning light.
- Causes: Aftermarket modifications can affect ESP by:
- Changing the vehicle’s ride height or suspension geometry
- Using wheels or tires with incorrect sizes or offsets
- Interfering with the wheel speed sensors or other ESP components
- Troubleshooting:
- Ensure that all wheels, tires, and suspension components are compatible with the vehicle.
- Check that the wheel speed sensors are properly installed and functioning correctly.
- Consider reverting to the original components if necessary.
If aftermarket modifications are suspected of causing the ESP issues, it’s essential to revert to the original components and see if the problem resolves.
Understanding these common causes can help you narrow down the potential issues and take the appropriate steps to diagnose and repair your Mercedes W204 ESP system.
3. Diagnosing the “ESP Inoperative” Warning
When the “ESP Inoperative” warning appears on your Mercedes W204, a systematic diagnostic approach is essential to pinpoint the root cause. This involves using diagnostic tools, visual inspections, and a methodical process of elimination. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you diagnose the problem:
3.1 Using a Diagnostic Scanner
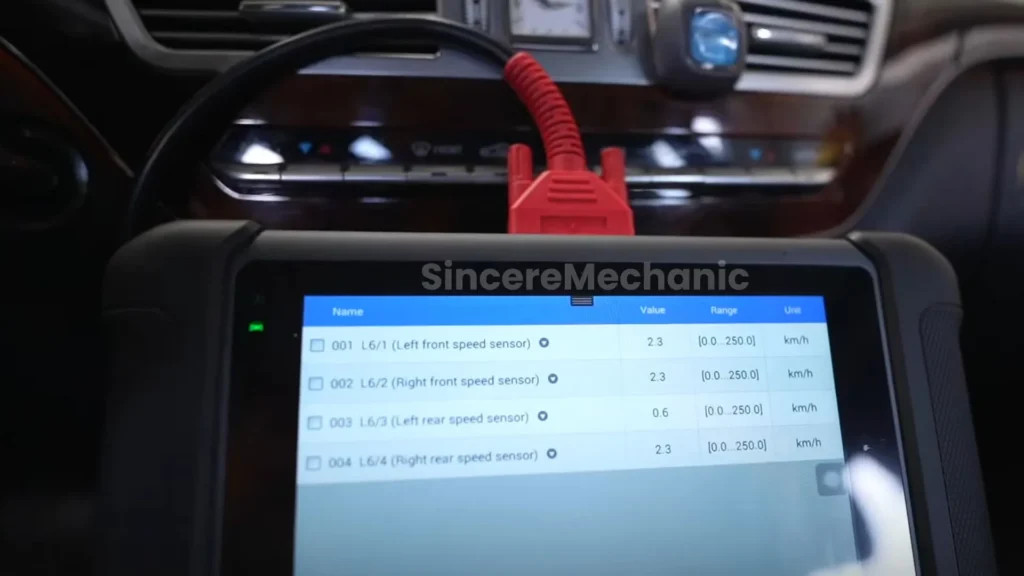
A diagnostic scanner is an invaluable tool for troubleshooting the “ESP Inoperative” warning. It can read fault codes stored in the vehicle’s computer system, providing valuable clues about the source of the problem.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the diagnostic scanner into the OBD-II port, typically located under the dashboard.
- Read Fault Codes: Turn on the ignition and follow the scanner’s instructions to read any stored fault codes.
- Interpret the Codes: Refer to the vehicle’s service manual or a reliable online resource to interpret the meaning of the fault codes. Common codes related to the ESP system include those for wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor, and yaw rate sensor.
- Clear the Codes: After noting the fault codes, clear them from the system. This will allow you to see if the same codes reappear after further testing.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of high-quality diagnostic scanners that are compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles. These scanners can help you quickly and accurately diagnose ESP issues, saving you time and money. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 to find the right diagnostic tool for your needs.
A diagnostic scanner is an essential tool for reading fault codes and troubleshooting the ESP system on your Mercedes W204.
3.2 Visual Inspection of Sensors and Wiring
A thorough visual inspection of the sensors and wiring related to the ESP system can often reveal obvious signs of damage or corrosion.
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Inspect the wheel speed sensors at each wheel for any physical damage, such as cracks or broken wires. Check the wiring and connectors for corrosion or loose connections.
- Steering Angle Sensor: Locate the steering angle sensor, typically located near the steering column, and inspect it for any damage or loose connections.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: Find the yaw rate sensor, usually located under the center console or seat, and inspect it for any damage or loose connections.
- Wiring Harnesses: Trace the wiring harnesses related to the ESP system and look for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires, cracked insulation, or corroded connectors.
3.3 Testing Sensor Functionality
If the visual inspection doesn’t reveal any obvious problems, the next step is to test the functionality of the sensors using a multimeter or oscilloscope.
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of each wheel speed sensor. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications. You can also use an oscilloscope to monitor the sensor’s signal output while rotating the wheel.
- Steering Angle Sensor: Use a diagnostic scanner to monitor the steering angle sensor’s output while turning the steering wheel. The readings should change smoothly and accurately reflect the steering wheel’s position.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: Use a diagnostic scanner to monitor the yaw rate sensor’s output while driving the vehicle. The readings should change in response to the vehicle’s rotational movements.
3.4 Checking the Brake System
Since the ESP system relies on the brake system to function properly, it’s essential to check the brake system for any issues.
- Brake Fluid Level: Check the brake fluid level in the master cylinder and top up if necessary.
- Brake Lines: Inspect the brake lines for any leaks or damage.
- Brake Pads and Rotors: Check the condition of the brake pads and rotors. Worn or damaged brake components can affect the ESP system’s performance.
- ABS Module: Use a diagnostic scanner to check for fault codes related to the ABS module.
3.5 Verifying Battery Voltage and Connections
A weak or failing battery can cause a variety of electrical problems, including issues with the ESP system.
- Battery Voltage: Use a multimeter to check the battery voltage. It should be around 12.6 volts with the engine off and around 14 volts with the engine running.
- Battery Connections: Inspect the battery terminals and connections for corrosion or looseness. Clean and tighten the connections if necessary.
By following these diagnostic steps, you can systematically identify the cause of the “ESP Inoperative” warning on your Mercedes W204 and take the appropriate steps to repair it.
4. Repairing the ESP System
Once you’ve identified the cause of the “ESP Inoperative” warning, the next step is to repair the system. The specific repair procedures will vary depending on the nature of the problem. Here are some common repair scenarios:
4.1 Replacing Faulty Sensors
If a sensor is found to be faulty, it should be replaced with a new one. Here’s how to replace a wheel speed sensor:
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative battery cable to prevent electrical shock.
- Remove the Wheel: Remove the wheel on the side where the faulty sensor is located.
- Locate the Sensor: Find the wheel speed sensor, typically located near the wheel hub.
- Disconnect the Sensor: Disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor.
- Remove the Sensor: Remove the sensor from its mounting bracket.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor in the mounting bracket and connect the electrical connector.
- Reinstall the Wheel: Reinstall the wheel and tighten the lug nuts to the proper torque.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Clear Fault Codes: Use a diagnostic scanner to clear any fault codes related to the wheel speed sensor.
Replacing other sensors, such as the steering angle sensor or yaw rate sensor, will involve similar steps. Be sure to consult the vehicle’s service manual for specific instructions.
4.2 Repairing Damaged Wiring
If damaged wiring is causing the ESP issues, it will need to be repaired or replaced.
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative battery cable to prevent electrical shock.
- Locate the Damage: Find the damaged section of wiring.
- Repair the Wiring: If the damage is minor, you may be able to repair the wiring by splicing in a new section of wire and using heat-shrink tubing to insulate the connection.
- Replace the Wiring: If the damage is extensive, it may be necessary to replace the entire wiring harness.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Clear Fault Codes: Use a diagnostic scanner to clear any fault codes related to the wiring repair.
4.3 Addressing Brake System Issues
If brake system problems are affecting the ESP system, they will need to be addressed.
- Low Brake Fluid: Top up the brake fluid level in the master cylinder.
- Air in Brake Lines: Bleed the brake lines to remove any air.
- Worn Brake Pads: Replace worn brake pads.
- Damaged Brake Rotors: Replace damaged brake rotors.
- ABS Module Issues: If the ABS module is faulty, it may need to be replaced or rebuilt.
4.4 Software Updates and Recalibration
In some cases, the ESP system may require a software update or recalibration after repairs.
- Connect Diagnostic Scanner: Connect a compatible diagnostic scanner to the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Check for Updates: Use the scanner to check for any available software updates for the ESP system.
- Install Updates: Follow the scanner’s instructions to install any available updates.
- Recalibrate Sensors: Use the scanner to recalibrate the steering angle sensor and other relevant sensors.
4.5 Checking Hydraulic Unit
If hydraulic unit problems are affecting the ESP system, they will need to be addressed.
- Fluid Check: Check the hydraulic fluid level in the master cylinder.
- Fluid Condition: Examine the fluid condition and check for any leaks
- Hydraulic Unit Replacement: If the hydraulic unit is faulty, it may need to be replaced or rebuilt.
After completing any repairs, it’s essential to test the ESP system to ensure that it’s functioning properly. This can be done by driving the vehicle in a safe area and performing some maneuvers that would typically activate the ESP system, such as sharp turns or sudden braking.
5. Maintaining Your Mercedes W204 ESP System
Proper maintenance is crucial for ensuring the long-term reliability and performance of your Mercedes W204 ESP system. Here are some tips to help you keep your ESP system in good condition:
5.1 Regular Inspections
- Visual Inspections: Regularly inspect the sensors, wiring, and connectors related to the ESP system for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Brake System Checks: Have the brake system inspected regularly, including the brake fluid level, brake lines, brake pads, and rotors.
5.2 Keeping Sensors Clean
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Keep the wheel speed sensors clean and free of debris.
- Other Sensors: Clean other sensors, such as the steering angle sensor and yaw rate sensor, as needed.
5.3 Maintaining Proper Tire Pressure
- Check Tire Pressure: Maintain proper tire pressure, as this can affect the ESP system’s performance.
- Consistent Tires: Use tires with the same size and tread pattern on all four wheels.
5.4 Addressing Issues Promptly
- Warning Signs: Address any warning signs of ESP problems promptly, such as the ESP warning light or unusual braking behavior.
- Professional Help: Seek professional help from a qualified technician for any ESP issues that you’re unable to resolve yourself.
5.5 Routine Diagnostic Scans
- Check For Codes: Perform routine diagnostic scans to check for any stored fault codes related to the ESP system.
- Preventative Maintenance: Address any potential issues before they become major problems.
5.6 Proper Battery Maintenance
- Battery Health: Ensure the battery is in good condition and properly charged.
- Clean Terminals: Clean the battery terminals and connections regularly to prevent corrosion.
By following these maintenance tips, you can help ensure that your Mercedes W204 ESP system remains in good working condition, providing you with enhanced safety and control on the road.
6. The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the importance of maintaining your Mercedes W204 ESP system. That’s why we offer a wide range of diagnostic tools and equipment to help you diagnose and repair any ESP issues.
6.1 Diagnostic Tools
We carry a variety of diagnostic scanners that are compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles, including the W204. These scanners can help you quickly and accurately diagnose ESP problems, saving you time and money.
6.2 Sensors and Components
We also offer a wide selection of sensors and components related to the ESP system, including wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, and yaw rate sensors. All of our parts are of the highest quality and are designed to meet or exceed OEM specifications.
6.3 Expert Advice
Our team of experts is always available to provide you with advice and support. Whether you’re a professional mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, we can help you find the right tools and parts for your needs.
6.4 Commitment to Quality
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we are committed to providing our customers with the highest quality products and services. We stand behind everything we sell and are dedicated to ensuring your satisfaction.
Don’t let ESP issues compromise your safety and driving experience. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at +1 (641) 206-8880, visit our website CARDIAGTECH.NET, or stop by our location at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, to learn more about our products and services. Let us help you keep your Mercedes W204 ESP system in top condition.
7. Real-World Scenarios and Case Studies
Understanding how the “ESP Inoperative” issue manifests in real-world situations can provide valuable insights. Here are a few case studies that illustrate common scenarios:
7.1 Case Study 1: Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
- Vehicle: 2010 Mercedes-Benz C300 (W204)
- Symptom: ESP Inoperative warning light illuminated on the dashboard.
- Diagnosis: A diagnostic scanner revealed a fault code related to the front left wheel speed sensor. Visual inspection confirmed that the sensor was damaged.
- Solution: The front left wheel speed sensor was replaced with a new one. The fault codes were cleared, and the ESP system functioned normally.
- Outcome: The vehicle’s ESP system was restored to proper working order, and the owner was able to drive with confidence.
7.2 Case Study 2: Steering Angle Sensor Calibration
- Vehicle: 2012 Mercedes-Benz C250 (W204)
- Symptom: ESP Inoperative warning light illuminated after a wheel alignment.
- Diagnosis: A diagnostic scanner indicated that the steering angle sensor was not properly calibrated.
- Solution: The steering angle sensor was recalibrated using a diagnostic scanner.
- Outcome: The ESP system was restored to proper working order, and the warning light was extinguished.
7.3 Case Study 3: Low Battery Voltage
- Vehicle: 2008 Mercedes-Benz C280 (W204)
- Symptom: Intermittent ESP Inoperative warning light, along with other electrical issues.
- Diagnosis: A battery test revealed that the battery was weak and not holding a charge.
- Solution: The battery was replaced with a new one.
- Outcome: The ESP system functioned normally, and the other electrical issues were resolved.
Real-world scenarios, like a faulty wheel speed sensor or low battery voltage, can trigger the “ESP Inoperative” warning in your Mercedes W204.
7.4 Case Study 4: ABS Module Failure
- Vehicle: 2011 Mercedes-Benz C350 (W204)
- Symptom: Both ABS and ESP warning lights illuminated. The ABS system was not functioning properly.
- Diagnosis: Diagnostic scan revealed the ABS Module failure.
- Solution: The ABS module was replaced.
- Outcome: The ESP and ABS systems were restored to proper working order, and the warning lights were extinguished.
These case studies demonstrate the importance of proper diagnosis and repair when addressing the “ESP Inoperative” warning on your Mercedes W204. By following a systematic approach and using the right tools and equipment, you can effectively resolve these issues and ensure the safety and performance of your vehicle.
8. Addressing Customer Concerns
We understand that dealing with the “ESP Inoperative” warning can be stressful. Here are some of the most common concerns we hear from our customers and how we address them:
8.1 “Is it Safe to Drive with the ESP Warning Light On?”
Driving with the ESP warning light on is not recommended, as it indicates that the ESP system is not functioning properly. This can compromise your vehicle’s stability and handling, especially in challenging driving conditions. It’s best to have the vehicle inspected and repaired as soon as possible.
8.2 “How Much Will it Cost to Repair the ESP System?”
The cost to repair the ESP system can vary depending on the nature of the problem. Simple repairs, such as replacing a faulty sensor, may cost a few hundred dollars. More complex repairs, such as replacing the ABS module, can cost significantly more. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we offer competitive pricing on all of our products and services.
8.3 “Can I Repair the ESP System Myself?”
Some ESP repairs, such as replacing a faulty sensor, can be done by experienced DIYers. However, other repairs, such as ABS module replacement, may require specialized tools and knowledge. If you’re not comfortable working on your vehicle’s ESP system, it’s best to seek professional help. We, at CARDIAGTECH.NET can guide you through the repair or help you find a professional in your area. Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for assistance.
8.4 “How Often Should I Have My ESP System Checked?”
It’s a good idea to have your ESP system checked regularly, especially if you notice any warning signs of problems. We recommend having your ESP system inspected at least once a year, or more often if you drive in challenging conditions.
8.5 “What Diagnostic Tools Do I Need to Diagnose ESP Problems?”
To diagnose ESP problems on your Mercedes W204, you’ll need a diagnostic scanner that is compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles. We carry a variety of high-quality diagnostic scanners that can help you quickly and accurately diagnose ESP issues.
8.6 “Can Aftermarket Modifications Affect My ESP System?”
Yes, aftermarket modifications, such as non-compatible wheels, tires, or suspension components, can interfere with ESP functionality. It’s essential to ensure that any aftermarket modifications are compatible with your vehicle’s ESP system.
We hope this addresses some of your concerns about the “ESP Inoperative” warning on your Mercedes W204. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we are here to help you with all of your ESP needs.
9. Call to Action: Get Your ESP System Checked Today!
Don’t let the “ESP Inoperative” warning compromise your safety and driving experience. Take action today and get your Mercedes W204 ESP system checked by a qualified technician. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET at +1 (641) 206-8880 to schedule a diagnostic appointment.
Why Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET?
- Expert Technicians: Our team of expert technicians has the knowledge and experience to diagnose and repair any ESP issues.
- State-of-the-Art Equipment: We use the latest diagnostic tools and equipment to ensure accurate and efficient repairs.
- Competitive Pricing: We offer competitive pricing on all of our products and services.
- Commitment to Satisfaction: We are committed to providing our customers with the highest level of satisfaction.
Benefits of a Properly Functioning ESP System
- Enhanced Safety: A properly functioning ESP system can help you maintain control of your vehicle in challenging driving conditions, reducing the risk of accidents.
- Improved Handling: The ESP system can improve your vehicle’s handling and stability, making it more enjoyable to drive.
- Increased Confidence: Knowing that your ESP system is working properly can give you increased confidence behind the wheel.
Act Now and Protect Yourself
Don’t wait until it’s too late. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today to schedule an ESP diagnostic appointment. We’ll help you keep your Mercedes W204 ESP system in top condition, ensuring your safety and driving enjoyment.
Remember, your safety is our top priority. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880, visit our website CARDIAGTECH.NET, or stop by our location at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, to learn more about our products and services. Let us help you keep your Mercedes W204 ESP system in top condition.
CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to help you keep your Mercedes W204 ESP system in top condition, ensuring your safety and driving enjoyment.
Here are some frequently asked questions about the “ESP Inoperative” warning on Mercedes W204 vehicles:
Q1: What does the “ESP Inoperative” warning mean?
A1: It means the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is not functioning correctly, potentially affecting vehicle stability and handling.
Q2: Is it safe to drive with the ESP warning light on?
A2: Not recommended. It compromises stability, especially in challenging conditions. Have it inspected promptly.
Q3: What are common causes of the “ESP Inoperative” warning?
A3: Faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor issues, yaw rate sensor malfunctions, brake system problems, low battery voltage, damaged wiring, and software errors.
Q4: How can I diagnose the “ESP Inoperative” warning?
A4: Use a diagnostic scanner to read fault codes, visually inspect sensors and wiring, test sensor functionality, and check the brake system.
Q5: Can I repair the ESP system myself?
A5: Some repairs, like replacing sensors, are DIY-friendly. Complex repairs may require professional help.
Q6: How much will it cost to repair the ESP system?
A6: Varies depending on the issue, from a few hundred dollars for sensors to more for complex problems.
Q7: How often should I have my ESP system checked?
A7: At least once a year, or more often if you drive in challenging conditions.
Q8: Can low battery voltage affect the ESP system?
A8: Yes, a weak battery can cause various electrical problems, including ESP issues.
Q9: Are aftermarket modifications a possible cause?
A9: Yes, non-compatible wheels, tires, or suspension parts can interfere with ESP functionality.
Q10: What role does CARDIAGTECH.NET play in ESP system maintenance?
A10: We offer diagnostic tools, sensors, and expert advice to help diagnose and repair ESP issues on Mercedes W204 vehicles. We can be contacted at +1 (641) 206-8880 for more information.