Mercedes Esp, or Electronic Stability Program, is a critical safety system designed to keep you in control. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the importance of this feature and offer the tools and knowledge you need to maintain and diagnose it effectively. Equip your repair toolkit with essential Mercedes ESP diagnostic and repair tools to ensure optimal performance, vehicle safety, and advanced stability control.
Contents
- 1. What is Mercedes ESP and Why Is It Important?
- 1.1 The Core Functionality of ESP
- 1.2 Historical Context and Development
- 1.3 The Importance of ESP in Modern Vehicles
- 2. How Mercedes ESP Works: A Detailed Explanation
- 2.1 Key Components of the ESP System
- 2.2 Sensor Technology and Data Processing
- 2.3 Intervention Mechanisms: Braking and Throttle Control
- 3. Benefits of Mercedes ESP: Safety and Performance
- 3.1 Enhanced Safety in Critical Situations
- 3.2 Improved Handling and Stability
- 3.3 Reduced Risk of Accidents
- 3.4 Confidence and Control for Drivers
- 4. Diagnosing Mercedes ESP Problems: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 4.1 Common Symptoms of ESP Malfunctions
- 4.2 Tools and Equipment Needed for Diagnosis
- 4.3 Step-by-Step Diagnostic Process
- 4.4 Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 4.5 Using Scan Tools and Software for Advanced Diagnostics
- 5. Repairing Mercedes ESP: Solutions and Best Practices
- 5.1 Common ESP Repairs and Solutions
- 5.2 Step-by-Step Repair Procedures
- 5.3 Best Practices for ESP Repairs
- 5.4 Ensuring Proper Calibration and Alignment
- 6. Maintaining Mercedes ESP: Tips for Longevity
- 6.1 Regular Inspections and Checks
- 6.2 Tire Maintenance and Alignment
- 6.3 Brake System Maintenance
- 6.4 Avoiding Aggressive Driving
- 6.5 Addressing Warning Lights Promptly
- 7. Upgrading Mercedes ESP: Enhancing Performance
- 7.1 Aftermarket ESP Tuning and Calibration
- 7.2 Performance Brake Upgrades
- 7.3 Suspension Upgrades
- 7.4 Wheel and Tire Upgrades
- 8. Mercedes ESP and 4MATIC: The Perfect Combination
- 8.1 How 4MATIC Enhances ESP Performance
- 8.2 Benefits of All-Wheel-Drive with ESP
- 8.3 Real-World Applications and Scenarios
- 9. The Future of Mercedes ESP: Innovations and Trends
- 9.1 Integration with Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
- 9.2 Predictive ESP Systems
- 9.3 Enhanced Sensor Technology
- 9.4 Over-the-Air Updates
- 10. Finding the Right Mercedes ESP Diagnostic Tools at CARDIAGTECH.NET
- 10.1 Comprehensive Range of Diagnostic Tools
- 10.2 Expert Advice and Support
- 10.3 High-Quality Products and Competitive Prices
- 10.4 Ensuring Vehicle Safety with Our Tools
1. What is Mercedes ESP and Why Is It Important?
Mercedes-Benz ESP, short for Electronic Stability Program, is a sophisticated safety feature that helps drivers maintain control of their vehicles in challenging driving conditions. Also known as electronic stability control (ESC), this system is designed to prevent skidding and loss of control by automatically intervening when it detects that a vehicle is not responding correctly to a driver’s inputs. It’s a cornerstone of modern automotive safety, significantly reducing the risk of accidents and enhancing overall driving confidence.
1.1 The Core Functionality of ESP
The primary function of Mercedes ESP is to monitor a vehicle’s direction and compare it to the driver’s intended path. Using a network of sensors, including wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, and yaw rate sensors, ESP can detect when a vehicle starts to deviate from its intended course. This typically occurs during emergency maneuvers, slippery road conditions, or when a driver overcorrects. When ESP detects a discrepancy, it selectively applies braking force to individual wheels to help steer the vehicle back on track. This can also involve reducing engine power to regain control.
1.2 Historical Context and Development
The development of electronic stability control systems like Mercedes ESP dates back to the late 20th century, with early prototypes emerging in the 1980s. Mercedes-Benz was among the pioneers in bringing this technology to market, introducing ESP in 1995 on the S-Class Coupe (C140). This innovation marked a significant advancement in automotive safety, paving the way for widespread adoption of ESC systems across the industry.
1.3 The Importance of ESP in Modern Vehicles
In today’s automotive landscape, ESP is considered an essential safety feature. Studies have shown that ESC systems can reduce single-vehicle crashes by a significant margin. In recognition of its life-saving potential, many countries have mandated the inclusion of ESC in all new passenger vehicles. Beyond regulatory requirements, ESP enhances the driving experience by providing an added layer of safety and stability, making it an indispensable component of modern vehicles.
2. How Mercedes ESP Works: A Detailed Explanation
Mercedes ESP is a marvel of automotive engineering, integrating several key components to ensure optimal vehicle stability. Understanding how these components work together provides valuable insight into the system’s effectiveness and the importance of proper maintenance.
2.1 Key Components of the ESP System
The ESP system comprises several critical sensors and actuators that work in concert to monitor and control vehicle stability:
- Wheel Speed Sensors: These sensors, typically located at each wheel, measure the rotational speed of each wheel. This data is crucial for detecting wheel spin or loss of traction.
- Steering Angle Sensor: Located in the steering column, this sensor measures the angle of the steering wheel, providing information about the driver’s intended direction.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: This sensor measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis (yaw rate), indicating whether the vehicle is turning more or less than intended.
- Lateral Acceleration Sensor: This sensor measures the vehicle’s sideways acceleration, helping to detect skidding or drifting.
- Brake Pressure Sensors: These sensors monitor the pressure in the brake lines, providing feedback on braking performance.
- Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU): The HCU is the heart of the ESP system. It contains a pump and valves that can independently apply braking force to each wheel.
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU): The ECU processes data from all the sensors and controls the HCU to execute corrective actions.
Diagram illustrating the main components of the Mercedes-Benz Electronic Stability Program, emphasizing wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor, yaw rate sensor, and the central ECU.
2.2 Sensor Technology and Data Processing
The ESP system relies on advanced sensor technology to gather real-time data about the vehicle’s dynamics. Wheel speed sensors use magnetic or optical principles to measure wheel rotation, while steering angle sensors employ encoders or resolvers to determine steering wheel position. Yaw rate sensors typically use microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) gyroscopes to measure the vehicle’s rotation.
The ECU processes this sensor data using complex algorithms to determine whether the vehicle is behaving as expected. These algorithms take into account factors such as vehicle speed, steering input, and road conditions to detect potential instabilities.
2.3 Intervention Mechanisms: Braking and Throttle Control
When the ESP system detects a loss of stability, it intervenes by selectively applying braking force to individual wheels. For example, if the vehicle is oversteering (turning more sharply than intended), ESP may apply braking to the outer front wheel to help bring the vehicle back on course. Conversely, if the vehicle is understeering (not turning enough), ESP may apply braking to the inner rear wheel.
In addition to braking, ESP can also reduce engine power to help regain control. By reducing torque to the wheels, ESP can prevent wheel spin and improve traction, particularly on slippery surfaces. The intervention is swift and subtle, often going unnoticed by the driver.
3. Benefits of Mercedes ESP: Safety and Performance
Mercedes ESP offers numerous benefits, enhancing both safety and driving performance. By preventing skidding and maintaining vehicle stability, ESP significantly reduces the risk of accidents and improves overall driving confidence.
3.1 Enhanced Safety in Critical Situations
The primary benefit of ESP is its ability to enhance safety in critical driving situations. Whether you’re navigating a sudden obstacle, encountering slippery road conditions, or making an emergency maneuver, ESP can help you maintain control of your vehicle. By automatically intervening to prevent skidding, ESP reduces the likelihood of accidents and helps protect you and your passengers.
3.2 Improved Handling and Stability
Beyond its safety benefits, ESP also improves handling and stability in everyday driving. By continuously monitoring vehicle dynamics and making subtle adjustments, ESP helps maintain optimal traction and control. This is particularly noticeable when cornering or driving on uneven surfaces, where ESP can help prevent body roll and improve overall stability.
3.3 Reduced Risk of Accidents
Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of ESP in reducing accidents. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), ESC systems can reduce single-vehicle crashes by as much as 35%. The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) has also found that ESC is particularly effective in preventing rollover crashes, which are often the most severe.
Table: Accident Reduction with Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
| Source | Finding |
|---|---|
| NHTSA (National Highway Traffic Safety Administration) | ESC reduces single-vehicle crashes by up to 35%. |
| IIHS (Insurance Institute for Highway Safety) | ESC is particularly effective in preventing rollover crashes. |
| European studies | ESC reduces all car accidents by 8%, potentially saving thousands of lives each year. |
| Analysis by Bosch | ESC can prevent up to 80% of all skidding accidents. |
3.4 Confidence and Control for Drivers
Ultimately, Mercedes ESP provides drivers with increased confidence and control behind the wheel. Knowing that ESP is there to help in challenging situations can reduce stress and enhance the overall driving experience. Whether you’re a seasoned driver or a novice, ESP offers an added layer of security and peace of mind.
4. Diagnosing Mercedes ESP Problems: A Step-by-Step Guide
Diagnosing ESP problems requires a systematic approach, combining visual inspection, diagnostic tools, and a thorough understanding of the system. By following a step-by-step guide, you can effectively identify and address ESP issues, ensuring optimal vehicle safety and performance.
4.1 Common Symptoms of ESP Malfunctions
Several symptoms may indicate an ESP malfunction. Recognizing these signs early can help prevent more serious problems:
- ESP Warning Light: The most obvious symptom is the illumination of the ESP warning light on the dashboard. This light may come on intermittently or remain on continuously.
- Reduced Stability: You may notice a decrease in vehicle stability, particularly when cornering or driving on slippery surfaces. The vehicle may feel less planted and more prone to skidding.
- Erratic Braking: ESP may engage unexpectedly, causing erratic braking or a pulsating sensation in the brake pedal.
- Loss of Power: In some cases, ESP may reduce engine power to prevent wheel spin, resulting in a noticeable loss of acceleration.
- ABS Light On: Since ESP relies on the ABS system, an ABS malfunction can also trigger the ESP warning light.
4.2 Tools and Equipment Needed for Diagnosis
To properly diagnose ESP problems, you’ll need the following tools and equipment:
- OBD-II Scanner: An OBD-II scanner is essential for reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the vehicle’s computer.
- Mercedes-Specific Diagnostic Software: For more in-depth diagnostics, you may need Mercedes-specific software such as XENTRY or DAS.
- Multimeter: A multimeter is useful for testing electrical circuits and sensors.
- Scan Tool with Live Data Capability: This tool allows you to monitor sensor data in real-time, helping you identify faulty components.
- Wiring Diagrams: Wiring diagrams can help you trace circuits and identify potential wiring issues.
4.3 Step-by-Step Diagnostic Process
Follow these steps to diagnose Mercedes ESP problems:
- Visual Inspection: Begin by visually inspecting the ESP system components, including sensors, wiring, and connectors. Look for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Use an OBD-II scanner or Mercedes-specific diagnostic software to read DTCs stored in the vehicle’s computer. Record all codes for further analysis.
- Research DTCs: Consult a repair manual or online database to research the meaning of each DTC. This will provide clues about the potential cause of the problem.
- Test Sensors: Use a multimeter or scan tool to test the ESP sensors, including wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor, and yaw rate sensor. Compare the sensor readings to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Check Wiring: Inspect the wiring and connectors associated with the ESP system. Look for any signs of damage, corrosion, or shorts.
- Monitor Live Data: Use a scan tool with live data capability to monitor sensor data in real-time. This can help you identify intermittent problems or subtle sensor issues.
- Perform Actuator Tests: Some diagnostic software allows you to perform actuator tests, which can help you verify the functionality of the HCU and other ESP components.
- Consult a Professional: If you’re unable to diagnose the problem yourself, consult a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician.
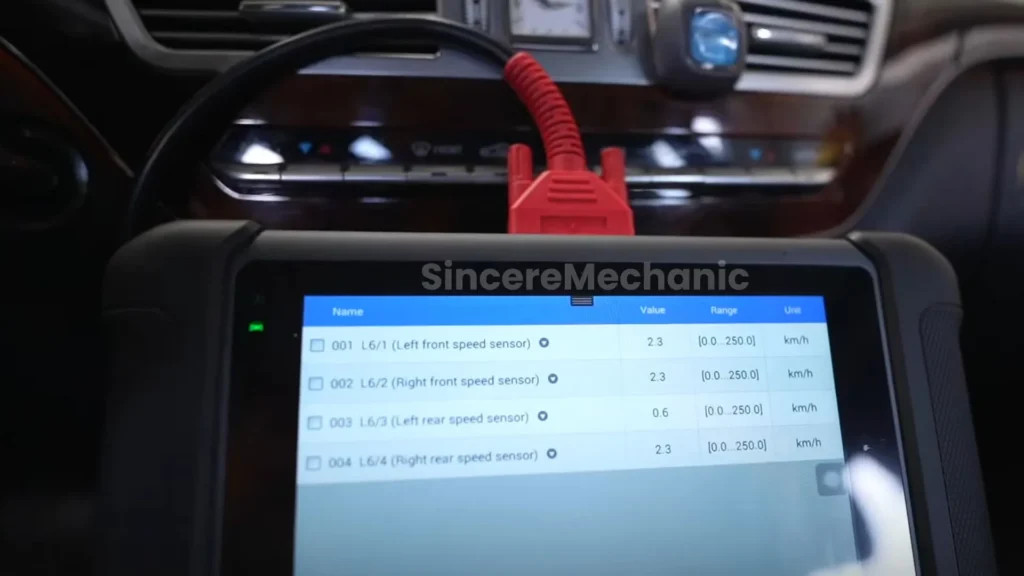
The Mercedes ESP Diagnostic Tool is essential for reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the vehicle’s computer.
4.4 Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
DTCs are an essential part of the diagnostic process, providing valuable information about the nature and location of the problem. Here are some common ESP-related DTCs and their possible causes:
- C1000: Control Unit Faulty
- Possible Causes: Faulty ECU, wiring issues, power supply problem
- C1100: Wheel Speed Sensor Front Right
- Possible Causes: Faulty sensor, wiring issues, damaged tone ring
- C1200: Steering Angle Sensor
- Possible Causes: Faulty sensor, misalignment, wiring issues
- C1300: Yaw Rate Sensor
- Possible Causes: Faulty sensor, wiring issues, incorrect installation
- C1400: Lateral Acceleration Sensor
- Possible Causes: Faulty sensor, wiring issues, incorrect installation
Table: Common ESP Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
| DTC Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| C1000 | Control Unit Faulty | Faulty ECU, wiring issues, power supply problem |
| C1100 | Wheel Speed Sensor Front Right | Faulty sensor, wiring issues, damaged tone ring |
| C1200 | Steering Angle Sensor | Faulty sensor, misalignment, wiring issues |
| C1300 | Yaw Rate Sensor | Faulty sensor, wiring issues, incorrect installation |
| C1400 | Lateral Acceleration Sensor | Faulty sensor, wiring issues, incorrect installation |
| C1500 | Brake Pressure Sensor | Faulty sensor, hydraulic issues, wiring problems |
| C1600 | Hydraulic Control Unit Malfunction | HCU failure, pump issues, valve problems |
| C1700 | ESP System Deactivated | Manual deactivation, system fault, sensor malfunction |
| C1800 | Communication Error with ECU | Wiring issues, ECU malfunction, CAN bus problems |
| C1900 | Calibration Required | Sensor replacement, system reset needed, software update required |
4.5 Using Scan Tools and Software for Advanced Diagnostics
Mercedes-specific diagnostic software such as XENTRY and DAS provides advanced diagnostic capabilities beyond those offered by generic OBD-II scanners. These tools allow you to access detailed system information, perform actuator tests, and calibrate sensors. They can also guide you through troubleshooting procedures, providing step-by-step instructions for diagnosing and repairing ESP problems.
5. Repairing Mercedes ESP: Solutions and Best Practices
Repairing Mercedes ESP problems requires careful attention to detail and adherence to best practices. Whether you’re replacing a faulty sensor, repairing damaged wiring, or recalibrating the system, following the correct procedures is essential for ensuring a safe and effective repair.
5.1 Common ESP Repairs and Solutions
Here are some common ESP repairs and solutions:
- Sensor Replacement: Faulty sensors are a common cause of ESP problems. Replacing a faulty wheel speed sensor, steering angle sensor, or yaw rate sensor can often resolve the issue.
- Wiring Repair: Damaged or corroded wiring can also cause ESP malfunctions. Repairing or replacing damaged wiring harnesses and connectors can restore proper system function.
- Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) Replacement: In some cases, the HCU may fail, requiring replacement. This is a more complex repair that should be performed by a qualified technician.
- Calibration: After replacing certain components, such as the steering angle sensor or yaw rate sensor, the ESP system may need to be calibrated. This involves using diagnostic software to reset the system and ensure that the sensors are properly aligned.
- Software Updates: In some cases, ESP problems can be resolved by updating the vehicle’s software. Mercedes-Benz releases software updates periodically to address known issues and improve system performance.
5.2 Step-by-Step Repair Procedures
When performing ESP repairs, follow these step-by-step procedures:
- Disconnect Battery: Before beginning any electrical repairs, disconnect the vehicle’s battery to prevent accidental shorts or electrical damage.
- Remove Faulty Component: Carefully remove the faulty component, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Install New Component: Install the new component, ensuring that it is properly aligned and connected.
- Reconnect Wiring: Reconnect any wiring harnesses or connectors that were disconnected during the repair.
- Calibrate System: If necessary, calibrate the ESP system using diagnostic software.
- Test System: After completing the repair, test the ESP system to ensure that it is functioning properly. Drive the vehicle in a safe area and perform maneuvers that would typically trigger ESP intervention, such as cornering or braking on a slippery surface.
- Clear DTCs: Clear any DTCs that may have been stored in the vehicle’s computer during the repair process.
5.3 Best Practices for ESP Repairs
Follow these best practices to ensure a safe and effective ESP repair:
- Use Genuine Parts: When replacing ESP components, use genuine Mercedes-Benz parts or high-quality aftermarket parts that meet the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions when performing ESP repairs. This will help you avoid mistakes and ensure that the repair is done correctly.
- Double-Check Connections: Before completing the repair, double-check all wiring connections to ensure that they are secure and properly connected.
- Test Drive Vehicle: After completing the repair, test drive the vehicle to ensure that the ESP system is functioning properly.
During Mercedes ESP repair, ensure that all wiring connections are secure and properly connected to prevent future malfunctions.
5.4 Ensuring Proper Calibration and Alignment
Proper calibration and alignment are essential for ensuring that the ESP system functions correctly. After replacing certain components, such as the steering angle sensor or yaw rate sensor, the system may need to be calibrated using diagnostic software. This involves resetting the system and ensuring that the sensors are properly aligned.
6. Maintaining Mercedes ESP: Tips for Longevity
Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of your Mercedes ESP system. By following a few simple tips, you can help prevent problems and keep your ESP system functioning optimally for years to come.
6.1 Regular Inspections and Checks
Regularly inspect the ESP system components for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Pay particular attention to the sensors, wiring, and connectors. Check the brake fluid level and condition, as this can affect the performance of the ESP system.
6.2 Tire Maintenance and Alignment
Proper tire maintenance and alignment are crucial for ensuring that the ESP system functions correctly. Uneven tire wear or misaligned wheels can affect the accuracy of the wheel speed sensors, leading to ESP malfunctions. Make sure to rotate your tires regularly and have your wheels aligned as needed.
6.3 Brake System Maintenance
The ESP system relies on the brake system to function properly, so it’s important to keep your brakes in good condition. Regularly inspect your brake pads, rotors, and calipers for wear and damage. Replace worn brake components as needed and flush the brake fluid every two years to remove contaminants and moisture.
6.4 Avoiding Aggressive Driving
Aggressive driving habits, such as hard braking and sharp cornering, can put extra stress on the ESP system. While ESP is designed to help you maintain control in challenging situations, it’s not a substitute for safe driving practices. Avoid aggressive driving and maintain a safe following distance to reduce the risk of accidents.
6.5 Addressing Warning Lights Promptly
If the ESP warning light illuminates on the dashboard, don’t ignore it. Have the system diagnosed and repaired as soon as possible to prevent further damage or safety risks. Continuing to drive with a malfunctioning ESP system can compromise your vehicle’s stability and increase the risk of accidents.
7. Upgrading Mercedes ESP: Enhancing Performance
While Mercedes ESP is a highly capable system, there are several ways to upgrade and enhance its performance. Whether you’re looking to improve handling, increase stability, or fine-tune the system for track use, several aftermarket options are available.
7.1 Aftermarket ESP Tuning and Calibration
Several aftermarket companies offer ESP tuning and calibration services for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. These services allow you to customize the ESP system to suit your driving style and preferences. You can adjust parameters such as the sensitivity of the sensors, the aggressiveness of the braking intervention, and the amount of engine power reduction.
7.2 Performance Brake Upgrades
Upgrading to high-performance brake components can improve the effectiveness of the ESP system. High-performance brake pads and rotors offer better stopping power and heat resistance, allowing the ESP system to intervene more effectively in emergency situations. Upgrading to stainless steel brake lines can also improve braking performance by reducing brake line expansion and providing a more consistent pedal feel.
7.3 Suspension Upgrades
Upgrading the suspension can also enhance the performance of the ESP system. Performance suspension components, such as lowering springs, stiffer shocks, and adjustable sway bars, can improve handling and reduce body roll, allowing the ESP system to maintain better control of the vehicle.
7.4 Wheel and Tire Upgrades
Upgrading to wider wheels and tires can also improve the performance of the ESP system. Wider tires offer more grip, allowing the ESP system to maintain better traction and control. However, it’s important to choose wheels and tires that are compatible with the ESP system to avoid triggering false alarms or malfunctions.
8. Mercedes ESP and 4MATIC: The Perfect Combination
Mercedes-Benz 4MATIC all-wheel-drive system works in harmony with ESP to provide superior traction and stability in all driving conditions. By distributing torque to all four wheels, 4MATIC enhances grip and reduces the likelihood of wheel spin, allowing the ESP system to intervene more effectively when needed.
8.1 How 4MATIC Enhances ESP Performance
4MATIC enhances ESP performance by providing a more stable and predictable platform for the system to work with. By distributing torque to all four wheels, 4MATIC reduces the likelihood of wheel spin, making it easier for the ESP system to maintain control of the vehicle. 4MATIC also improves traction on slippery surfaces, allowing the ESP system to intervene more effectively in challenging driving conditions.
8.2 Benefits of All-Wheel-Drive with ESP
The combination of all-wheel-drive and ESP offers numerous benefits:
- Improved Traction: All-wheel-drive provides superior traction in all driving conditions, reducing the likelihood of wheel spin and improving acceleration.
- Enhanced Stability: All-wheel-drive improves stability, making the vehicle more resistant to skidding and loss of control.
- Increased Safety: The combination of all-wheel-drive and ESP provides an added layer of safety, reducing the risk of accidents in challenging driving conditions.
- Enhanced Performance: All-wheel-drive improves handling and cornering performance, making the vehicle more enjoyable to drive.
8.3 Real-World Applications and Scenarios
The benefits of all-wheel-drive with ESP are particularly noticeable in real-world driving scenarios such as:
- Driving in Snow or Ice: All-wheel-drive provides superior traction on snow and ice, allowing you to maintain control of the vehicle in slippery conditions.
- Driving in Rain: All-wheel-drive improves traction in the rain, reducing the risk of hydroplaning and loss of control.
- Driving on Gravel or Dirt Roads: All-wheel-drive provides better traction on gravel and dirt roads, allowing you to maintain control of the vehicle on uneven surfaces.
- Towing: All-wheel-drive improves traction when towing, making it easier to pull heavy loads up hills or on slippery surfaces.
9. The Future of Mercedes ESP: Innovations and Trends
The future of Mercedes ESP is bright, with numerous innovations and trends on the horizon. As automotive technology continues to advance, ESP systems will become even more sophisticated and capable, further enhancing safety and performance.
9.1 Integration with Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
One of the key trends in ESP development is the integration with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). ADAS technologies such as adaptive cruise control, lane departure warning, and automatic emergency braking rely on the same sensors and data as ESP, allowing for seamless integration and enhanced functionality.
9.2 Predictive ESP Systems
Future ESP systems will be even more proactive, using predictive algorithms to anticipate potential instabilities before they occur. These systems will analyze data from various sources, such as GPS, weather sensors, and traffic cameras, to predict road conditions and adjust the ESP system accordingly.
9.3 Enhanced Sensor Technology
Advancements in sensor technology will also play a key role in the future of ESP. Higher-resolution sensors will provide more accurate and detailed data about the vehicle’s dynamics, allowing the ESP system to intervene more precisely and effectively.
9.4 Over-the-Air Updates
Over-the-air (OTA) updates will allow Mercedes-Benz to continuously improve the ESP system by delivering software updates remotely. This will enable the company to address known issues, enhance performance, and add new features without requiring drivers to visit a service center.
10. Finding the Right Mercedes ESP Diagnostic Tools at CARDIAGTECH.NET
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the critical role Mercedes ESP plays in vehicle safety and performance. That’s why we offer a comprehensive range of diagnostic tools and equipment to help you maintain, diagnose, and repair ESP systems effectively.
10.1 Comprehensive Range of Diagnostic Tools
We offer a wide selection of diagnostic tools, from basic OBD-II scanners to advanced Mercedes-specific diagnostic software such as XENTRY and DAS. Our tools are designed to provide accurate and reliable diagnostic information, helping you identify and address ESP problems quickly and efficiently.
10.2 Expert Advice and Support
Our team of experienced technicians can provide expert advice and support to help you choose the right diagnostic tools for your needs. We can also assist you with troubleshooting and repair procedures, ensuring that you have the knowledge and resources you need to keep your Mercedes ESP system functioning optimally.
10.3 High-Quality Products and Competitive Prices
We offer only high-quality diagnostic tools from trusted brands, ensuring that you get the best possible performance and reliability. We also offer competitive prices, making it affordable to equip your shop with the tools you need to service Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
10.4 Ensuring Vehicle Safety with Our Tools
By using our diagnostic tools to maintain and repair Mercedes ESP systems, you can help ensure the safety of your customers and their vehicles. A properly functioning ESP system can significantly reduce the risk of accidents, protecting drivers and passengers from harm.
Is your Mercedes-Benz ESP system acting up? Don’t compromise on safety. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET for expert advice and the best diagnostic tools. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States. Let us help you keep your Mercedes running smoothly and safely.
1. What does the ESP light mean on my Mercedes-Benz?
The ESP light indicates that the Electronic Stability Program is active or that there is a malfunction in the system. If the light stays on, it signals a need for diagnostic attention.
2. Can I drive my Mercedes-Benz with the ESP light on?
While you can drive with the ESP light on, it’s not recommended. The ESP system may not function correctly, reducing stability control. Get it checked by a professional as soon as possible.
3. How do I reset the ESP system on my Mercedes-Benz?
Resetting the ESP system typically involves using a diagnostic tool to clear any stored trouble codes. In some cases, a steering angle sensor calibration may be required.
4. What are common causes of ESP system failure in Mercedes-Benz vehicles?
Common causes include faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor issues, yaw rate sensor problems, and hydraulic control unit malfunctions.
5. How often should I have my Mercedes-Benz ESP system checked?
It’s a good practice to have your ESP system checked during regular maintenance intervals or if you notice any warning lights or performance issues.
6. Is it safe to disable ESP in my Mercedes-Benz?
Disabling ESP is generally not recommended for normal driving conditions. ESP is designed to enhance safety and stability, so disabling it can reduce control in critical situations.
7. Can low tire pressure affect the ESP system?
Yes, low tire pressure can affect the ESP system. The system relies on accurate wheel speed data, and low tire pressure can cause inaccurate readings, leading to ESP malfunctions.
8. What is the difference between ESP and ABS in a Mercedes-Benz?
ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) prevents the wheels from locking up during braking, while ESP (Electronic Stability Program) helps maintain directional control by preventing skidding. ESP often utilizes ABS components to function.
9. How much does it cost to repair the ESP system on a Mercedes-Benz?
The cost of ESP repair varies depending on the issue and the parts needed. Sensor replacements can range from $200 to $500, while more complex repairs like HCU replacement can cost over $1,000.
10. Where can I find reliable diagnostic tools for my Mercedes-Benz ESP system?
You can find reliable diagnostic tools at CARDIAGTECH.NET. We offer a comprehensive range of tools and expert support to help you maintain and repair your Mercedes-Benz ESP system effectively.