Is your Mercedes Benz Esp Malfunctioning? CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to help you understand the ESP system, diagnose the issue, and find the right tools to get it fixed. We’ll cover everything from common causes to troubleshooting steps, ensuring your Mercedes-Benz is back to its optimal performance. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice and solutions, or visit us at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States. Unlock peak performance with diagnostic tools, stability control, and brake assist.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Mercedes Benz ESP System
- 1.1 What is ESP and How Does it Work?
- 1.2 The Role of ESP in Vehicle Safety
- 1.3 Related Systems: ABS, BAS, and Traction Control
- 2. Common Symptoms of Mercedes Benz ESP Malfunction
- 2.1 ESP Warning Light Illumination
- 2.2 Reduced Stability and Handling
- 2.3 Unusual Braking Behavior
- 2.4 Engine Performance Issues
- 3. Potential Causes of ESP Malfunction
- 3.1 Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
- 3.2 Steering Angle Sensor Problems
- 3.3 Yaw Rate Sensor Issues
- 3.4 Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) Malfunctions
- 3.5 ECU (Electronic Control Unit) Problems
- 3.6 Low Brake Fluid Level
- 4. Diagnosing a Mercedes Benz ESP Malfunction
- 4.1 Using a Diagnostic Scanner
- 4.2 Checking Wheel Speed Sensors
- 4.3 Examining the Steering Angle Sensor
- 4.4 Inspecting the Yaw Rate Sensor
- 4.5 Checking the Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU)
- 4.6 Verifying the ECU (Electronic Control Unit)
- 4.7 Assessing Brake Fluid Levels and Condition
- 5. Repairing a Mercedes Benz ESP Malfunction
- 5.1 Replacing Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
- 5.2 Calibrating the Steering Angle Sensor
- 5.3 Replacing a Yaw Rate Sensor
- 5.4 Addressing Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) Issues
- 5.5 Rectifying ECU (Electronic Control Unit) Problems
- 5.6 Flushing and Replacing Brake Fluid
- 6. Preventing Future ESP Malfunctions
- 6.1 Regular Maintenance Checks
- 6.2 Proper Tire Maintenance
- 6.3 Driving Habits and Conditions
- 6.4 Keeping the System Clean
- 7. Choosing the Right Diagnostic Tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET
- 7.1 Basic Code Readers vs. Advanced Scanners
- 7.2 Features to Look for in a Diagnostic Tool
- 7.3 Recommended Diagnostic Tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET
- 8.1 Factors Affecting Repair Costs
- 8.2 Estimated Costs for Common Repairs
- 8.3 DIY vs. Professional Repair
1. Understanding the Mercedes Benz ESP System
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in your Mercedes-Benz is a critical safety feature designed to prevent skidding and maintain control during challenging driving conditions. The ESP system integrates various sensors and actuators to monitor and adjust vehicle dynamics, ensuring optimal stability and handling. Knowing how the ESP system works is the first step in addressing any potential issues.
1.1 What is ESP and How Does it Work?
ESP, short for Electronic Stability Program, is a sophisticated system that enhances vehicle stability by detecting and reducing loss of traction. It works by monitoring wheel speed, steering angle, and yaw rate (the rate at which the car is turning). If the system detects a discrepancy between the driver’s intended direction and the vehicle’s actual movement, it selectively applies brakes to individual wheels and adjusts engine power to help steer the car back on course.
- Wheel Speed Sensors: These sensors monitor the rotational speed of each wheel, providing data on whether a wheel is slipping or locking up.
- Steering Angle Sensor: This sensor measures the angle of the steering wheel, indicating the driver’s intended direction.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: This sensor measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis, detecting if the car is turning more or less than intended.
- Brake Actuators: These components apply braking force to individual wheels as needed to correct oversteer or understeer.
- Engine Control Unit (ECU): The ECU processes data from the sensors and controls the brake actuators and engine power to maintain stability.
This intricate interplay of sensors and actuators allows ESP to respond quickly and effectively to potential loss of control situations, enhancing overall safety and driving confidence.
1.2 The Role of ESP in Vehicle Safety
ESP plays a pivotal role in enhancing vehicle safety by preventing skidding and loss of control. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), ESP can reduce single-vehicle crashes by up to 35%. This is because ESP helps drivers maintain control during emergency maneuvers, such as sudden braking or swerving to avoid an obstacle.
ESP is particularly effective in adverse weather conditions, such as rain, snow, and ice, where the risk of skidding is higher. By selectively applying brakes to individual wheels, ESP can help prevent the car from spinning out or sliding off the road, reducing the likelihood of accidents.
Moreover, ESP can also improve overall driving stability and handling, even in normal driving conditions. By continuously monitoring vehicle dynamics and making small adjustments as needed, ESP can help keep the car on its intended path, reducing driver fatigue and improving comfort.
1.3 Related Systems: ABS, BAS, and Traction Control
ESP often works in conjunction with other vehicle safety systems, such as Anti-lock Braking System (ABS), Brake Assist System (BAS), and Traction Control System (TCS), to provide comprehensive protection.
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): ABS prevents the wheels from locking up during hard braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control. It modulates brake pressure to each wheel independently, preventing skidding and shortening stopping distances.
- Brake Assist System (BAS): BAS detects emergency braking situations by monitoring the speed and force with which the driver presses the brake pedal. If BAS detects an emergency, it applies maximum braking force to help the driver stop the car as quickly as possible.
- Traction Control System (TCS): TCS prevents wheel spin during acceleration by reducing engine power and applying brakes to the spinning wheel. This helps maintain traction and prevents the car from losing control on slippery surfaces.
Together, ESP, ABS, BAS, and TCS form a comprehensive suite of safety systems that work seamlessly to enhance vehicle stability, control, and overall safety. Proper maintenance and diagnostics of these systems are essential to ensure they function correctly and provide the intended level of protection. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools and equipment to help you keep these systems in top condition. Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for more information.
2. Common Symptoms of Mercedes Benz ESP Malfunction
Recognizing the symptoms of an ESP malfunction is crucial for timely diagnosis and repair. The ESP system communicates potential issues through warning lights and changes in vehicle behavior, alerting the driver to a problem that needs attention. Being aware of these symptoms can help prevent more severe issues and ensure your safety on the road.
2.1 ESP Warning Light Illumination
The most common symptom of an ESP malfunction is the illumination of the ESP warning light on the dashboard. This light, often depicted as a car skidding, indicates that the ESP system has detected a problem or has been deactivated. The light may appear in different ways, providing additional clues about the nature of the issue:
- Constant Illumination: A continuously lit ESP warning light typically indicates a malfunction within the system. This could be due to a faulty sensor, a problem with the ECU, or a wiring issue.
- Flashing Light: A flashing ESP warning light usually means that the ESP system is actively engaged and working to stabilize the vehicle. This can occur during slippery conditions or when the car detects a loss of traction.
- ESP and ABS Lights Together: If both the ESP and ABS warning lights are illuminated, it often indicates a problem that affects both systems. This could be due to a shared sensor or a fault in the hydraulic control unit.
When the ESP warning light comes on, it is essential to investigate the issue promptly. Ignoring the warning light can lead to reduced stability and control, increasing the risk of accidents. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides a variety of diagnostic tools that can help you identify the specific cause of the ESP warning light and take appropriate action.
2.2 Reduced Stability and Handling
An ESP malfunction can manifest as a noticeable reduction in vehicle stability and handling. This can be particularly evident during cornering or when driving on uneven surfaces. Symptoms may include:
- Difficulty Maintaining Direction: The car may feel unstable and require constant steering corrections to stay on course.
- Increased Body Roll: The car may exhibit excessive body roll during turns, making it feel less planted and secure.
- Skidding or Slipping: The wheels may lose traction more easily, leading to skidding or slipping, especially in wet or icy conditions.
These handling issues can make driving more challenging and increase the risk of accidents. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to have your ESP system inspected and repaired as soon as possible. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers expert diagnostic services and high-quality repair tools to help you restore your vehicle’s stability and handling. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 to schedule a consultation.
2.3 Unusual Braking Behavior
Another symptom of an ESP malfunction can be unusual braking behavior. Since ESP works closely with the braking system, any issues with ESP can affect how the brakes perform. This may include:
- Uneven Braking: The brakes may apply unevenly, causing the car to pull to one side during braking.
- Delayed Braking Response: There may be a delay between pressing the brake pedal and the car actually slowing down.
- Increased Stopping Distance: The stopping distance may be longer than usual, making it harder to stop the car in an emergency.
These braking issues can compromise safety and increase the risk of collisions. If you notice any unusual braking behavior, it is essential to have your ESP system and braking system inspected by a qualified technician. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides advanced diagnostic tools and equipment to help you identify and resolve braking system issues quickly and effectively.
2.4 Engine Performance Issues
In some cases, an ESP malfunction can also lead to engine performance issues. This is because the ESP system can affect engine control to maintain stability. Symptoms may include:
- Reduced Engine Power: The engine may feel less responsive, with reduced power and acceleration.
- Rough Idling: The engine may idle roughly or stall frequently.
- Hesitation During Acceleration: The engine may hesitate or stumble when accelerating.
These engine performance issues can affect overall drivability and fuel efficiency. If you experience any of these symptoms along with the ESP warning light, it is essential to have your ESP system and engine control system inspected. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers comprehensive diagnostic services and high-quality repair tools to help you restore your vehicle’s engine performance and stability.
Recognizing these common symptoms of a Mercedes Benz ESP malfunction can help you take timely action and prevent more severe issues. Regular maintenance and diagnostic checks are essential to ensure your ESP system is functioning correctly and providing the intended level of protection. CARDIAGTECH.NET is your trusted partner for all your automotive diagnostic and repair needs. Visit our website or call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 to learn more about our products and services.
3. Potential Causes of ESP Malfunction
Understanding the potential causes of an ESP malfunction is crucial for effective diagnosis and repair. The ESP system is complex and relies on various sensors, actuators, and electronic components to function correctly. Identifying the root cause of the problem can help you address it efficiently and prevent recurrence.
3.1 Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
One of the most common causes of ESP malfunction is a faulty wheel speed sensor. These sensors monitor the rotational speed of each wheel and provide critical data to the ESP system. If a wheel speed sensor fails or provides inaccurate data, the ESP system may not be able to function correctly.
- Sensor Failure: The sensor itself may fail due to physical damage, corrosion, or wear and tear.
- Wiring Issues: The wiring connecting the sensor to the ECU may be damaged, causing intermittent or complete loss of signal.
- Contamination: The sensor may be contaminated with dirt, debris, or brake dust, affecting its accuracy.
Symptoms of a faulty wheel speed sensor may include the ESP warning light, ABS warning light, reduced traction control, and erratic braking behavior. To diagnose a faulty wheel speed sensor, you can use a diagnostic scanner to read the sensor data and check for error codes. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of high-quality diagnostic scanners that can help you identify wheel speed sensor issues quickly and accurately.
3.2 Steering Angle Sensor Problems
The steering angle sensor measures the angle of the steering wheel and provides data on the driver’s intended direction. If the steering angle sensor malfunctions, the ESP system may not be able to accurately determine the driver’s input, leading to reduced stability and control.
- Sensor Calibration: The steering angle sensor may need to be calibrated to ensure accurate readings.
- Sensor Failure: The sensor itself may fail due to electrical or mechanical issues.
- Wiring Problems: The wiring connecting the sensor to the ECU may be damaged or corroded.
Symptoms of a steering angle sensor problem may include the ESP warning light, difficulty maintaining direction, and erratic steering behavior. To diagnose a steering angle sensor problem, you can use a diagnostic scanner to read the sensor data and perform a calibration procedure. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides professional-grade diagnostic tools that can help you troubleshoot and resolve steering angle sensor issues effectively.
3.3 Yaw Rate Sensor Issues
The yaw rate sensor measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis, detecting if the car is turning more or less than intended. If the yaw rate sensor malfunctions, the ESP system may not be able to accurately assess the vehicle’s movement, leading to reduced stability and control.
- Sensor Failure: The sensor itself may fail due to internal component issues.
- Wiring Problems: The wiring connecting the sensor to the ECU may be damaged or corroded.
- Mounting Issues: The sensor may be improperly mounted, affecting its accuracy.
Symptoms of a yaw rate sensor problem may include the ESP warning light, difficulty maintaining direction, and erratic handling behavior. To diagnose a yaw rate sensor problem, you can use a diagnostic scanner to read the sensor data and check for error codes. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a variety of diagnostic tools and equipment to help you identify and resolve yaw rate sensor issues quickly and accurately.
3.4 Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) Malfunctions
The Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) is a critical component of the ESP system, responsible for applying braking force to individual wheels as needed to correct oversteer or understeer. If the HCU malfunctions, the ESP system may not be able to effectively control braking, leading to reduced stability and control.
- Internal Failure: The HCU may fail due to internal component issues, such as valve failures or pump problems.
- Electrical Issues: The electrical components of the HCU may malfunction, preventing it from operating correctly.
- Hydraulic Problems: The hydraulic system within the HCU may develop leaks or blockages, affecting its performance.
Symptoms of an HCU malfunction may include the ESP warning light, ABS warning light, unusual braking behavior, and reduced stability. To diagnose an HCU malfunction, you can use a diagnostic scanner to read the system data and perform diagnostic tests. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides advanced diagnostic tools and equipment to help you troubleshoot and resolve HCU issues effectively.
3.5 ECU (Electronic Control Unit) Problems
The ECU is the brain of the ESP system, responsible for processing data from the sensors and controlling the actuators. If the ECU malfunctions, the ESP system may not be able to function correctly.
- Software Issues: The ECU software may be corrupted or outdated, leading to errors in system operation.
- Hardware Failure: The ECU hardware may fail due to electrical damage, overheating, or internal component issues.
- Wiring Problems: The wiring connecting the ECU to the sensors and actuators may be damaged or corroded.
Symptoms of an ECU problem may include the ESP warning light, ABS warning light, reduced stability, and various other system malfunctions. To diagnose an ECU problem, you can use a diagnostic scanner to read the system data, check for error codes, and perform diagnostic tests. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers professional-grade diagnostic tools and equipment to help you troubleshoot and resolve ECU issues effectively.
3.6 Low Brake Fluid Level
While seemingly simple, a low brake fluid level can also trigger the ESP warning light. The ESP system relies on the hydraulic pressure of the brake fluid to function correctly. If the brake fluid level is too low, the system may not be able to generate enough pressure to apply the brakes effectively, leading to reduced stability and control.
- Leaks: Brake fluid leaks can cause the fluid level to drop over time.
- Worn Brake Pads: As brake pads wear down, the fluid level in the reservoir may drop.
- System Issues: Problems within the braking system can also lead to low brake fluid levels.
Symptoms of low brake fluid may include the ESP warning light, ABS warning light, soft brake pedal, and increased stopping distance. To check the brake fluid level, simply inspect the brake fluid reservoir under the hood. If the level is low, you should top it off and inspect the braking system for leaks or other issues. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of brake service tools and equipment to help you maintain your braking system and ensure optimal performance.
Understanding these potential causes of a Mercedes Benz ESP malfunction can help you diagnose and address the issue effectively. Regular maintenance and diagnostic checks are essential to ensure your ESP system is functioning correctly and providing the intended level of protection. CARDIAGTECH.NET is your trusted partner for all your automotive diagnostic and repair needs. Visit our website or call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 to learn more about our products and services.
4. Diagnosing a Mercedes Benz ESP Malfunction
Diagnosing a Mercedes Benz ESP malfunction requires a systematic approach to identify the root cause of the problem. With the right tools and knowledge, you can effectively troubleshoot the issue and restore your vehicle’s stability and control. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a comprehensive range of diagnostic tools and equipment to help you through the process.
4.1 Using a Diagnostic Scanner
A diagnostic scanner is an essential tool for diagnosing ESP malfunctions. It allows you to read error codes, view live data, and perform diagnostic tests, providing valuable insights into the system’s operation. Here’s how to use a diagnostic scanner effectively:
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the diagnostic scanner into the OBD-II port, typically located under the dashboard.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “on” position without starting the engine.
- Select Your Vehicle: Choose your vehicle’s make, model, and year from the scanner’s menu.
- Read Error Codes: Select the “Read Codes” or “Trouble Codes” option to view any stored error codes related to the ESP system.
- Interpret the Codes: Use the scanner’s built-in database or a reference guide to interpret the error codes and identify the affected components.
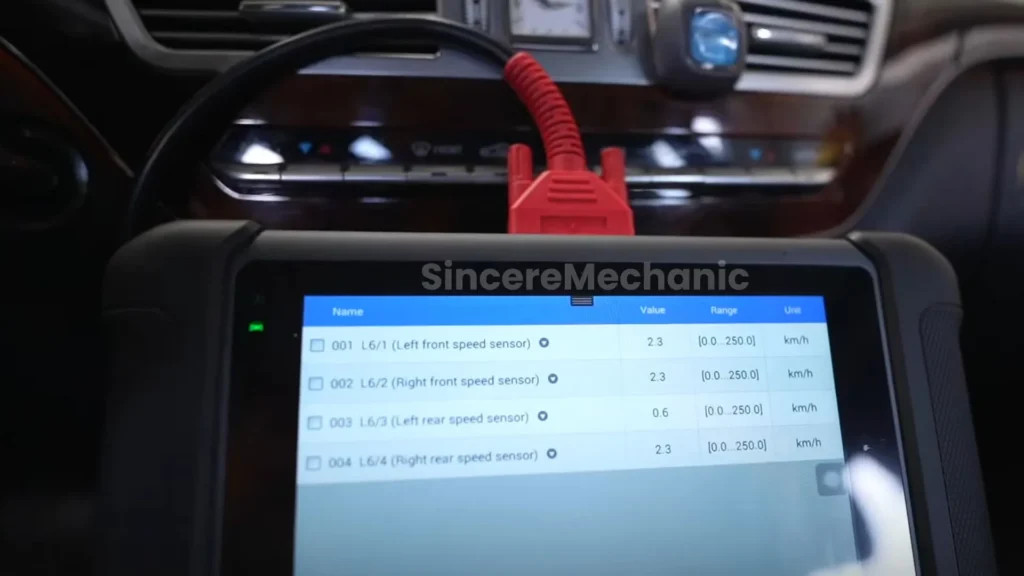
- View Live Data: Select the “Live Data” or “Data Stream” option to view real-time data from the ESP sensors, such as wheel speed, steering angle, and yaw rate.
- Perform Diagnostic Tests: Use the scanner to perform specific diagnostic tests, such as actuator tests or sensor calibration procedures.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of diagnostic scanners, from basic code readers to advanced professional-grade tools. Our scanners are compatible with Mercedes Benz vehicles and provide comprehensive diagnostic capabilities. Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 to find the right diagnostic scanner for your needs.
4.2 Checking Wheel Speed Sensors
Wheel speed sensors are a common source of ESP malfunctions. Here’s how to check them effectively:
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the sensors and wiring for any visible damage, such as cracks, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Resistance Test: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of each sensor. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications to identify any faulty sensors.
- Signal Test: Use an oscilloscope or a diagnostic scanner to monitor the sensor’s output signal while rotating the wheel. Look for any irregularities or dropouts in the signal.
- Air Gap Check: Verify that the air gap between the sensor and the tone ring is within the specified range.
If you identify a faulty wheel speed sensor, replace it with a new, high-quality sensor from CARDIAGTECH.NET. We offer a wide selection of wheel speed sensors for Mercedes Benz vehicles, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
4.3 Examining the Steering Angle Sensor
The steering angle sensor is another critical component of the ESP system. Here’s how to examine it effectively:
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the sensor and wiring for any visible damage or loose connections.
- Data Monitoring: Use a diagnostic scanner to monitor the sensor’s output data while turning the steering wheel. Look for any irregularities or inconsistencies in the readings.
- Calibration Check: Verify that the sensor is properly calibrated. Use a diagnostic scanner to perform a calibration procedure if necessary.
If you identify a faulty steering angle sensor, replace it with a new, high-quality sensor from CARDIAGTECH.NET. We offer a range of steering angle sensors for Mercedes Benz vehicles, ensuring accurate and reliable steering input data.
4.4 Inspecting the Yaw Rate Sensor
The yaw rate sensor measures the vehicle’s rotation and is crucial for ESP function. Inspect it as follows:
- Visual Inspection: Check the sensor and its wiring for any signs of damage or loose connections.
- Data Monitoring: Use a diagnostic scanner to monitor the sensor’s output data while driving the vehicle. Look for any erratic or inconsistent readings.
- Mounting Check: Verify that the sensor is securely mounted and properly aligned.
If you find a faulty yaw rate sensor, replace it with a new, high-quality sensor from CARDIAGTECH.NET. Our yaw rate sensors are designed to provide accurate and reliable data, ensuring optimal ESP performance.
4.5 Checking the Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU)
The HCU controls braking force to individual wheels and requires careful inspection:
- Visual Inspection: Check the HCU and its hydraulic lines for any signs of leaks or damage.
- Actuator Test: Use a diagnostic scanner to perform an actuator test on the HCU, verifying that each valve is functioning correctly.
- Pressure Test: Use a hydraulic pressure gauge to measure the pressure output of the HCU. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications.
If you identify a faulty HCU, consider replacing it with a remanufactured or new unit from CARDIAGTECH.NET. We offer a range of HCUs for Mercedes Benz vehicles, providing reliable performance and long-lasting durability.
4.6 Verifying the ECU (Electronic Control Unit)
The ECU is the brain of the ESP system and requires thorough verification:
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the ECU and its wiring for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Data Monitoring: Use a diagnostic scanner to monitor the ECU’s input and output data, verifying that it is processing information correctly.
- Software Update: Check for any available software updates for the ECU. Use a diagnostic scanner to perform a software update if necessary.
If you suspect a faulty ECU, consider replacing it with a new or remanufactured unit from CARDIAGTECH.NET. We offer a range of ECUs for Mercedes Benz vehicles, programmed and tested to ensure optimal performance and compatibility.
4.7 Assessing Brake Fluid Levels and Condition
Low or contaminated brake fluid can affect ESP performance. Assess as follows:
- Fluid Level Check: Inspect the brake fluid reservoir and verify that the fluid level is within the specified range.
- Fluid Condition Check: Inspect the brake fluid for any signs of contamination, such as dirt, debris, or discoloration.
- Fluid Test: Use a brake fluid tester to measure the moisture content of the fluid. If the moisture content is too high, replace the fluid with fresh, high-quality brake fluid from CARDIAGTECH.NET.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a complete range of brake service tools and equipment, including brake fluid testers, bleeders, and replacement fluids. Visit our website or call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 to learn more about our products and services.
By following these diagnostic steps and using the right tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET, you can effectively diagnose a Mercedes Benz ESP malfunction and restore your vehicle’s stability and control. Regular maintenance and diagnostic checks are essential to ensure your ESP system is functioning correctly and providing the intended level of protection.
5. Repairing a Mercedes Benz ESP Malfunction
Once you have diagnosed the cause of the ESP malfunction, the next step is to repair it. The repair process will vary depending on the specific issue, but with the right tools and knowledge, you can effectively restore your vehicle’s stability and control. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a comprehensive range of repair tools and equipment to help you through the process.
5.1 Replacing Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
Replacing a faulty wheel speed sensor is a common repair for ESP malfunctions. Here’s how to do it effectively:
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical damage.
- Locate the Sensor: Locate the faulty wheel speed sensor on the affected wheel.
- Remove the Wheel: Remove the wheel to access the sensor.
- Disconnect the Sensor: Disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor.
- Remove the Sensor: Remove the sensor from its mounting location.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor in the mounting location.
- Connect the Sensor: Connect the electrical connector to the new sensor.
- Reinstall the Wheel: Reinstall the wheel.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Test the System: Use a diagnostic scanner to clear any error codes and verify that the ESP system is functioning correctly.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide selection of high-quality wheel speed sensors for Mercedes Benz vehicles. Our sensors are designed to provide accurate and reliable data, ensuring optimal ESP performance.
5.2 Calibrating the Steering Angle Sensor
Calibrating the steering angle sensor is essential after replacing the sensor or performing certain repairs. Here’s how to do it:
- Connect the Scanner: Connect a diagnostic scanner to the OBD-II port.
- Select Your Vehicle: Choose your vehicle’s make, model, and year from the scanner’s menu.
- Access Calibration Function: Navigate to the “Steering Angle Sensor Calibration” function in the scanner’s menu.
- Follow Instructions: Follow the on-screen instructions to calibrate the sensor. This typically involves turning the steering wheel to specific positions and pressing a button on the scanner.
- Verify Calibration: Verify that the calibration was successful by monitoring the sensor’s output data while turning the steering wheel.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers professional-grade diagnostic tools that can perform steering angle sensor calibration quickly and accurately. Our scanners are compatible with Mercedes Benz vehicles and provide comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
5.3 Replacing a Yaw Rate Sensor
Replacing a yaw rate sensor involves these steps:
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Locate the Sensor: Find the yaw rate sensor, usually under a seat or in the center console.
- Disconnect the Sensor: Disconnect the electrical connector.
- Remove the Sensor: Remove the sensor from its mounting.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor in its place.
- Connect the Sensor: Reconnect the electrical connector.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the battery’s negative terminal.
- Test the System: Use a diagnostic scanner to clear codes and verify proper ESP function.
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides high-quality yaw rate sensors for Mercedes Benz vehicles, ensuring accurate and reliable performance.
5.4 Addressing Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) Issues
Repairing HCU issues can be complex, often requiring professional expertise. Options include:
- Professional Repair: Take the vehicle to a trusted mechanic for HCU repair or replacement.
- HCU Replacement: Replace the HCU with a new or remanufactured unit from CARDIAGTECH.NET.
- Bleeding the System: After HCU work, bleed the brake system to remove air, ensuring proper function.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of HCUs for Mercedes Benz vehicles, providing reliable performance and durability.
5.5 Rectifying ECU (Electronic Control Unit) Problems
ECU issues can be resolved through:
- Software Update: Update the ECU software using a diagnostic scanner.
- ECU Replacement: Replace the ECU with a new or remanufactured unit from CARDIAGTECH.NET.
- Professional Programming: Have a professional program the new ECU to match your vehicle’s specifications.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a variety of ECUs for Mercedes Benz vehicles, pre-programmed and tested for optimal compatibility.
5.6 Flushing and Replacing Brake Fluid
Maintaining proper brake fluid levels and condition is crucial. Here’s how to do it:
- Brake Fluid Flush: Use a brake bleeder to flush the old brake fluid from the system.
- Fill with New Fluid: Fill the system with fresh, high-quality brake fluid from CARDIAGTECH.NET.
- Bleed the Brakes: Bleed the brakes to remove any air from the lines.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a complete range of brake service tools and equipment, including brake fluid testers, bleeders, and replacement fluids.
By following these repair steps and using the right tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET, you can effectively repair a Mercedes Benz ESP malfunction and restore your vehicle’s stability and control. Regular maintenance and diagnostic checks are essential to ensure your ESP system is functioning correctly and providing the intended level of protection.
6. Preventing Future ESP Malfunctions
Preventing future ESP malfunctions involves regular maintenance and proactive care. By following these tips, you can keep your ESP system functioning correctly and ensure optimal vehicle stability and safety.
6.1 Regular Maintenance Checks
Regular maintenance checks are essential for preventing ESP malfunctions. This includes:
- Checking Wheel Speed Sensors: Inspect the wheel speed sensors and wiring for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Monitoring Brake Fluid Levels: Keep an eye on the brake fluid level and top it off as needed.
- Inspecting Brake Components: Inspect the brake pads, rotors, and calipers for wear and tear.
- Performing Diagnostic Scans: Use a diagnostic scanner to check for any stored error codes related to the ESP system.
6.2 Proper Tire Maintenance
Proper tire maintenance is crucial for ESP performance. This includes:
- Maintaining Correct Tire Pressure: Keep your tires inflated to the recommended pressure.
- Regular Tire Rotations: Rotate your tires regularly to ensure even wear.
- Replacing Worn Tires: Replace worn tires promptly to maintain optimal traction.
6.3 Driving Habits and Conditions
Your driving habits and the conditions you drive in can also affect ESP performance. Consider the following:
- Avoid Aggressive Driving: Avoid sudden acceleration, braking, and steering maneuvers.
- Drive Carefully in Adverse Conditions: Drive cautiously in rain, snow, and ice.
- Address Issues Promptly: If you notice any signs of ESP malfunction, address the issue promptly to prevent further damage.
6.4 Keeping the System Clean
Keeping the ESP system clean is crucial for optimal performance. This includes:
- Cleaning Wheel Speed Sensors: Clean the wheel speed sensors regularly to remove dirt, debris, and brake dust.
- Flushing Brake Fluid: Flush the brake fluid every two to three years to remove contaminants.
- Protecting Wiring: Protect the wiring and connectors from corrosion and damage.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of cleaning and maintenance products to help you keep your ESP system in top condition. Visit our website or call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 to learn more about our products and services.
By following these preventive measures, you can minimize the risk of ESP malfunctions and ensure your Mercedes Benz remains stable and safe on the road. Remember, regular maintenance and proactive care are key to keeping your vehicle in top condition.
7. Choosing the Right Diagnostic Tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET
Selecting the right diagnostic tools is essential for accurately diagnosing and repairing ESP malfunctions. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of high-quality diagnostic tools designed to meet the needs of both professional technicians and DIY enthusiasts.
7.1 Basic Code Readers vs. Advanced Scanners
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a variety of code readers and scanners, each with its own set of features and capabilities.
- Basic Code Readers: These are simple, handheld devices that can read and clear basic OBD-II error codes. They are ideal for quick diagnostics and basic maintenance tasks.
- Advanced Scanners: These are more sophisticated tools that can read and clear advanced error codes, view live data, perform actuator tests, and perform other diagnostic functions. They are ideal for professional technicians and experienced DIYers.
7.2 Features to Look for in a Diagnostic Tool
When choosing a diagnostic tool from CARDIAGTECH.NET, consider the following features:
- Compatibility: Ensure that the tool is compatible with your Mercedes Benz vehicle.
- Functionality: Choose a tool that offers the features you need, such as code reading, live data, actuator tests, and sensor calibration.
- Ease of Use: Select a tool that is easy to use and navigate.
- Reliability: Choose a tool from a reputable brand known for its quality and reliability.
- Updates: Ensure that the tool can be updated with the latest software and vehicle data.
7.3 Recommended Diagnostic Tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools that are highly recommended for diagnosing and repairing Mercedes Benz ESP malfunctions. Some of our top picks include:
- Launch X431 V+: This advanced diagnostic scanner offers comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, including code reading, live data, actuator tests, and sensor calibration.
- Autel MaxiSys MS906BT: This professional-grade scanner is known for its accuracy, reliability, and ease of use. It offers a wide range of diagnostic functions and is compatible with a wide range of vehicles.
- iCarsoft MB V3.0: A more affordable option, this scanner is specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, offering comprehensive diagnostics, including ESP-related codes and live data.
By choosing the right diagnostic tool from CARDIAGTECH.NET, you can effectively diagnose and repair Mercedes Benz ESP malfunctions and ensure your vehicle remains stable and safe on the road. Visit our website or call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 to learn more about our diagnostic tools and equipment.
The cost of repairing an ESP malfunction can vary depending on the cause of the problem and the extent of the damage. Understanding the potential costs involved can help you budget for repairs and make informed decisions.
8.1 Factors Affecting Repair Costs
Several factors can affect the cost of repairing an ESP malfunction, including:
- Type of Repair: Simple repairs, such as replacing a faulty wheel speed sensor, will typically be less expensive than more complex repairs, such as replacing the HCU or ECU.
- Parts Costs: The cost of replacement parts can vary depending on the brand, quality, and availability.
- Labor Costs: Labor costs can vary depending on the mechanic’s hourly rate and the complexity of the repair.
- Location: Repair costs can vary depending on the location of the repair shop.
8.2 Estimated Costs for Common Repairs
Here are some estimated costs for common ESP repairs:
| Repair | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| Replacing a Wheel Speed Sensor | $150 – $300 |
| Calibrating the Steering Angle Sensor | $100 – $200 |
| Replacing a Yaw Rate Sensor | $200 – $400 |
| Replacing the Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) | $800 – $1500 |
| Replacing the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) | $1000 – $2000+ |
| Brake Fluid Flush | $80 – $150 |
Please note that these are just estimates, and the actual cost of repair may vary depending on the factors mentioned above.
8.3 DIY vs. Professional Repair
One important decision to make is whether to attempt the repair yourself or take your vehicle to a professional mechanic.
- DIY Repair: DIY repair can save you money on labor costs, but it requires technical knowledge, specialized tools, and access to accurate repair information.
- Professional Repair: Professional repair can be more expensive, but it ensures that the repair is done correctly and safely. It also provides peace of mind knowing that the mechanic is experienced and qualified.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of diagnostic and repair tools to help you with DIY repairs. However, if you are not comfortable performing the repair yourself, it is always best to take your vehicle to a qualified mechanic.