Esp Mercedes Benz C240 is crucial for vehicle stability and safety, and CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to help you understand and address related issues. This comprehensive guide explores the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in your Mercedes-Benz C240, offering insights into its function, common problems, and effective solutions with the diagnostic tools. Learn how to maintain your ESP system for optimal performance with ABS integration and vehicle dynamics control.
Contents
- 1. Understanding ESP in Your Mercedes Benz C240
- 1.1. What is ESP?
- 1.2. How ESP Works in Mercedes Benz C240
- 1.3. Benefits of ESP
- 2. Common ESP Problems in Mercedes Benz C240
- 2.1. ESP Warning Light
- 2.2. Sensor Malfunctions
- 2.3. ABS Integration Issues
- 3. Diagnosing ESP Problems in Your C240
- 3.1. Visual Inspection
- 3.2. Using Diagnostic Tools
- 3.3. Interpreting Error Codes
- 4. Solutions for ESP Problems in Mercedes Benz C240
- 4.1. Replacing Faulty Sensors
- 4.2. Repairing Wiring Issues
- 4.3. Reprogramming the ESP Module
- 5. Maintaining Your ESP System
- 5.1. Regular Inspections
- 5.2. Tire Maintenance
- 5.3. Brake System Maintenance
- 6. Advanced ESP Features in Mercedes Benz C240
- 6.1. Brake Assist System (BAS)
- 6.2. Traction Control System (TCS)
- 6.3. Adaptive ESP
- 7. ESP Mercedes Benz C240: Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
- Step 1: Understand the ESP System
- Step 2: Identify the Symptoms
- Step 3: Initial Checks
- Step 4: Use an OBD-II Scanner
- Step 5: Diagnose the Trouble Codes
- Step 6: Advanced Troubleshooting
- Step 7: Professional Assistance
- Step 8: Preventive Measures
- 8. ESP Mercedes Benz C240: What to Do When the Light Stays On
- Step 1: Understand the Significance
- Step 2: Initial Assessment
- Step 3: Use an OBD-II Scanner for Diagnostic Codes
- Step 4: Diagnose the Trouble Codes
- Step 5: Inspect and Test Wheel Speed Sensors
- Step 6: Check the Steering Angle Sensor
- Step 7: Examine the ABS (Anti-lock Braking System)
- Step 8: Advanced Troubleshooting
- Step 9: Professional Assistance
- Step 10: Preventive Measures
- 9. ESP Mercedes Benz C240: How To Reset ESP Light
- Step 1: Understand the ESP System
- Step 2: Initial Checks
- Step 3: Steering Wheel Reset Method
- Step 4: Driving the Vehicle Method
- Step 5: Using an OBD-II Scanner
- Step 6: Check the Wheel Speed Sensors
- Step 7: Check the Steering Angle Sensor
- Step 8: Battery Reset Method (If Applicable)
- Step 9: Professional Assistance
- Step 10: Preventive Measures
- 10.1. Comprehensive Diagnostic Tools
- 10.2. Expert Support and Guidance
- 10.3. High-Quality Replacement Parts
1. Understanding ESP in Your Mercedes Benz C240
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is a vital safety feature in your Mercedes Benz C240, designed to prevent skidding and maintain control during challenging driving conditions. It integrates with several other systems, including the anti-lock braking system (ABS) and traction control, to enhance vehicle stability.
1.1. What is ESP?
ESP stands for Electronic Stability Program. It is a computerized technology that enhances the safety of a vehicle’s stability by detecting and reducing loss of traction (skidding). When ESP detects a loss of steering control, it automatically applies the brakes to help steer the vehicle where the driver intends to go. Braking is automatically applied to individual wheels, such as the outer front wheel to counter oversteer or the inner rear wheel to counter understeer.
- Core Function: Prevents skidding and loss of control.
- Integration: Works with ABS, traction control, and other systems.
- Benefit: Enhances safety in adverse driving conditions.
1.2. How ESP Works in Mercedes Benz C240
The ESP system in your Mercedes Benz C240 uses sensors to monitor the vehicle’s direction and compares it to the driver’s intended path. If a discrepancy is detected, ESP selectively applies brakes to individual wheels to correct the vehicle’s trajectory.
- Sensors: Monitor wheel speed, steering angle, and yaw rate.
- Computer Analysis: Compares actual direction with intended direction.
- Corrective Action: Applies brakes to individual wheels to stabilize the vehicle.
1.3. Benefits of ESP
Having a functioning ESP system in your Mercedes Benz C240 offers numerous benefits, primarily enhancing safety and control in various driving conditions.
- Enhanced Safety: Reduces the risk of accidents caused by skidding.
- Improved Control: Maintains vehicle stability in adverse conditions.
- Better Handling: Enhances overall driving experience.
2. Common ESP Problems in Mercedes Benz C240
Several issues can affect the ESP system in your Mercedes Benz C240, leading to warning lights and compromised performance. Identifying these common problems is the first step toward effective troubleshooting.
2.1. ESP Warning Light
The ESP warning light on your Mercedes Benz C240 dashboard indicates an issue with the ESP system. The light may either flash or remain illuminated, each signaling a different condition.
- Flashing Light: Indicates ESP is actively engaged, correcting a skid.
- Solid Light: Indicates ESP is disabled or malfunctioning.
- Initial Action: Check for any unusual driving conditions or recent incidents.
2.2. Sensor Malfunctions
Faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, or yaw rate sensors can disrupt the ESP system’s ability to accurately monitor the vehicle’s dynamics, leading to malfunctions.
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Provide data on wheel rotation.
- Steering Angle Sensors: Measure the angle of the steering wheel.
- Yaw Rate Sensors: Detect the vehicle’s rotation.
2.3. ABS Integration Issues
Since ESP relies on the ABS system, problems with ABS can also affect ESP functionality. Issues such as faulty ABS sensors or a malfunctioning ABS module can trigger the ESP warning light.
- ABS Sensors: Essential for ESP to function correctly.
- ABS Module: Controls the ABS system and interacts with ESP.
- Diagnostic Check: Use a diagnostic tool to check ABS codes.
3. Diagnosing ESP Problems in Your C240
Diagnosing ESP problems in your Mercedes Benz C240 requires a systematic approach, starting with identifying symptoms and using diagnostic tools to pinpoint the root cause.
3.1. Visual Inspection
Begin with a visual inspection of the ESP system components, checking for any obvious signs of damage or wear.
- Wiring: Inspect for frayed or damaged wires.
- Connectors: Check for loose or corroded connectors.
- Sensors: Look for physical damage to sensors.
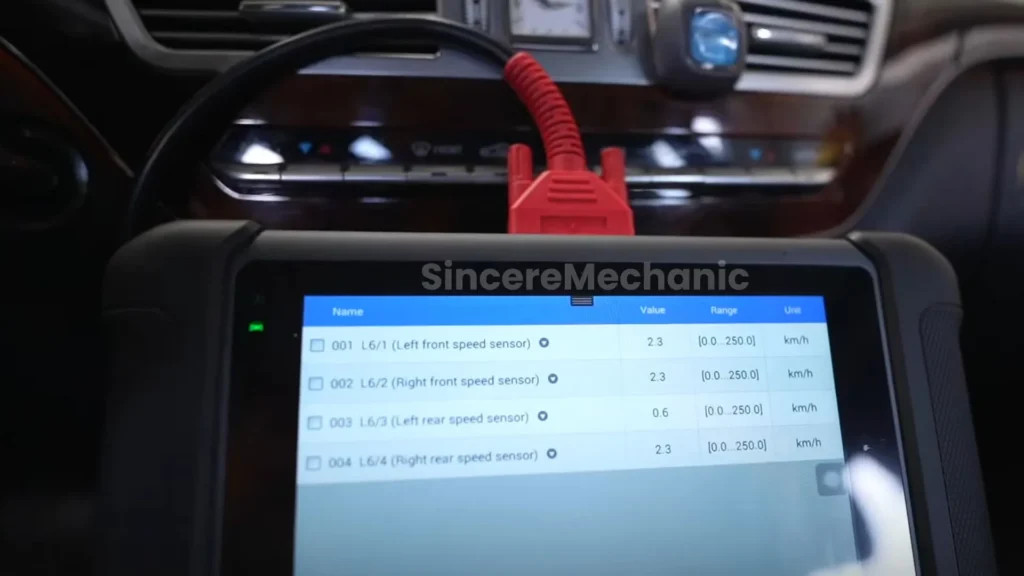
3.2. Using Diagnostic Tools
Diagnostic tools are essential for reading error codes and accessing detailed information about the ESP system’s status. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools suitable for Mercedes Benz C240.
- OBD-II Scanners: Read generic and manufacturer-specific codes.
- Advanced Diagnostic Tools: Provide in-depth analysis of the ESP system.
- Live Data: Monitor sensor readings in real-time.
3.3. Interpreting Error Codes
Understanding the error codes retrieved from the diagnostic tool is crucial for accurate diagnosis. Common ESP-related error codes include sensor failures, communication issues, and module malfunctions.
- C0031: Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
- C0034: Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
- C1000: Control Unit Fault.
- Note: Always refer to the Mercedes-Benz repair manual for specific code definitions.
4. Solutions for ESP Problems in Mercedes Benz C240
Addressing ESP problems in your Mercedes Benz C240 involves targeted solutions based on the diagnosis. This may include replacing faulty sensors, repairing wiring issues, or reprogramming the ESP module.
4.1. Replacing Faulty Sensors
If a sensor is identified as faulty, replacement is usually necessary. Ensure you use high-quality replacement parts to maintain the integrity of the ESP system.
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Replace if readings are erratic or non-existent.
- Steering Angle Sensors: Replace if causing inaccurate steering input.
- Yaw Rate Sensors: Replace if the vehicle stability is compromised.
4.2. Repairing Wiring Issues
Damaged or corroded wiring can disrupt the ESP system’s communication. Repairing or replacing the affected wiring can restore proper functionality.
- Inspect Wires: Look for cuts, breaks, or corrosion.
- Use Quality Connectors: Ensure secure and reliable connections.
- Professional Help: If wiring repairs are complex, seek professional assistance.
4.3. Reprogramming the ESP Module
In some cases, the ESP module may need to be reprogrammed to resolve software glitches or compatibility issues. This requires specialized equipment and expertise.
- Software Updates: Ensure the ESP module has the latest software.
- Professional Reprogramming: Use a certified Mercedes-Benz technician.
- Compatibility: Ensure the software is compatible with your C240 model.
5. Maintaining Your ESP System
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the long-term reliability and effectiveness of the ESP system in your Mercedes Benz C240.
5.1. Regular Inspections
Conduct regular inspections of the ESP system components, including sensors, wiring, and connectors, to identify potential issues before they escalate.
- Check Sensors: Ensure sensors are clean and properly mounted.
- Inspect Wiring: Look for signs of wear or damage.
- Test Functionality: Use a diagnostic tool to check sensor readings.
5.2. Tire Maintenance
Proper tire maintenance, including maintaining correct tire pressure and ensuring even wear, is essential for optimal ESP performance.
- Tire Pressure: Maintain the recommended tire pressure.
- Tire Condition: Replace worn tires to ensure adequate traction.
- Wheel Alignment: Ensure proper wheel alignment for even tire wear.
5.3. Brake System Maintenance
Since ESP relies on the brake system, regular brake maintenance is crucial. This includes checking brake pads, rotors, and fluid levels.
- Brake Pads: Replace worn brake pads.
- Brake Rotors: Ensure rotors are in good condition.
- Brake Fluid: Maintain proper fluid levels and replace as needed.
6. Advanced ESP Features in Mercedes Benz C240
The ESP system in your Mercedes Benz C240 may include advanced features that enhance its functionality and effectiveness.
6.1. Brake Assist System (BAS)
The Brake Assist System (BAS) detects emergency braking situations and applies maximum braking force to help prevent accidents.
- Emergency Detection: Senses rapid brake pedal application.
- Maximum Braking: Applies full braking force immediately.
- Integration: Works in conjunction with ESP and ABS.
6.2. Traction Control System (TCS)
The Traction Control System (TCS) prevents wheel spin during acceleration, ensuring optimal traction on slippery surfaces.
- Wheel Spin Detection: Monitors wheel speed during acceleration.
- Engine Power Reduction: Reduces engine power to prevent wheel spin.
- Brake Application: Applies brakes to spinning wheel to transfer power.
6.3. Adaptive ESP
Adaptive ESP adjusts the ESP system’s parameters based on driving conditions and vehicle load, optimizing stability and control.
- Driving Condition Adjustment: Adapts to different road surfaces.
- Vehicle Load Adjustment: Optimizes for different vehicle weights.
- Enhanced Stability: Provides optimal stability in all situations.
7. ESP Mercedes Benz C240: Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
When the ESP (Electronic Stability Program) warning light illuminates in your Mercedes Benz C240, it indicates a potential issue with the vehicle’s stability control system. Addressing this promptly is crucial to ensure your safety and maintain optimal handling. Here’s a comprehensive, step-by-step guide to help you troubleshoot the ESP system.
Step 1: Understand the ESP System
Before diving into troubleshooting, it’s essential to understand what the ESP system does and how it functions in your Mercedes Benz C240.
- What ESP Does: The ESP system is designed to prevent skidding and maintain directional control during adverse driving conditions. It monitors various sensors to detect when the vehicle is not traveling in the direction the driver intends and selectively applies the brakes to individual wheels to correct the vehicle’s path.
- Key Components:
- Wheel speed sensors
- Steering angle sensor
- Yaw rate sensor
- Lateral acceleration sensor
- ESP control module
- Hydraulic modulator unit (part of the ABS system)
Step 2: Identify the Symptoms
The ESP warning light can appear in different ways, each indicating a specific condition:
- Solid ESP Warning Light:
- Indicates a malfunction in the ESP system.
- The system is likely disabled, and stability control is not active.
- Flashing ESP Warning Light:
- Indicates the ESP system is actively engaged, correcting a loss of traction.
- This typically occurs during slippery conditions or when the vehicle detects a skid.
Step 3: Initial Checks
Before using diagnostic tools, perform these initial checks:
- Check the ESP Button:
- Some Mercedes Benz C240 models have an ESP on/off button. Ensure the ESP system is not manually turned off. The button is usually located on the center console.
- Restart the Vehicle:
- Turn off the engine, wait a few minutes, and restart the vehicle. This can sometimes reset the system and clear temporary errors.
- Check Tire Pressure:
- Ensure all tires are properly inflated. Uneven tire pressure can affect the ESP system’s performance.
- Refer to the sticker on the driver’s side doorjamb for the recommended tire pressure.
Step 4: Use an OBD-II Scanner
An OBD-II scanner can retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the ESP control module.
- Connect the Scanner:
- Plug the OBD-II scanner into the diagnostic port, usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Turn On the Ignition:
- Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Read the Codes:
- Follow the scanner’s instructions to read the stored codes.
- Record all ESP-related codes. Common codes might include:
- C1000 – Control unit fault
- C1100 – Left front wheel speed sensor fault
- C1101 – Right front wheel speed sensor fault
- C1120 – Steering angle sensor fault
- Clear the Codes (Optional):
- After recording the codes, you can clear them to see if they reappear. This can help determine if the issue is intermittent or persistent.
Step 5: Diagnose the Trouble Codes
Each DTC provides valuable information about the potential problem. Here’s how to diagnose some common codes:
-
C1000 – Control Unit Fault:
- Description: This code indicates a fault within the ESP control module itself.
- Possible Causes:
- Software glitch
- Internal electronic failure
- Voltage issues
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check the module’s power and ground connections.
- Ensure the vehicle’s battery is in good condition.
- Try reprogramming the module with updated software (requires specialized equipment).
- If the problem persists, the module may need to be replaced.
-
C1100/C1101 – Wheel Speed Sensor Fault:
- Description: These codes indicate a problem with the wheel speed sensors, which are crucial for the ESP system to detect wheel slippage.
- Possible Causes:
- Damaged or dirty sensor
- Faulty sensor wiring
- Damaged sensor ring (reluctor ring) on the wheel hub
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Inspect the sensor for physical damage and clean any debris.
- Check the sensor wiring for breaks, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Use a multimeter to test the sensor’s resistance (refer to the vehicle’s service manual for specifications).
- Inspect the sensor ring for damage or corrosion.
- Replace the sensor if it’s faulty or the wiring is damaged.
-
C1120 – Steering Angle Sensor Fault:
- Description: This code indicates a problem with the steering angle sensor, which tells the ESP system the direction the driver intends to go.
- Possible Causes:
- Misalignment of the sensor
- Faulty sensor wiring
- Damaged sensor
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Ensure the sensor is properly calibrated. This may require a diagnostic tool to perform a steering angle sensor reset.
- Check the sensor wiring for breaks, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Replace the sensor if necessary.
Step 6: Advanced Troubleshooting
If the basic checks and code diagnoses don’t resolve the issue, consider these advanced steps:
- Check the ABS System: The ESP system relies on the ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) to function correctly. Issues with the ABS can trigger the ESP warning light. Use the OBD-II scanner to check for ABS-related codes and address them.
- Inspect the Hydraulic Modulator Unit: The hydraulic modulator unit controls the brake pressure to individual wheels. If it’s malfunctioning, it can affect the ESP system. Inspect the unit for leaks or damage and consider having it tested by a professional.
- Review the Vehicle Service Manual: The vehicle service manual provides detailed troubleshooting steps and wiring diagrams specific to your Mercedes Benz C240 model.
Step 7: Professional Assistance
If you’re unable to diagnose or repair the ESP issue yourself, it’s best to seek professional assistance. A qualified mechanic with experience in Mercedes Benz vehicles can perform a thorough diagnosis and repair.
- When to Seek Professional Help:
- You’re uncomfortable working on the vehicle’s electrical or braking systems.
- You’re unable to identify the cause of the problem.
- The problem persists after attempting basic troubleshooting steps.
Step 8: Preventive Measures
After resolving the ESP issue, take these steps to prevent future problems:
- Regular Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for your Mercedes Benz C240.
- Tire Care: Ensure proper tire inflation, rotation, and replacement.
- Brake System Service: Regularly inspect and service the brake system, including brake pads, rotors, and fluid.
- Address Issues Promptly: If you notice any warning lights or unusual behavior, address them promptly to prevent further damage.
By following these steps, you can effectively troubleshoot the ESP system in your Mercedes Benz C240 and maintain optimal vehicle stability and safety. Remember to prioritize safety and seek professional help when needed.
8. ESP Mercedes Benz C240: What to Do When the Light Stays On
When the ESP (Electronic Stability Program) light remains illuminated on your Mercedes Benz C240 dashboard, it signifies an issue within the vehicle’s stability control system. This means the ESP system is not functioning as intended, which can compromise your safety, especially in adverse driving conditions. Here’s a detailed guide on what to do when the ESP light stays on, including troubleshooting steps and potential solutions.
Step 1: Understand the Significance
Before taking any action, it’s important to understand what the persistent ESP light indicates.
- System Malfunction: A steady ESP light typically means the system has detected a fault and has been disabled.
- Compromised Stability: Without a functioning ESP, your vehicle might be more susceptible to skidding or loss of control in challenging driving situations.
- Safety Concern: Driving with a malfunctioning ESP system can be risky, especially in wet, icy, or uneven road conditions.
Step 2: Initial Assessment
Begin with a few simple checks to see if the issue can be resolved quickly:
- Check the ESP Button:
- Verify that the ESP system hasn’t been accidentally turned off. Some Mercedes Benz C240 models have an ESP on/off button, usually located on the center console.
- Ensure the button is in the “on” position.
- Restart the Vehicle:
- Turn off the engine, wait a few minutes, and then restart the vehicle. Sometimes, this can reset the system and clear temporary errors.
- Observe if the ESP light turns off after restarting.
- Check Tire Pressure:
- Ensure that all tires are properly inflated. Uneven tire pressure can affect the ESP system’s performance.
- Use a tire pressure gauge to check the pressure in each tire and adjust as necessary. Refer to the sticker on the driver’s side doorjamb for the recommended tire pressure.
Step 3: Use an OBD-II Scanner for Diagnostic Codes
An OBD-II scanner is essential for retrieving diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the ESP control module.
- Connect the Scanner:
- Plug the OBD-II scanner into the diagnostic port, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Turn On the Ignition:
- Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Read the Codes:
- Follow the scanner’s instructions to read the stored codes.
- Record all ESP-related codes. Common codes might include:
- C1000 – Control unit fault
- C1100 – Left front wheel speed sensor fault
- C1101 – Right front wheel speed sensor fault
- C1120 – Steering angle sensor fault
- Clear the Codes (Optional):
- After recording the codes, you can clear them to see if they reappear. This can help determine if the issue is intermittent or persistent.
Step 4: Diagnose the Trouble Codes
Each DTC provides valuable information about the potential problem. Here’s how to diagnose some common codes:
-
C1000 – Control Unit Fault:
- Description: This code indicates a fault within the ESP control module itself.
- Possible Causes:
- Software glitch
- Internal electronic failure
- Voltage issues
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check the module’s power and ground connections.
- Ensure the vehicle’s battery is in good condition.
- Try reprogramming the module with updated software (requires specialized equipment).
- If the problem persists, the module may need to be replaced.
-
C1100/C1101 – Wheel Speed Sensor Fault:
- Description: These codes indicate a problem with the wheel speed sensors, which are crucial for the ESP system to detect wheel slippage.
- Possible Causes:
- Damaged or dirty sensor
- Faulty sensor wiring
- Damaged sensor ring (reluctor ring) on the wheel hub
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Inspect the sensor for physical damage and clean any debris.
- Check the sensor wiring for breaks, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Use a multimeter to test the sensor’s resistance (refer to the vehicle’s service manual for specifications).
- Inspect the sensor ring for damage or corrosion.
- Replace the sensor if it’s faulty or the wiring is damaged.
-
C1120 – Steering Angle Sensor Fault:
- Description: This code indicates a problem with the steering angle sensor, which tells the ESP system the direction the driver intends to go.
- Possible Causes:
- Misalignment of the sensor
- Faulty sensor wiring
- Damaged sensor
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Ensure the sensor is properly calibrated. This may require a diagnostic tool to perform a steering angle sensor reset.
- Check the sensor wiring for breaks, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Replace the sensor if necessary.
Step 5: Inspect and Test Wheel Speed Sensors
Since wheel speed sensors are a common cause of ESP issues, perform a thorough inspection and test:
- Visual Inspection:
- Locate the wheel speed sensors behind each wheel hub.
- Check for any visible damage, such as cracks, breaks, or frayed wires.
- Clean any dirt or debris from the sensor.
- Wiring Check:
- Inspect the wiring connected to the sensors for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the wires.
- Sensor Testing:
- Use a multimeter to test the resistance of each sensor. Refer to the vehicle’s service manual for the correct resistance values.
- Compare the readings from each sensor. A significant difference may indicate a faulty sensor.
Step 6: Check the Steering Angle Sensor
The steering angle sensor is crucial for the ESP system to determine the driver’s intended direction.
- Location: The steering angle sensor is typically located near the steering column.
- Calibration:
- Ensure the sensor is properly calibrated. This may require a diagnostic tool to perform a steering angle sensor reset.
- Follow the vehicle’s service manual for the correct calibration procedure.
- Wiring and Connections:
- Check the wiring and connections to the sensor for any damage or loose connections.
Step 7: Examine the ABS (Anti-lock Braking System)
The ESP system relies on the ABS to function correctly. Issues with the ABS can trigger the ESP warning light.
- Check ABS Codes:
- Use the OBD-II scanner to check for ABS-related codes.
- Address any ABS issues before proceeding with ESP troubleshooting.
- Inspect ABS Components:
- Check the ABS pump, modulator, and sensors for any signs of damage or leaks.
Step 8: Advanced Troubleshooting
If the basic checks and code diagnoses don’t resolve the issue, consider these advanced steps:
- Inspect the Hydraulic Modulator Unit:
- The hydraulic modulator unit controls the brake pressure to individual wheels. If it’s malfunctioning, it can affect the ESP system.
- Inspect the unit for leaks or damage and consider having it tested by a professional.
- Review the Vehicle Service Manual:
- The vehicle service manual provides detailed troubleshooting steps and wiring diagrams specific to your Mercedes Benz C240 model.
Step 9: Professional Assistance
If you’re unable to diagnose or repair the ESP issue yourself, it’s best to seek professional assistance. A qualified mechanic with experience in Mercedes Benz vehicles can perform a thorough diagnosis and repair.
- When to Seek Professional Help:
- You’re uncomfortable working on the vehicle’s electrical or braking systems.
- You’re unable to identify the cause of the problem.
- The problem persists after attempting basic troubleshooting steps.
Step 10: Preventive Measures
After resolving the ESP issue, take these steps to prevent future problems:
- Regular Maintenance:
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for your Mercedes Benz C240.
- Tire Care:
- Ensure proper tire inflation, rotation, and replacement.
- Brake System Service:
- Regularly inspect and service the brake system, including brake pads, rotors, and fluid.
- Address Issues Promptly:
- If you notice any warning lights or unusual behavior, address them promptly to prevent further damage.
By following these steps, you can effectively address the issue when the ESP light stays on in your Mercedes Benz C240 and maintain optimal vehicle stability and safety. Remember to prioritize safety and seek professional help when needed.
9. ESP Mercedes Benz C240: How To Reset ESP Light
The ESP (Electronic Stability Program) light on your Mercedes Benz C240 can sometimes illuminate due to minor glitches or after certain maintenance procedures. Resetting the ESP light can often resolve these issues. Here’s a detailed guide on how to reset the ESP light on your Mercedes Benz C240, covering various methods and troubleshooting steps.
Step 1: Understand the ESP System
Before attempting to reset the ESP light, it’s important to understand the ESP system and why the light might be on.
- Function: The ESP system helps prevent skidding and maintains directional control by monitoring and adjusting the vehicle’s stability.
- Reasons for Illumination: The ESP light can illuminate due to:
- Temporary system glitches
- Low battery voltage
- Wheel speed sensor issues
- Steering angle sensor problems
- After performing wheel alignment or suspension work
Step 2: Initial Checks
Before attempting a reset, perform these initial checks:
- Check Tire Pressure:
- Ensure all tires are properly inflated. Uneven tire pressure can trigger the ESP light.
- Refer to the sticker on the driver’s side doorjamb for the recommended tire pressure.
- Restart the Vehicle:
- Turn off the engine, wait a few minutes, and restart the vehicle. This can sometimes reset the system and clear temporary errors.
- Observe if the ESP light turns off after restarting.
- Check the ESP Button:
- Verify that the ESP system hasn’t been accidentally turned off. Some Mercedes Benz C240 models have an ESP on/off button, usually located on the center console.
- Ensure the button is in the “on” position.
Step 3: Steering Wheel Reset Method
This method involves turning the steering wheel to its full lock positions, which can recalibrate the ESP system.
- Start the Engine:
- Start the engine and ensure the vehicle is stationary.
- Turn the Steering Wheel Fully to the Left:
- Turn the steering wheel all the way to the left until it reaches the maximum lock.
- Hold the steering wheel in this position for a few seconds (approximately 5-10 seconds).
- Turn the Steering Wheel Fully to the Right:
- Turn the steering wheel all the way to the right until it reaches the maximum lock.
- Hold the steering wheel in this position for a few seconds (approximately 5-10 seconds).
- Return the Steering Wheel to the Center:
- Return the steering wheel to the center position.
- Turn Off the Engine:
- Turn off the engine and remove the key from the ignition.
- Restart the Engine:
- Restart the engine and check if the ESP light has turned off.
Step 4: Driving the Vehicle Method
Driving the vehicle for a short distance can sometimes reset the ESP system.
- Start the Engine:
- Start the engine and ensure the vehicle is safe to drive.
- Drive Straight:
- Drive the vehicle straight at a steady speed (approximately 10-20 mph) for a short distance (about 100-200 feet).
- Perform a Gentle Turn:
- Make a gentle turn to the left or right.
- Observe the ESP Light:
- Check if the ESP light has turned off during or after the driving sequence.
Step 5: Using an OBD-II Scanner
An OBD-II scanner can be used to clear any stored codes that might be causing the ESP light to illuminate.
- Connect the Scanner:
- Plug the OBD-II scanner into the diagnostic port, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Turn On the Ignition:
- Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Read the Codes:
- Follow the scanner’s instructions to read the stored codes.
- Record all ESP-related codes.
- Clear the Codes:
- Use the scanner to clear the codes.
- Follow the scanner’s instructions to clear the codes.
- Restart the Vehicle:
- Turn off the engine, remove the key, and restart the vehicle to see if the ESP light has been reset.
Step 6: Check the Wheel Speed Sensors
Faulty wheel speed sensors can cause the ESP light to illuminate. Inspecting and cleaning these sensors can sometimes resolve the issue.
- Locate the Sensors:
- Locate the wheel speed sensors behind each wheel hub.
- Inspect the Sensors:
- Check for any visible damage, such as cracks, breaks, or frayed wires.
- Clean the Sensors:
- Clean any dirt or debris from the sensors and the sensor rings.
- Test the Sensors:
- Use a multimeter to test the resistance of each sensor. Refer to the vehicle’s service manual for the correct resistance values.
- Replace any faulty sensors.
- Reset the System:
- After cleaning or replacing the sensors, try resetting the ESP light using one of the methods described above.
Step 7: Check the Steering Angle Sensor
A miscalibrated or faulty steering angle sensor can also cause the ESP light to illuminate.
- Calibration:
- Ensure the sensor is properly calibrated. This may require a diagnostic tool to perform a steering angle sensor reset.
- Follow the vehicle’s service manual for the correct calibration procedure.
- Wiring and Connections:
- Check the wiring and connections to the sensor for any damage or loose connections.
- Replacement:
- Replace the sensor if necessary.
- Reset the System:
- After calibrating or replacing the sensor, try resetting the ESP light using one of the methods described above.
Step 8: Battery Reset Method (If Applicable)
Disconnecting and reconnecting the battery can sometimes reset the ESP system, but this method should be used with caution as it can also reset other electronic systems in the vehicle.
- Disconnect the Battery:
- Ensure the engine is off and remove the key from the ignition.
- Disconnect the negative (-) battery cable first, followed by the positive (+) cable.
- Wait for about 15-20 minutes.
- Reconnect the Battery:
- Reconnect the positive (+) battery cable first, followed by the negative (-) cable.
- Ensure the connections are secure.
- Start the Engine:
- Start the engine and check if the ESP light has turned off.
- Note: This method may reset other electronic systems, such as the radio and seat memory, so be prepared to reprogram them.
Step 9: Professional Assistance
If you’ve tried all the above methods and the ESP light still remains illuminated, it’s best to seek professional assistance.
- Qualified Mechanic:
- A qualified mechanic with experience in Mercedes Benz vehicles can perform a thorough diagnosis and repair.
- Advanced Diagnostic Tools:
- Professional mechanics have access to advanced diagnostic tools that can pinpoint the exact cause of the issue.
- Complex Issues:
- Some ESP problems require specialized knowledge and equipment to resolve.
Step 10: Preventive Measures
After resetting the ESP light, take these steps to prevent future problems:
- Regular Maintenance:
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for your Mercedes Benz C240.
- Tire Care:
- Ensure proper tire inflation, rotation, and replacement.
- Brake System Service:
- Regularly inspect and service the brake system, including brake pads, rotors, and fluid.
- Address Issues Promptly:
- If you notice any warning lights or unusual behavior, address them promptly to prevent further damage.
By following these steps, you can effectively reset the ESP light on your Mercedes Benz C240 and maintain optimal vehicle stability and safety. Remember to prioritize safety and seek professional help when needed.
When it comes to diagnosing, repairing, and maintaining the ESP system in your Mercedes Benz C240, choosing the right tools and resources is crucial. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a comprehensive range of diagnostic tools and expert support, making it the ideal choice for addressing your ESP needs.
10.1. Comprehensive Diagnostic Tools
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides a wide selection of OBD-II scanners and advanced diagnostic tools specifically designed for Mercedes Benz vehicles.
-
OBD-II Scanners:
- Read and clear generic and manufacturer-specific codes.
- Easy to use and provide essential diagnostic information.
-
Advanced Diagnostic Tools:
- Offer in-depth analysis of the ESP system.
- Provide live data, sensor readings, and advanced troubleshooting capabilities.
-
Compatibility:
- Tools are fully compatible with Mercedes Benz C240 models.
- Ensure accurate and reliable diagnostics.
10.2. Expert Support and Guidance
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers expert support and guidance to help you diagnose and resolve ESP issues effectively.
-
Technical Support:
- Access to knowledgeable technicians who can assist with diagnostic and repair procedures.
- Support available via phone, email, and online chat.
-
Troubleshooting Resources:
- Detailed troubleshooting guides and manuals specific to Mercedes Benz vehicles.
- Step-by-step instructions for diagnosing and repairing ESP problems.
-
Community Forum:
- Connect with other Mercedes Benz owners and enthusiasts.
- Share experiences, ask questions, and receive valuable insights.
10.3. High-Quality Replacement Parts
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of high-quality replacement parts for the ESP system, ensuring reliable and long-lasting repairs.
-
Sensors:
- Wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, and yaw rate sensors.
- Manufactured to meet or exceed OEM specifications.
-
Modules:
- ESP control modules and ABS modules.
- Programmed and tested for optimal performance.
-
Wiring and Connectors:
- Durable wiring harnesses and connectors.
- Ensure secure and reliable connections.