Esp Mercedes Benz, also known as Electronic Stability Program, is a crucial safety system. This system enhances vehicle control, preventing skidding. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides advanced tools to diagnose and maintain ESP systems, ensuring optimal performance. Stability control, traction control, and anti-lock braking systems are vital components, offering drivers enhanced safety and peace of mind.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in Mercedes-Benz
- 1.1 The Role of ESP in Mercedes-Benz Safety Systems
- 1.2 Historical Development of ESP
- 1.3 Benefits of ESP in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 2. How ESP Works in a Mercedes-Benz
- 2.1 The Role of Sensors in ESP Functionality
- 2.2 ESP System Components
- 2.3 Corrective Actions Taken by ESP
- 2.4 Real-World Scenario: ESP in Action
- 3. Diagnosing ESP Issues in Mercedes-Benz
- 3.1 Common Symptoms of ESP Malfunctions
- 3.2 Diagnostic Tools for ESP Systems
- 3.2.1 Key Diagnostic Tools:
- 3.3 Step-by-Step Diagnostic Process
- 3.4 Common ESP Trouble Codes and Their Meanings
- 3.5 Using CARDIAGTECH.NET Tools for ESP Diagnostics
- 4. Repairing ESP Systems in Mercedes-Benz
- 4.1 Common ESP Repairs
- 4.2 Tools and Equipment for ESP Repairs
- 4.3 Step-by-Step Repair Procedures
- 4.4 Safety Precautions During ESP Repairs
- 4.5 Post-Repair Testing and Verification
- 4.6 ESP Calibration and Programming
- 5. Maintaining ESP Systems in Mercedes-Benz
- 5.1 Regular Inspection and Maintenance
- 5.2 Best Practices for ESP System Longevity
- 5.3 The Importance of Professional Service
- 5.4 Leveraging CARDIAGTECH.NET for ESP Maintenance
- 6. ESP System Upgrades and Enhancements
- 6.1 Aftermarket ESP Enhancements
- 6.2 Integrating Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
- 6.3 Customizing ESP Settings
- 6.4 Professional Installation and Calibration
- 7. Why ESP is Essential for Mercedes-Benz Owners
- 7.1 Safety Benefits of ESP
- 7.2 Cost Savings with ESP
- 7.3 Peace of Mind for Drivers and Passengers
- 7.4 CARDIAGTECH.NET Commitment to ESP Safety
- 8. ESP and Vehicle Handling Dynamics
- 8.1 Oversteer and Understeer Correction
- 8.2 Enhancing Cornering Stability
- 8.3 Improving Traction on Slippery Surfaces
- 8.4 Limiting Wheel Spin
- 8.5 Adapting to Driving Conditions
- 8.6 ESP and Performance Driving
- 9. Future Trends in ESP Technology
- 9.1 Integration with Autonomous Driving Systems
- 9.2 Enhanced Sensor Technology
- 9.3 Predictive ESP Systems
- 9.4 Over-the-Air Updates
- 9.5 Enhanced Customization
- 9.6 The Role of AI and Machine Learning
- 10. Finding the Right ESP Diagnostic and Repair Tools at CARDIAGTECH.NET
- 10.1 Selecting the Right Diagnostic Scanner
- 10.2 Choosing the Right Repair Tools and Equipment
- 10.3 Expert Advice and Support
- 10.4 Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET Today
1. Understanding Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in Mercedes-Benz
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP), a cornerstone of modern automotive safety, is designed to prevent skidding and loss of control in challenging driving conditions. Often referred to as electronic stability control (ESC) or dynamic stability control, this system represents a significant advancement in vehicle safety technology. ESP works by continuously monitoring the vehicle’s direction and comparing it to the driver’s intended path. When a discrepancy is detected, indicating a potential loss of control, the system intervenes by selectively applying brakes to individual wheels. This corrective action helps to steer the vehicle back on course, preventing skidding and maintaining stability. ESP is particularly effective in adverse weather conditions such as rain, snow, or ice, where the risk of losing control is significantly higher.
1.1 The Role of ESP in Mercedes-Benz Safety Systems
Mercedes-Benz integrates ESP as a key component of its comprehensive suite of safety technologies. These include the anti-lock braking system (ABS), traction control system (TCS), and brake assist. These systems work in synergy to provide a safety net for drivers, enhancing control and reducing the risk of accidents. ESP is particularly valuable, automatically intervening to help drivers maintain control during unexpected situations, making it an essential safety feature.
1.2 Historical Development of ESP
Mercedes-Benz, in collaboration with Bosch, pioneered the development of ESP, introducing it to the market in 1995. This innovation marked a significant milestone in automotive safety, setting a new standard for vehicle stability and control. The introduction of ESP was a game-changer, demonstrating the potential of technology to enhance driving safety. ESP has since become a standard feature in most Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
1.3 Benefits of ESP in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- Enhanced Safety: Reduces the risk of accidents by preventing skidding and loss of control.
- Improved Handling: Enhances vehicle stability, particularly in corners.
- Reduced Skidding: Minimizes understeer and oversteer, common causes of skidding.
- Increased Confidence: Provides drivers with greater assurance in challenging driving conditions.
2. How ESP Works in a Mercedes-Benz
ESP functions through a network of sensors that continuously monitor various parameters of the vehicle’s motion. These sensors include:
- Steering Angle Sensor: Measures the angle of the steering wheel, indicating the driver’s intended direction.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: Detects the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis, indicating whether the car is turning as intended.
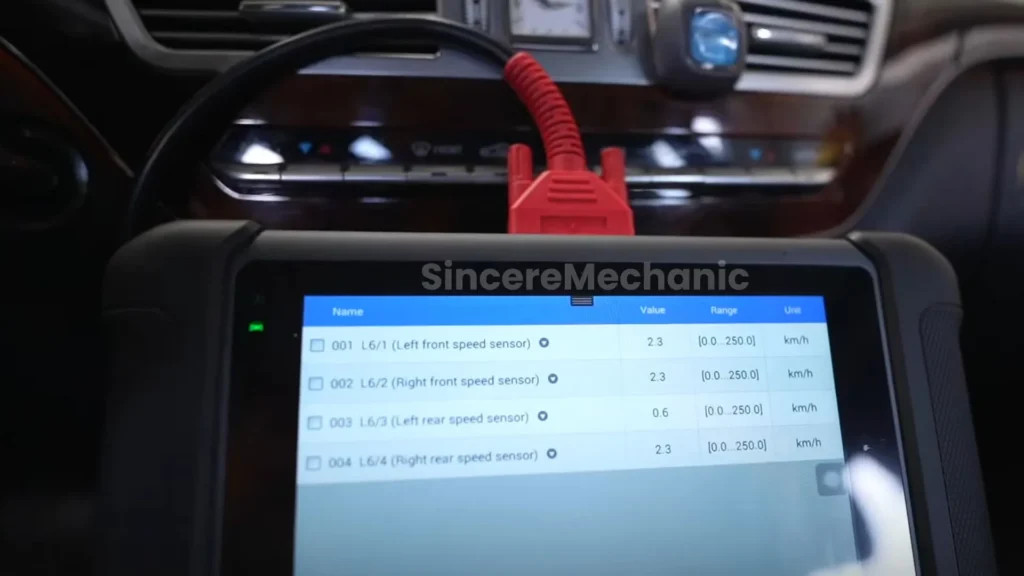
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Monitor the speed of each wheel, providing data on vehicle speed and potential wheel slippage.
- Lateral Acceleration Sensor: Measures the sideways force acting on the vehicle.
When these sensors detect a discrepancy between the driver’s intended direction and the vehicle’s actual path, the ESP system activates. This discrepancy could be due to slippery road conditions, sudden maneuvers, or other factors that cause the vehicle to deviate from its intended course.
2.1 The Role of Sensors in ESP Functionality
The sensors are crucial for the ESP system to accurately assess the vehicle’s stability and detect potential loss of control. The data from these sensors is fed into a central control unit, which processes the information and determines the appropriate corrective action. This real-time data analysis allows the ESP system to respond quickly and effectively to changing driving conditions.
2.2 ESP System Components
The ESP system consists of several key components that work together to maintain vehicle stability:
- Control Unit: Processes sensor data and determines corrective actions.
- Hydraulic Unit: Applies braking force to individual wheels as needed.
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Monitor wheel speeds for signs of slippage.
- Steering Angle Sensor: Measures the driver’s steering input.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: Detects the vehicle’s rotation.
2.3 Corrective Actions Taken by ESP
When the ESP system detects a loss of control, it takes several corrective actions to stabilize the vehicle:
- Selective Braking: Applies brakes to individual wheels to correct oversteer or understeer.
- Engine Torque Reduction: Reduces engine power to help regain traction.
- Brake Force Distribution: Adjusts brake force distribution to maintain stability.
These actions are performed automatically and almost instantaneously, often without the driver even noticing. The ESP system works subtly in the background, providing an added layer of safety and control.
2.4 Real-World Scenario: ESP in Action
Consider a scenario where a driver is navigating a sharp turn on a wet road. As the vehicle begins to skid, the ESP system detects the loss of traction and automatically applies the brakes to the outer wheels. This corrective action helps to steer the vehicle back on course, preventing it from spinning out of control. This illustrates how ESP can intervene to prevent accidents and maintain stability in challenging driving conditions.
3. Diagnosing ESP Issues in Mercedes-Benz
Diagnosing ESP issues in a Mercedes-Benz requires a systematic approach that combines visual inspection, diagnostic tools, and a thorough understanding of the system’s operation. ESP malfunctions can manifest in various ways, including warning lights on the dashboard, erratic handling, or a complete loss of stability control.
3.1 Common Symptoms of ESP Malfunctions
- Warning Lights: The ESP warning light on the dashboard is the most obvious sign of a problem.
- Erratic Handling: The vehicle may exhibit unusual handling characteristics, such as pulling to one side or feeling unstable in corners.
- Loss of Stability Control: The ESP system may fail to engage in situations where it is needed, such as during skidding or loss of traction.
- ABS Issues: Since ESP relies on the ABS system, problems with ABS can also affect ESP functionality.
3.2 Diagnostic Tools for ESP Systems
To accurately diagnose ESP issues, technicians rely on specialized diagnostic tools that can communicate with the vehicle’s computer system. These tools allow technicians to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), view live sensor data, and perform system tests.
3.2.1 Key Diagnostic Tools:
- OBD-II Scanners: These scanners can read generic DTCs related to the ESP system.
- Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis: This is a dealer-level diagnostic tool that provides in-depth access to the vehicle’s computer systems.
- Launch X431: A versatile diagnostic tool that supports a wide range of vehicle makes and models.
- Autel MaxiSys: Another popular diagnostic tool known for its comprehensive coverage and advanced features.
- iCarsoft MB II: A scanner specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, offering detailed diagnostic capabilities.
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides a range of diagnostic tools to help technicians accurately diagnose and repair ESP systems. Our tools are designed to meet the needs of both professional mechanics and DIY enthusiasts, offering reliable performance and comprehensive coverage.
3.3 Step-by-Step Diagnostic Process
- Visual Inspection: Check for any obvious signs of damage or wear, such as broken sensors or damaged wiring.
- Read DTCs: Use a diagnostic scanner to read any diagnostic trouble codes stored in the vehicle’s computer system.
- Review Freeze Frame Data: Examine the freeze frame data associated with the DTCs to understand the conditions under which the fault occurred.
- Live Data Analysis: Monitor live sensor data to identify any sensors that are not functioning correctly.
- System Tests: Perform system tests using the diagnostic tool to verify the operation of the ESP system.
- Component Testing: Test individual components, such as sensors and actuators, to identify any faulty parts.
- Wiring and Connections: Inspect the wiring and connections associated with the ESP system for corrosion, damage, or loose connections.
3.4 Common ESP Trouble Codes and Their Meanings
Understanding common ESP trouble codes can help streamline the diagnostic process and identify the root cause of the problem.
| Trouble Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| C1000 | Control Unit Fault | Faulty control unit, wiring issues |
| C1100 | Wheel Speed Sensor Malfunction | Faulty wheel speed sensor, damaged wiring, ABS module issues |
| C1200 | Steering Angle Sensor Fault | Faulty steering angle sensor, calibration issues |
| C1300 | Yaw Rate Sensor Fault | Faulty yaw rate sensor, wiring problems |
| C1400 | Lateral Acceleration Sensor Fault | Faulty lateral acceleration sensor, wiring issues |
| C1500 | Hydraulic Unit Malfunction | Faulty hydraulic unit, low brake fluid |
| C1600 | Communication Error with Other Modules | Wiring issues, faulty control unit, CAN bus problems |
3.5 Using CARDIAGTECH.NET Tools for ESP Diagnostics
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools that can help you diagnose ESP issues in Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Our tools provide access to detailed diagnostic information, including DTCs, live data, and system tests. They also support advanced functions such as component testing and calibration, allowing you to perform comprehensive diagnostics and repairs.
For instance, our OBD-II scanners can quickly read and clear ESP-related DTCs, while our Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis tool offers dealer-level diagnostic capabilities. With CARDIAGTECH.NET tools, you can confidently diagnose and resolve ESP issues, ensuring the safety and reliability of your Mercedes-Benz.
4. Repairing ESP Systems in Mercedes-Benz
Repairing ESP systems in Mercedes-Benz vehicles requires a combination of technical knowledge, specialized tools, and attention to detail. Once the diagnostic process has identified the root cause of the problem, the next step is to perform the necessary repairs.
4.1 Common ESP Repairs
- Sensor Replacement: Faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, yaw rate sensors, and lateral acceleration sensors are common ESP issues that require replacement.
- Wiring Repair: Damaged or corroded wiring can cause ESP malfunctions. Repairing or replacing the affected wiring can restore proper functionality.
- Hydraulic Unit Repair: Issues with the hydraulic unit, such as leaks or malfunctioning valves, may require repair or replacement.
- Control Unit Replacement: In some cases, the ESP control unit itself may be faulty and require replacement.
- Brake System Repairs: Since ESP relies on the ABS system, addressing issues with the brake system, such as faulty ABS modules or brake fluid leaks, can also resolve ESP problems.
4.2 Tools and Equipment for ESP Repairs
Performing ESP repairs requires a range of specialized tools and equipment, including:
- Diagnostic Scanners: To verify the effectiveness of the repairs and clear any remaining DTCs.
- Multimeters: To test the continuity and voltage of wiring and components.
- Brake Bleeding Equipment: To bleed the brake system after performing repairs to the hydraulic unit.
- Torque Wrenches: To ensure that components are tightened to the correct specifications.
- Specialized Hand Tools: Such as sensor sockets and wiring tools, to facilitate the repair process.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a comprehensive selection of tools and equipment to support ESP repairs. Our products are designed to meet the needs of professional mechanics and DIY enthusiasts alike, providing reliable performance and durability.
4.3 Step-by-Step Repair Procedures
-
Sensor Replacement:
- Disconnect the negative battery cable.
- Locate the faulty sensor and disconnect its electrical connector.
- Remove the sensor from its mounting location.
- Install the new sensor and connect the electrical connector.
- Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Use a diagnostic scanner to clear any DTCs and verify the operation of the ESP system.
-
Wiring Repair:
- Disconnect the negative battery cable.
- Locate the damaged wiring and inspect it for corrosion or breaks.
- Repair the wiring using appropriate connectors and wiring tools.
- Protect the repaired wiring with heat shrink tubing or electrical tape.
- Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Use a diagnostic scanner to clear any DTCs and verify the operation of the ESP system.
-
Hydraulic Unit Repair:
- Disconnect the negative battery cable.
- Locate the hydraulic unit and disconnect its electrical connectors and brake lines.
- Remove the hydraulic unit from its mounting location.
- Repair or replace the hydraulic unit as needed.
- Install the hydraulic unit and connect the electrical connectors and brake lines.
- Bleed the brake system to remove any air from the lines.
- Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Use a diagnostic scanner to clear any DTCs and verify the operation of the ESP system.
-
Control Unit Replacement:
- Disconnect the negative battery cable.
- Locate the ESP control unit and disconnect its electrical connectors.
- Remove the control unit from its mounting location.
- Install the new control unit and connect the electrical connectors.
- Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Use a diagnostic scanner to program the new control unit and verify the operation of the ESP system.
4.4 Safety Precautions During ESP Repairs
When performing ESP repairs, it is essential to follow proper safety precautions to protect yourself and prevent damage to the vehicle.
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery cable before working on the ESP system to prevent electrical shocks and accidental activation of components.
- Wear Safety Glasses: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris and chemicals.
- Use Proper Tools: Use the correct tools for the job to avoid damaging components and ensure proper repairs.
- Follow Torque Specifications: Tighten fasteners to the correct torque specifications to prevent damage and ensure proper operation.
- Bleed the Brakes: Bleed the brake system after performing repairs to the hydraulic unit to remove any air from the lines.
4.5 Post-Repair Testing and Verification
After completing ESP repairs, it is essential to perform thorough testing and verification to ensure that the system is functioning correctly.
- Read DTCs: Use a diagnostic scanner to read any remaining DTCs and verify that all faults have been resolved.
- Live Data Analysis: Monitor live sensor data to ensure that all sensors are functioning correctly and providing accurate readings.
- System Tests: Perform system tests using the diagnostic tool to verify the operation of the ESP system.
- Road Test: Perform a road test to evaluate the performance of the ESP system in real-world driving conditions.
4.6 ESP Calibration and Programming
In some cases, ESP repairs may require calibration or programming of the system to ensure proper operation. This is particularly common when replacing sensors or the control unit.
- Steering Angle Sensor Calibration: The steering angle sensor may need to be calibrated after replacement to ensure accurate readings.
- Yaw Rate Sensor Calibration: The yaw rate sensor may need to be calibrated after replacement to ensure accurate readings.
- Control Unit Programming: The ESP control unit may need to be programmed with the correct vehicle-specific data after replacement.
CARDIAGTECH.NET tools support ESP calibration and programming, allowing you to perform these tasks quickly and easily.
5. Maintaining ESP Systems in Mercedes-Benz
Maintaining the ESP system in your Mercedes-Benz is crucial for ensuring its continued reliability and effectiveness. Regular maintenance can help prevent ESP malfunctions and prolong the life of the system.
5.1 Regular Inspection and Maintenance
- Check Brake Fluid Levels: Low brake fluid levels can affect the operation of the ESP system. Check the brake fluid level regularly and top it off as needed.
- Inspect Brake Pads and Rotors: Worn brake pads and rotors can reduce the effectiveness of the ESP system. Inspect the brake pads and rotors regularly and replace them as needed.
- Check Tire Condition: Uneven tire wear or low tire pressure can affect the stability of the vehicle and the operation of the ESP system. Check the tire condition and pressure regularly and maintain proper inflation.
- Inspect Wiring and Connectors: Inspect the wiring and connectors associated with the ESP system for corrosion, damage, or loose connections.
5.2 Best Practices for ESP System Longevity
- Avoid Aggressive Driving: Aggressive driving, such as hard braking and cornering, can put excessive strain on the ESP system and reduce its lifespan.
- Address Issues Promptly: If you notice any symptoms of ESP malfunction, such as warning lights or erratic handling, address the issue promptly to prevent further damage.
- Use Quality Parts: When performing repairs, use high-quality parts that meet or exceed OEM specifications to ensure proper operation and longevity.
- Follow Maintenance Schedule: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for the ESP system to ensure that it is properly maintained.
5.3 The Importance of Professional Service
While some ESP maintenance tasks can be performed by DIY enthusiasts, it is essential to seek professional service for more complex issues. Certified technicians have the knowledge, skills, and equipment to accurately diagnose and repair ESP systems.
- Accurate Diagnosis: Professional technicians can accurately diagnose ESP issues using specialized diagnostic tools and techniques.
- Proper Repairs: Professional technicians can perform ESP repairs correctly, ensuring that the system is functioning properly.
- Calibration and Programming: Professional technicians can calibrate and program the ESP system as needed to ensure proper operation.
5.4 Leveraging CARDIAGTECH.NET for ESP Maintenance
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of products and services to support ESP maintenance. Our diagnostic tools can help you monitor the health of your ESP system, while our repair tools and equipment can help you perform necessary repairs.
For instance, our OBD-II scanners can read and clear ESP-related DTCs, while our Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis tool offers dealer-level diagnostic capabilities. With CARDIAGTECH.NET tools, you can confidently maintain your ESP system and ensure the safety and reliability of your Mercedes-Benz.
6. ESP System Upgrades and Enhancements
While ESP is a standard feature in most Mercedes-Benz vehicles, there are several upgrades and enhancements that can further improve its performance and functionality.
6.1 Aftermarket ESP Enhancements
- Performance Brake Systems: Upgrading to a performance brake system can improve the effectiveness of the ESP system by providing better stopping power and control.
- Suspension Upgrades: Upgrading the suspension can improve the stability and handling of the vehicle, enhancing the performance of the ESP system.
- Tire Upgrades: Upgrading to high-performance tires can improve traction and grip, enhancing the effectiveness of the ESP system.
6.2 Integrating Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
Integrating ADAS technologies, such as adaptive cruise control, lane departure warning, and blind-spot monitoring, can further enhance the safety and functionality of the ESP system.
- Adaptive Cruise Control: This system automatically adjusts the vehicle’s speed to maintain a safe following distance from the vehicle ahead, reducing the risk of accidents.
- Lane Departure Warning: This system alerts the driver if the vehicle begins to drift out of its lane, helping to prevent accidents caused by driver fatigue or distraction.
- Blind-Spot Monitoring: This system alerts the driver if there is a vehicle in their blind spot, helping to prevent accidents during lane changes.
6.3 Customizing ESP Settings
Some Mercedes-Benz vehicles allow you to customize the ESP settings to suit your driving style and preferences. This can include adjusting the sensitivity of the system or disabling it altogether in certain situations.
- Adjusting Sensitivity: Adjusting the sensitivity of the ESP system can make it more or less responsive to changes in vehicle stability.
- Disabling ESP: In some situations, such as driving on loose gravel or sand, it may be desirable to disable the ESP system to allow for more wheel spin.
6.4 Professional Installation and Calibration
When performing ESP upgrades and enhancements, it is essential to seek professional installation and calibration to ensure proper operation. Certified technicians have the knowledge, skills, and equipment to install and calibrate ESP systems correctly.
CARDIAGTECH.NET can connect you with certified technicians who can perform ESP upgrades and enhancements on your Mercedes-Benz.
7. Why ESP is Essential for Mercedes-Benz Owners
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is an essential safety feature for Mercedes-Benz owners, providing enhanced control and reducing the risk of accidents. ESP helps prevent skidding and loss of control in challenging driving conditions, such as rain, snow, or ice.
7.1 Safety Benefits of ESP
- Reduced Accident Risk: ESP helps prevent accidents by maintaining vehicle stability.
- Improved Handling: ESP enhances vehicle control, especially in corners.
- Confidence in Challenging Conditions: ESP gives drivers greater assurance in adverse weather conditions.
7.2 Cost Savings with ESP
- Lower Insurance Premiums: Vehicles with ESP may qualify for lower insurance premiums due to their enhanced safety features.
- Reduced Repair Costs: ESP can help prevent accidents, reducing the risk of costly repairs.
- Increased Vehicle Value: Vehicles with ESP may have higher resale values due to their enhanced safety features.
7.3 Peace of Mind for Drivers and Passengers
ESP provides peace of mind for drivers and passengers, knowing that the vehicle is equipped with advanced safety technology that can help prevent accidents.
7.4 CARDIAGTECH.NET Commitment to ESP Safety
CARDIAGTECH.NET is committed to providing products and services that support ESP safety. Our diagnostic tools can help you monitor the health of your ESP system, while our repair tools and equipment can help you perform necessary repairs.
We understand the importance of ESP in maintaining vehicle safety, and we are dedicated to providing our customers with the tools and resources they need to keep their ESP systems functioning properly.
8. ESP and Vehicle Handling Dynamics
ESP plays a crucial role in influencing vehicle handling dynamics, ensuring that the vehicle responds predictably and safely to driver inputs. Understanding how ESP interacts with vehicle handling can provide valuable insights into its effectiveness and limitations.
8.1 Oversteer and Understeer Correction
One of the primary functions of ESP is to correct oversteer and understeer, two common types of vehicle instability.
- Oversteer: Occurs when the rear wheels lose traction, causing the vehicle to spin out. ESP corrects oversteer by applying brakes to the outer front wheel, helping to pull the vehicle back into line.
- Understeer: Occurs when the front wheels lose traction, causing the vehicle to plow straight ahead instead of turning. ESP corrects understeer by applying brakes to the inner rear wheel, helping to rotate the vehicle and restore steering control.
8.2 Enhancing Cornering Stability
ESP enhances cornering stability by selectively applying brakes to individual wheels to maintain the vehicle’s intended path. This helps to prevent the vehicle from leaning excessively or losing traction, improving handling and control.
8.3 Improving Traction on Slippery Surfaces
ESP improves traction on slippery surfaces by detecting wheel slippage and selectively applying brakes to the spinning wheels. This helps to transfer power to the wheels with better traction, improving acceleration and stability.
8.4 Limiting Wheel Spin
ESP limits wheel spin by detecting excessive wheel rotation and reducing engine power to the spinning wheels. This helps to prevent loss of traction and improve acceleration.
8.5 Adapting to Driving Conditions
ESP adapts to driving conditions by continuously monitoring vehicle speed, steering angle, and other parameters. This allows the system to adjust its intervention strategies to suit the specific driving situation.
8.6 ESP and Performance Driving
While ESP is primarily a safety feature, it can also enhance performance driving by improving handling and control. However, in some situations, such as track driving, it may be desirable to disable the ESP system to allow for more wheel spin and greater driver control.
9. Future Trends in ESP Technology
ESP technology continues to evolve, with ongoing advancements aimed at further improving its performance and functionality.
9.1 Integration with Autonomous Driving Systems
ESP is increasingly being integrated with autonomous driving systems to provide enhanced safety and control. This integration allows the vehicle to automatically respond to changing driving conditions and prevent accidents.
9.2 Enhanced Sensor Technology
Advancements in sensor technology are improving the accuracy and reliability of ESP systems. New sensors, such as radar and lidar, can provide more detailed information about the vehicle’s surroundings, allowing the ESP system to respond more effectively to potential hazards.
9.3 Predictive ESP Systems
Predictive ESP systems use advanced algorithms and sensor data to anticipate potential loss of control situations before they occur. This allows the system to intervene proactively, preventing accidents before they happen.
9.4 Over-the-Air Updates
Over-the-air updates allow manufacturers to improve the performance and functionality of ESP systems remotely. This ensures that vehicles are always equipped with the latest safety technology.
9.5 Enhanced Customization
Future ESP systems may offer greater customization options, allowing drivers to tailor the system’s settings to suit their driving style and preferences.
9.6 The Role of AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are playing an increasing role in the development of ESP technology. These technologies can be used to analyze vast amounts of data and identify patterns that can be used to improve the performance and functionality of ESP systems.
10. Finding the Right ESP Diagnostic and Repair Tools at CARDIAGTECH.NET
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the importance of having the right tools for diagnosing and repairing ESP systems in Mercedes-Benz vehicles. That’s why we offer a comprehensive selection of diagnostic scanners, repair tools, and equipment to meet the needs of professional mechanics and DIY enthusiasts alike.
10.1 Selecting the Right Diagnostic Scanner
Choosing the right diagnostic scanner is crucial for accurately diagnosing ESP issues. Consider the following factors when selecting a scanner:
- Compatibility: Ensure that the scanner is compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles and supports ESP diagnostics.
- Features: Look for a scanner that offers advanced features such as DTC reading, live data analysis, and system tests.
- Ease of Use: Choose a scanner that is easy to use and has a user-friendly interface.
- Price: Consider your budget and choose a scanner that offers the best value for your money.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic scanners to suit different needs and budgets. Our selection includes OBD-II scanners, Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis tools, and other advanced diagnostic equipment.
10.2 Choosing the Right Repair Tools and Equipment
Having the right repair tools and equipment is essential for performing ESP repairs safely and effectively. Consider the following factors when selecting repair tools:
- Quality: Choose high-quality tools that are designed to withstand the rigors of professional use.
- Durability: Look for tools that are made from durable materials and are built to last.
- Functionality: Choose tools that are specifically designed for ESP repairs, such as sensor sockets and wiring tools.
- Safety: Ensure that the tools meet all relevant safety standards.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a comprehensive selection of repair tools and equipment to support ESP repairs. Our products are designed to meet the needs of professional mechanics and DIY enthusiasts alike.
10.3 Expert Advice and Support
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we are committed to providing our customers with expert advice and support. Our knowledgeable staff can help you select the right tools and equipment for your needs and provide guidance on diagnosing and repairing ESP systems.
We also offer a range of resources to support our customers, including technical articles, videos, and online forums. Our goal is to provide you with the tools and knowledge you need to maintain and repair your ESP system effectively.
10.4 Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET Today
If you are looking for high-quality ESP diagnostic and repair tools, look no further than CARDIAGTECH.NET. We offer a comprehensive selection of products at competitive prices, along with expert advice and support.
Contact us today to learn more about our products and services and find the right tools for your needs.
Address: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: CARDIAGTECH.NET
Don’t wait until your ESP system fails. Invest in the right tools and knowledge today to ensure the safety and reliability of your Mercedes-Benz.
Why wait? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today to get personalized advice on the best tools for your needs. Enhance your efficiency, accuracy, and safety with our top-of-the-line diagnostic and repair equipment. Click on the Whatsapp button for immediate assistance and special offers tailored just for you.
- What is ESP in a Mercedes-Benz?
- ESP, or Electronic Stability Program, is a safety feature that helps prevent skidding and loss of control by monitoring the vehicle’s direction and selectively applying brakes to individual wheels.
- How does ESP work?
- ESP uses sensors to monitor the vehicle’s steering angle, yaw rate, and wheel speed. If it detects a loss of control, it applies brakes to individual wheels to help steer the vehicle back on course.
- What are the benefits of ESP?
- ESP enhances safety by reducing the risk of accidents, improves handling, reduces skidding, and increases driver confidence.
- How do I know if my ESP system is malfunctioning?
- Common symptoms include the ESP warning light on the dashboard, erratic handling, loss of stability control, and ABS issues.
- What are common ESP trouble codes?
- Common codes include C1000 (Control Unit Fault), C1100 (Wheel Speed Sensor Malfunction), and C1200 (Steering Angle Sensor Fault).
- Can I repair ESP issues myself?
- Some basic maintenance can be done, but complex ESP repairs should be performed by certified technicians with specialized tools.
- What tools are needed for ESP diagnostics?
- Diagnostic scanners like OBD-II scanners, Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis, Launch X431, Autel MaxiSys, and iCarsoft MB II are essential.
- How can CARDIAGTECH.NET help with ESP maintenance?
- CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools and repair equipment to help you maintain and repair ESP systems effectively.
- Is ESP calibration necessary after repairs?
- Yes, especially after replacing sensors or the control unit, ESP calibration is crucial for proper operation.
- How does ESP integrate with other safety systems?
- ESP works with ABS, TCS, and brake assist to provide a comprehensive safety net, enhancing control and reducing accident risks.