Esp Inoperative Mercedes W211 issues can be frustrating, but CARDIAGTECH.NET offers expert solutions. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of diagnosing and resolving ESP malfunctions, ensuring your Mercedes W211 performs optimally. We delve into common causes, diagnostic steps, and effective repair strategies. Addressing associated issues like cruise control malfunctions and speedtronic problems can improve your vehicle’s reliability.
Contents
- 1. Understanding ESP Inoperative Issues in Mercedes W211
- 1.1 What Does ESP Do?
- 1.2 Common Symptoms of ESP Malfunction
- 2. Diagnosing ESP Inoperative on a Mercedes W211
- 2.1 Preliminary Checks
- 2.2 Using Diagnostic Tools
- 2.3 Interpreting Fault Codes
- 2.4 Checking Sensor Data
- 3. Common Causes of ESP Inoperative in Mercedes W211
- 3.1 Wheel Speed Sensor Issues
- 3.2 Steering Angle Sensor Problems
- 3.3 Yaw Rate Sensor Failures
- 3.4 ESP Control Module Issues
- 3.5 Brake System Issues
- 4. Step-by-Step Repair Guide
- 4.1 Replacing a Wheel Speed Sensor
- 4.2 Recalibrating the Steering Angle Sensor
- 4.3 Checking and Repairing Wiring Issues
- 4.4 Replacing the Yaw Rate Sensor
- 4.5 Addressing Brake System Issues
- 5. Maintaining Your Mercedes W211 ESP System
- 5.1 Regular Inspections
- 5.2 Proper Tire Maintenance
- 5.3 Routine Diagnostic Scans
- 6. Benefits of a Properly Functioning ESP System
- 6.1 Enhanced Safety
- 6.2 Improved Handling
- 6.3 Reduced Accident Risk
- 6.4 Optimal Performance
- 7. Cost Considerations for ESP Repairs
- 7.1 Component Costs
- 7.2 Labor Costs
- 7.3 Diagnostic Costs
- 8. Choosing the Right Repair Shop
- 8.1 Expertise and Experience
- 8.2 Certifications
- 8.3 Customer Reviews
- 8.4 Diagnostic Equipment
- 9. ESP and Related Systems: ABS, BAS, and More
- 9.1 ABS (Anti-lock Braking System)
- 9.2 BAS (Brake Assist System)
- 9.3 Interaction with Cruise Control and Speedtronic
- 10. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
- 10.1 Oscilloscope Testing
- 10.2 Voltage Drop Testing
- 10.3 Component Testing
- 11. ESP Inoperative and Run Flat Indicator
- 11.1 Checking Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS)
- 11.2 Resetting the TPMS
- 12. When to Consult a Professional
- 12.1 Complex Diagnostic Issues
- 12.2 Advanced Repairs
- 12.3 Safety Concerns
- 13. Case Studies: Real-World ESP Inoperative Scenarios
- 13.1 Case Study 1: Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
- 13.2 Case Study 2: Steering Angle Sensor Calibration
- 13.3 Case Study 3: Wiring Issue
- 14. The Future of ESP Technology
- 14.1 Integration with Autonomous Driving Systems
- 14.2 Advanced Sensor Technology
- 14.3 Over-the-Air Updates
- 15. Why Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET for Your Diagnostic Needs?
1. Understanding ESP Inoperative Issues in Mercedes W211
Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is a crucial safety system in Mercedes-Benz vehicles, including the W211 series. The ESP system integrates anti-lock brakes (ABS), traction control (TCS), and yaw control to maintain vehicle stability, especially in challenging driving conditions. When the “ESP Inoperative” message appears on your Mercedes W211 dashboard, it indicates a malfunction within this system. According to a report by Bosch, ESP systems can reduce accidents by up to 40%. The system uses various sensors to monitor wheel speed, steering angle, and yaw rate, comparing these inputs to the driver’s intended path. If a discrepancy is detected, the ESP intervenes by applying individual brakes or reducing engine power to help the driver maintain control.
1.1 What Does ESP Do?
ESP enhances vehicle safety by preventing skidding and loss of control. ESP works by monitoring several factors, including:
- Steering Angle: The angle of the steering wheel indicates the driver’s intended direction.
- Wheel Speed: Sensors at each wheel measure their speed to detect any variations that could lead to skidding.
- Yaw Rate: This measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis, indicating whether the car is turning as intended.
When ESP detects a potential loss of control, it takes corrective action by:
- Applying Brakes: Selectively applies brakes to individual wheels to correct oversteer or understeer.
- Reducing Engine Power: Decreases engine power to reduce wheel spin and improve traction.
1.2 Common Symptoms of ESP Malfunction
Recognizing the symptoms of ESP malfunction in your Mercedes W211 is crucial for timely diagnosis and repair. Here are some common signs:
- Warning Light Illumination: The ESP warning light on the dashboard illuminates, often accompanied by a message such as “ESP Inoperative” or “ESP Malfunction.”
- Reduced Traction Control: The vehicle may experience wheel spin or loss of traction, especially on slippery surfaces.
- ABS Issues: Problems with the anti-lock braking system can sometimes be related to ESP malfunctions, leading to longer stopping distances or erratic braking behavior.
- Cruise Control and Speedtronic Inoperative: The cruise control and speedtronic systems may become disabled when the ESP system malfunctions.
- Erratic Steering: In some cases, the steering may feel unusual or difficult to control.
- Hold Function Problems: The “hold” function on the brakes may not engage or disengage properly.
2. Diagnosing ESP Inoperative on a Mercedes W211
Diagnosing an ESP inoperative issue on a Mercedes W211 requires a systematic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you identify the root cause:
2.1 Preliminary Checks
Before diving into complex diagnostics, perform these preliminary checks:
- Check the Battery: Ensure the battery is in good condition and fully charged. Low voltage can cause various electronic issues, including ESP malfunctions. Use a multimeter to check the battery voltage. A healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts when the engine is off and between 13.7 and 14.7 volts when the engine is running.
- Inspect Fuses and Relays: Locate the ESP-related fuses and relays in the fuse box and check for any blown fuses or faulty relays. Replace any damaged components. The fuse box diagrams are typically located in the owner’s manual or on the fuse box cover.
- Tire Condition and Pressure: Verify that all tires are in good condition and properly inflated. Uneven tire wear or incorrect tire pressure can affect the ESP system’s performance. Use a tire pressure gauge to check the pressure and compare it to the recommended values on the tire placard, usually found on the driver’s side doorjamb.
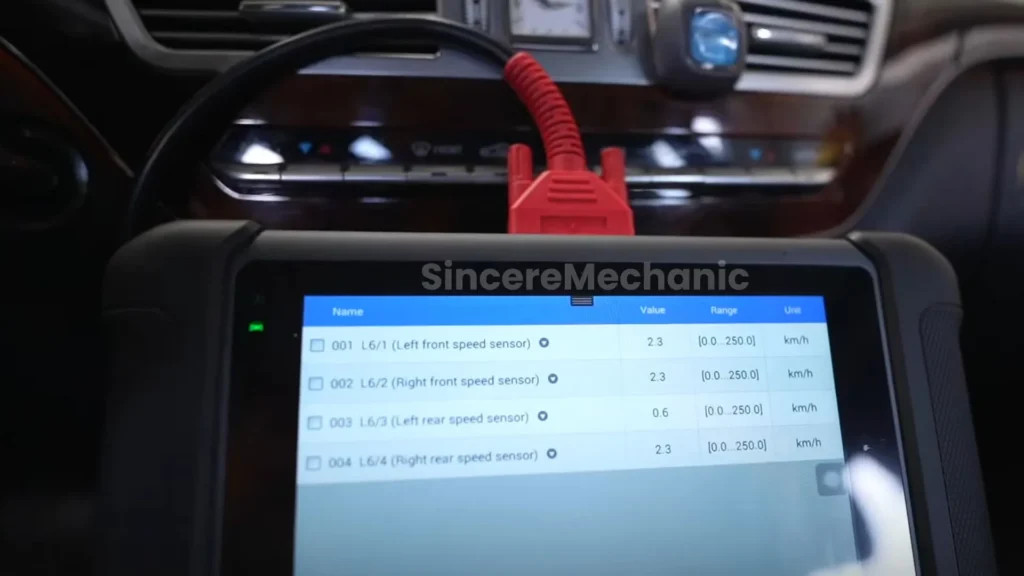
2.2 Using Diagnostic Tools
Advanced diagnostic tools are essential for accurately diagnosing ESP issues.
- OBD-II Scanner: Connect an OBD-II scanner to the vehicle’s diagnostic port to read any stored fault codes. These codes provide valuable information about the specific problem within the ESP system. Common codes related to ESP issues include C0031 (Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction), C0034 (Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction), and C0037 (Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction).
- Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis: For a more in-depth diagnosis, use the Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis system. This tool provides access to detailed diagnostic information and allows you to perform specific tests and calibrations. The Star Diagnosis system can read manufacturer-specific codes and provide guided diagnostics to pinpoint the exact cause of the ESP malfunction.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice on selecting the right tool for your needs. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States.
2.3 Interpreting Fault Codes
Fault codes provide crucial clues about the nature of the ESP problem. Here’s how to interpret them:
- Research the Codes: Look up the specific fault codes in a Mercedes-Benz repair manual or online database to understand their meaning and potential causes. Websites like MBWorld and BenzWorld offer forums where you can discuss fault codes with other Mercedes-Benz owners and mechanics.
- Prioritize Codes: Some codes may be more critical than others. Prioritize diagnosing the codes that are directly related to the ESP system. For example, codes related to wheel speed sensors or the yaw rate sensor should be investigated first.
- Clear Codes and Retest: After addressing the identified issues, clear the fault codes using the diagnostic tool and retest the system to see if the codes reappear. This helps confirm whether the repair was successful.
2.4 Checking Sensor Data
Live sensor data can reveal whether the sensors are providing accurate readings.
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Monitor the wheel speed sensors using the diagnostic tool while driving the vehicle. Ensure that all sensors are providing consistent and accurate readings. Inconsistent readings can indicate a faulty sensor or wiring issue.
- Steering Angle Sensor: Check the steering angle sensor data to verify that it accurately reflects the steering wheel position. A faulty steering angle sensor can cause the ESP system to misinterpret the driver’s intentions and activate unnecessarily.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: Monitor the yaw rate sensor data to ensure it is providing accurate readings of the vehicle’s rotation. A faulty yaw rate sensor can lead to incorrect ESP interventions.
3. Common Causes of ESP Inoperative in Mercedes W211
Several factors can trigger the “ESP Inoperative” warning in a Mercedes W211. Understanding these common causes can help you narrow down the diagnosis and implement effective repairs.
3.1 Wheel Speed Sensor Issues
Wheel speed sensors are critical for the ESP system to function correctly. These sensors measure the speed of each wheel and provide data to the ESP control module.
- Sensor Failure: Wheel speed sensors can fail due to physical damage, contamination, or electrical issues. A faulty sensor will send incorrect data to the ESP module, triggering the “ESP Inoperative” warning. Replacement wheel speed sensors typically cost between $50 and $200, depending on the brand and quality.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged or corroded wiring to the wheel speed sensors can also cause ESP malfunctions. Inspect the wiring harness for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires or corroded connectors. Repairing or replacing the wiring can resolve the issue. Wiring repair kits are available for around $20 to $50.
- Sensor Contamination: Debris, such as brake dust or road grime, can accumulate on the wheel speed sensors, affecting their accuracy. Clean the sensors and the surrounding area to ensure proper function. Use a specialized sensor cleaner for best results.
3.2 Steering Angle Sensor Problems
The steering angle sensor measures the position of the steering wheel and provides data to the ESP module.
- Sensor Malfunction: A faulty steering angle sensor can send incorrect data to the ESP module, leading to ESP malfunctions. This can occur due to wear and tear or electrical issues. Replacement steering angle sensors typically cost between $150 and $400.
- Calibration Issues: The steering angle sensor may need to be recalibrated after certain repairs, such as wheel alignment or steering component replacement. Use a diagnostic tool to perform the calibration procedure. The Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis system is recommended for this task.
- Wiring Problems: Similar to wheel speed sensors, damaged or corroded wiring to the steering angle sensor can cause issues. Inspect the wiring harness and connectors for any signs of damage and repair as needed.
3.3 Yaw Rate Sensor Failures
The yaw rate sensor measures the vehicle’s rotation and provides data to the ESP module.
- Sensor Failure: A faulty yaw rate sensor can send incorrect data to the ESP module, leading to ESP malfunctions. This can occur due to physical damage or electrical issues. Replacement yaw rate sensors typically cost between $200 and $500.
- Installation Issues: Ensure the yaw rate sensor is properly installed and aligned. Incorrect installation can affect its accuracy. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper installation.
- Wiring Problems: Check the wiring and connectors to the yaw rate sensor for any signs of damage and repair as needed.
3.4 ESP Control Module Issues
The ESP control module processes data from various sensors and controls the ESP system.
- Module Failure: The ESP control module can fail due to electrical issues or internal component failure. A faulty module may need to be replaced or reprogrammed. Replacement ESP control modules can cost between $500 and $1500.
- Software Issues: Software glitches or corruption can also cause ESP malfunctions. Check for any available software updates for the ESP module and install them using a diagnostic tool.
- Wiring Problems: Check the wiring and connectors to the ESP control module for any signs of damage and repair as needed.
3.5 Brake System Issues
Issues within the brake system can also affect the ESP system.
- Brake Pad Wear: Worn brake pads can affect the ABS and ESP systems. Replace worn brake pads to ensure proper brake system function. High-quality brake pads typically cost between $50 and $150 per set.
- Brake Fluid Level: Low brake fluid level can affect the brake system’s performance and trigger ESP malfunctions. Check the brake fluid level and top up as needed. Use the recommended brake fluid type for your Mercedes W211.
- ABS Pump Failure: A faulty ABS pump can affect the ESP system. Test the ABS pump using a diagnostic tool and replace if necessary. Replacement ABS pumps can cost between $300 and $800.
4. Step-by-Step Repair Guide
Repairing ESP inoperative issues in a Mercedes W211 requires a systematic approach. Follow these steps to address common problems:
4.1 Replacing a Wheel Speed Sensor
- Gather Tools and Parts: You will need a new wheel speed sensor, a socket set, a wrench, and a diagnostic tool.
- Locate the Sensor: Identify the faulty wheel speed sensor based on the diagnostic fault codes. The sensor is typically located near the wheel hub.
- Disconnect the Sensor: Disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor.
- Remove the Old Sensor: Remove the bolt or screw that secures the sensor to the hub. Carefully remove the old sensor.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor, ensuring it is properly seated. Tighten the bolt or screw to the specified torque.
- Reconnect the Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the sensor.
- Test the System: Use a diagnostic tool to clear the fault codes and test the ESP system.
4.2 Recalibrating the Steering Angle Sensor
- Gather Tools: You will need a diagnostic tool that supports steering angle sensor calibration, such as the Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis system.
- Access Calibration Function: Connect the diagnostic tool to the vehicle and access the steering angle sensor calibration function.
- Follow On-Screen Instructions: Follow the on-screen instructions provided by the diagnostic tool to perform the calibration procedure. This typically involves turning the steering wheel to specific angles.
- Verify Calibration: After completing the calibration, verify that the steering angle sensor is providing accurate readings.
4.3 Checking and Repairing Wiring Issues
- Inspect Wiring: Visually inspect the wiring harnesses and connectors associated with the ESP system. Look for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires, corroded connectors, or loose connections.
- Test Continuity: Use a multimeter to test the continuity of the wires. Disconnect the battery before testing to prevent electrical shock.
- Repair or Replace Wiring: Repair any damaged wires by splicing in new sections or replacing the entire wiring harness. Clean corroded connectors with electrical contact cleaner.
- Secure Connections: Ensure all connections are secure and properly insulated.
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides a wide range of high-quality wiring repair kits and electrical components. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice on selecting the right parts for your Mercedes W211.
4.4 Replacing the Yaw Rate Sensor
- Locate the Sensor: The yaw rate sensor is typically located under the driver’s seat or in the center console. Refer to the vehicle’s repair manual for the exact location.
- Disconnect the Sensor: Disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor.
- Remove the Old Sensor: Remove the bolts or screws that secure the sensor to the vehicle. Carefully remove the old sensor.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor, ensuring it is properly aligned. Tighten the bolts or screws to the specified torque.
- Reconnect the Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the sensor.
- Test the System: Use a diagnostic tool to clear the fault codes and test the ESP system.
4.5 Addressing Brake System Issues
- Check Brake Pads: Inspect the brake pads for wear. Replace if they are below the recommended thickness.
- Check Brake Fluid Level: Ensure the brake fluid level is within the specified range. Top up as needed with the recommended brake fluid type.
- Test ABS Pump: Use a diagnostic tool to test the ABS pump. If the pump is not functioning correctly, it may need to be replaced.
5. Maintaining Your Mercedes W211 ESP System
Regular maintenance is essential to keep your Mercedes W211 ESP system functioning correctly.
5.1 Regular Inspections
Perform regular inspections of the ESP system components.
- Check Wheel Speed Sensors: Inspect the wheel speed sensors for damage or contamination.
- Inspect Wiring: Check the wiring and connectors for any signs of damage.
- Monitor Brake System: Regularly check the brake pads and brake fluid level.
5.2 Proper Tire Maintenance
Proper tire maintenance is crucial for ESP system performance.
- Maintain Correct Tire Pressure: Ensure all tires are inflated to the recommended pressure.
- Check Tire Wear: Regularly check the tire tread depth and replace tires when they are worn.
- Use Matching Tires: Use matching tires on all four wheels to ensure consistent performance.
5.3 Routine Diagnostic Scans
Perform routine diagnostic scans to identify any potential issues before they become major problems.
- Use OBD-II Scanner: Regularly use an OBD-II scanner to check for any stored fault codes.
- Address Issues Promptly: Address any identified issues promptly to prevent further damage.
6. Benefits of a Properly Functioning ESP System
A properly functioning ESP system offers numerous benefits.
6.1 Enhanced Safety
ESP enhances vehicle safety by preventing skidding and loss of control, especially in challenging driving conditions.
6.2 Improved Handling
ESP improves vehicle handling by maintaining stability and control.
6.3 Reduced Accident Risk
ESP reduces the risk of accidents by helping the driver maintain control of the vehicle.
6.4 Optimal Performance
ESP ensures optimal vehicle performance by maintaining stability and control.
7. Cost Considerations for ESP Repairs
Understanding the potential costs associated with ESP repairs can help you budget effectively.
7.1 Component Costs
- Wheel Speed Sensors: $50 – $200 each
- Steering Angle Sensor: $150 – $400
- Yaw Rate Sensor: $200 – $500
- ESP Control Module: $500 – $1500
- Brake Pads: $50 – $150 per set
- ABS Pump: $300 – $800
7.2 Labor Costs
Labor costs for ESP repairs can vary depending on the complexity of the job and the hourly rate of the mechanic. Typical labor costs range from $100 to $500.
7.3 Diagnostic Costs
Diagnostic costs can range from $50 to $200, depending on the diagnostic tools used and the time required to diagnose the problem.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers competitive prices on high-quality diagnostic tools and replacement parts. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for a quote. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States.
8. Choosing the Right Repair Shop
Selecting the right repair shop is crucial for ensuring quality ESP repairs.
8.1 Expertise and Experience
Choose a repair shop with expertise and experience in Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
8.2 Certifications
Look for certifications such as ASE (Automotive Service Excellence) certification.
8.3 Customer Reviews
Check customer reviews and ratings to gauge the quality of the repair shop’s service.
8.4 Diagnostic Equipment
Ensure the repair shop has the necessary diagnostic equipment, such as the Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis system.
9. ESP and Related Systems: ABS, BAS, and More
The ESP system is often integrated with other safety systems, such as ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) and BAS (Brake Assist System). Understanding how these systems interact can help you diagnose and repair ESP issues more effectively.
9.1 ABS (Anti-lock Braking System)
ABS prevents the wheels from locking up during hard braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control. The ESP system relies on the ABS to function correctly. If the ABS is not working properly, it can affect the ESP system. Common ABS issues include faulty wheel speed sensors, a malfunctioning ABS pump, and wiring problems.
9.2 BAS (Brake Assist System)
BAS detects emergency braking situations and applies maximum braking force to help reduce stopping distances. The ESP system works in conjunction with the BAS to provide optimal braking performance. If the BAS is not functioning correctly, it can affect the ESP system. Common BAS issues include a faulty brake booster and wiring problems.
9.3 Interaction with Cruise Control and Speedtronic
The ESP system is also integrated with cruise control and speedtronic systems. When the ESP system malfunctions, these systems may become disabled. Addressing the ESP issue will typically resolve the cruise control and speedtronic problems.
10. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
For complex ESP issues, advanced diagnostic techniques may be necessary.
10.1 Oscilloscope Testing
Use an oscilloscope to analyze the signals from the wheel speed sensors and other components. This can help identify intermittent problems or signal abnormalities.
10.2 Voltage Drop Testing
Perform voltage drop testing to identify wiring issues, such as corroded connections or damaged wires.
10.3 Component Testing
Test individual components, such as the yaw rate sensor and steering angle sensor, to verify their functionality.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of advanced diagnostic tools and training resources. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for more information.
11. ESP Inoperative and Run Flat Indicator
Sometimes, an ESP inoperative message is accompanied by a “Run Flat Inoperative” indicator. This can be due to a shared sensor or control module, or it could indicate separate but related issues. Addressing the ESP problem often resolves the run-flat indicator issue as well.
11.1 Checking Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS)
Ensure the tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) is functioning correctly. Low tire pressure can trigger both the “Run Flat Inoperative” and “ESP Inoperative” messages.
11.2 Resetting the TPMS
After adjusting the tire pressure, reset the TPMS to clear the warning messages.
12. When to Consult a Professional
While some ESP repairs can be performed by experienced DIY mechanics, others require professional expertise.
12.1 Complex Diagnostic Issues
If you are unable to diagnose the ESP problem using basic diagnostic tools and techniques, consult a professional mechanic.
12.2 Advanced Repairs
For advanced repairs, such as replacing the ESP control module or recalibrating the steering angle sensor, it is best to consult a professional.
12.3 Safety Concerns
If you are not comfortable working on the ESP system, consult a professional to ensure your safety and the proper functioning of the system.
Don’t let ESP issues compromise your driving experience. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice and high-quality diagnostic tools. Visit us at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States.
13. Case Studies: Real-World ESP Inoperative Scenarios
Examining real-world scenarios can provide valuable insights into diagnosing and resolving ESP inoperative issues.
13.1 Case Study 1: Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
A Mercedes W211 owner reported an “ESP Inoperative” message on the dashboard. Diagnostic scans revealed a fault code indicating a faulty left front wheel speed sensor. After replacing the sensor, the ESP system functioned correctly.
13.2 Case Study 2: Steering Angle Sensor Calibration
Another Mercedes W211 owner experienced ESP malfunctions after a wheel alignment. Diagnostic scans indicated that the steering angle sensor needed to be recalibrated. After performing the calibration procedure, the ESP system functioned correctly.
13.3 Case Study 3: Wiring Issue
A Mercedes W211 owner reported intermittent ESP malfunctions. After inspecting the wiring harnesses, a corroded connector was found. Repairing the connector resolved the ESP issue.
14. The Future of ESP Technology
ESP technology continues to evolve, with new features and improvements being developed.
14.1 Integration with Autonomous Driving Systems
ESP systems are being integrated with autonomous driving systems to enhance safety and stability.
14.2 Advanced Sensor Technology
New sensor technologies are being developed to improve the accuracy and reliability of ESP systems.
14.3 Over-the-Air Updates
Over-the-air software updates are being used to improve the performance of ESP systems and address any potential issues.
15. Why Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET for Your Diagnostic Needs?
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the complexities of modern vehicle systems, including the ESP in your Mercedes W211. That’s why we offer a comprehensive range of diagnostic tools and equipment to help you accurately identify and resolve any issues. Our products are designed for both professional mechanics and DIY enthusiasts, ensuring you have the right tools for the job. Here’s why you should choose us:
- Extensive Product Range: We offer a wide selection of OBD-II scanners, diagnostic software, and specialized tools for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Expert Support: Our team of experienced technicians can provide expert advice and support to help you diagnose and repair ESP issues.
- High-Quality Products: We only offer high-quality products from trusted brands, ensuring reliable performance and accurate results.
- Competitive Prices: We offer competitive prices on all our products, making professional-grade diagnostic tools accessible to everyone.
Take control of your Mercedes W211’s maintenance and repair needs with CARDIAGTECH.NET. Contact us today at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website to explore our full range of products. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States.
1. What does “ESP Inoperative” mean on my Mercedes W211?
“ESP Inoperative” indicates a malfunction in the Electronic Stability Program, which helps prevent skidding and loss of control.
2. Can I drive my Mercedes W211 with the ESP light on?
It is generally safe to drive with the ESP light on, but exercise caution as the ESP system is not functioning, and your vehicle may be more prone to skidding.
3. What are the common causes of ESP inoperative in a W211?
Common causes include faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor issues, yaw rate sensor failures, and problems with the ESP control module.
4. How do I diagnose an ESP inoperative issue?
Use an OBD-II scanner to read fault codes and check sensor data. For more in-depth diagnosis, use the Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis system.
5. Can a low battery cause ESP inoperative?
Yes, a low battery can cause various electronic issues, including ESP malfunctions. Ensure your battery is in good condition.
6. How much does it cost to repair an ESP inoperative issue?
Repair costs vary depending on the cause. Component costs range from $50 for a wheel speed sensor to $1500 for an ESP control module, plus labor costs.
7. Can I replace a wheel speed sensor myself?
Yes, if you have mechanical experience, you can replace a wheel speed sensor yourself. Follow the step-by-step guide provided in this article.
8. Do I need to recalibrate the steering angle sensor after a wheel alignment?
Yes, the steering angle sensor may need to be recalibrated after certain repairs, such as wheel alignment.
9. Where is the yaw rate sensor located in a Mercedes W211?
The yaw rate sensor is typically located under the driver’s seat or in the center console. Refer to your vehicle’s repair manual for the exact location.
10. How can CARDIAGTECH.NET help with ESP inoperative issues?
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools, expert support, and high-quality replacement parts to help you diagnose and repair ESP issues in your Mercedes W211. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880.
Ready to get your Mercedes W211 back on track? Don’t wait for ESP issues to escalate. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET now at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice and premium diagnostic tools. Our team is ready to assist you at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States. Take the first step towards a smoother, safer driving experience today!