Are you experiencing an ESP Inoperative message in your Mercedes A Class? Don’t worry, CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to guide you through understanding the causes, troubleshooting steps, and potential fixes for this common issue. Addressing this promptly ensures your vehicle’s safety systems function correctly, providing a smooth and secure driving experience. We’ll explore related aspects like stability control malfunctions, ABS issues, and steering angle sensor problems.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Mercedes-Benz ESP Inoperative
- 2. How ESP Works in a Mercedes-Benz
- 3. Common Causes of ESP Inoperative in Mercedes A Class
- 4. Detailed Explanation of Potential Causes
- 4.1. Damaged or Faulty ABS Wheel Speed Sensor
- 4.2. Weak or Dead 12-Volt Battery
- 4.3. Bad Alternator or Voltage Regulator
- 4.4. Steering Angle Sensor Calibration or Replacement
- 5. Step-by-Step Guide to Resetting the ESP Warning Light
- 6. Advanced Diagnostic Procedures
- 6.1. Using an OBD-II Scanner
- 6.2. Live Data Analysis
- 7. The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET in Solving ESP Issues
- 7.1. High-Quality Diagnostic Tools
- 7.2. Premium Replacement Parts
- 7.3. Expert Technical Support
- 8. The Importance of Professional Assistance
- 9. Preventive Maintenance Tips to Avoid ESP Issues
- 10. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 11. ESP and Other Safety Systems
- 11.1. ESP and ABS (Anti-lock Braking System)
- 11.2. ESP and Traction Control System (TCS)
- 11.3. ESP and Brake Assist System (BAS)
- 11.4. ESP and Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
- 12. The Impact of Tire Condition on ESP Performance
- 13. Real-World Scenarios Where ESP is Crucial
- 14. ESP System Malfunctions and Safety Risks
- 15. The Future of ESP Technology
- 16. ESP System and Legal Considerations
- 17. Purchasing Guide for ESP Related Components at CARDIAGTECH.NET
- 18. Cost Analysis of ESP Repairs
- 19. Understanding Mercedes-Benz ESP Warning Messages
- 20. ESP and Vehicle Modifications
- 21. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET for Expert Assistance
1. Understanding Mercedes-Benz ESP Inoperative
Mercedes-Benz vehicles incorporate advanced technology to optimize performance and safety. The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is a crucial system designed to maintain vehicle stability by preventing skidding and loss of control. When the ESP Inoperative warning appears in your Mercedes A Class, it signals a potential problem within this system that requires attention.
The primary function of ESP is to keep your vehicle moving in the intended direction. It achieves this by monitoring wheel speed, steering angle, and other factors to detect and correct deviations from the driver’s intended path. ESP works alongside other safety systems like ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) to ensure optimal stability in various driving conditions.
2. How ESP Works in a Mercedes-Benz
ESP actively prevents your Mercedes-Benz from experiencing wheel spin or skidding, situations where the tires lose traction. By integrating data from multiple sensors, ESP makes precise adjustments to maintain control.
Here’s how it works:
- ABS Integration: ESP utilizes the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) to prevent wheel lock-up during braking, maximizing stopping power.
- Data Analysis: Sensors constantly monitor wheel speed, steering angle, and yaw rate (the vehicle’s rotation).
- Individual Wheel Control: ESP can apply braking force to individual wheels to correct oversteer (rear end sliding out) or understeer (front end plowing straight).
- Engine Management: In some situations, ESP may also reduce engine power to help regain control.
By intervening automatically and precisely, ESP helps drivers maintain control in challenging situations such as wet roads, icy conditions, and emergency maneuvers.
 Mercedes-Benz ESP reset & fix
Mercedes-Benz ESP reset & fix
3. Common Causes of ESP Inoperative in Mercedes A Class
Several factors can trigger the ESP Inoperative warning in your Mercedes A Class. Identifying the root cause is the first step toward resolving the issue. Here are some of the most common culprits:
- Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors: These sensors monitor the speed of each wheel and provide crucial data to the ESP system. Damage, dirt, or corrosion can cause inaccurate readings, leading to ESP malfunction.
- Low Battery Voltage: The ESP system relies on a stable voltage supply to function correctly. A weak or failing battery can cause the system to shut down or generate errors.
- Steering Angle Sensor Issues: The steering angle sensor informs the ESP system about the driver’s intended direction. Miscalibration or a faulty sensor can disrupt ESP operation.
- Brake Light Switch Malfunction: The brake light switch signals the ESP system when the brakes are applied. A faulty switch can send incorrect signals, leading to ESP deactivation.
- Faulty ABS Module: The ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) module and ESP system are interconnected and often work together. If there is a problem with the ABS module, it can directly trigger the ESP inoperative warning.
4. Detailed Explanation of Potential Causes
Let’s delve deeper into each of these potential causes:
4.1. Damaged or Faulty ABS Wheel Speed Sensor
Wheel speed sensors are essential for the ESP system to accurately monitor wheel rotation. These sensors are typically located near each wheel hub and can be susceptible to damage from road debris, corrosion, and wear and tear.
Symptoms of a faulty wheel speed sensor:
- ESP Inoperative warning light
- ABS warning light
- Traction control light
- Erratic braking behavior
- Speedometer malfunction
Troubleshooting steps:
- Visual Inspection: Check the sensors and wiring for any signs of damage.
- Scan for Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to check for specific fault codes related to the wheel speed sensors.
- Sensor Testing: Use a multimeter to test the sensor’s resistance and signal output.
- Replacement: Replace the faulty sensor with a new, high-quality replacement from CARDIAGTECH.NET.
4.2. Weak or Dead 12-Volt Battery
Mercedes-Benz vehicles are sensitive to voltage fluctuations. A weak or failing battery can cause various electrical issues, including ESP malfunction.
Symptoms of a weak battery:
- Slow engine cranking
- Dim headlights
- Electrical system malfunctions
- ESP Inoperative warning light
Troubleshooting steps:
- Battery Voltage Test: Use a multimeter to check the battery’s voltage. A fully charged battery should read around 12.6 volts.
- Load Test: Perform a load test to assess the battery’s ability to deliver power under load.
- Charging System Check: Inspect the alternator and charging system to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Battery Replacement: Replace the battery if it fails the voltage or load test.
4.3. Bad Alternator or Voltage Regulator
The alternator is responsible for charging the battery and providing power to the vehicle’s electrical system while the engine is running. A faulty alternator or voltage regulator can cause voltage fluctuations and lead to ESP issues.
Symptoms of a bad alternator:
- Dim headlights
- Battery warning light
- Electrical system malfunctions
- Stalling or rough running engine
Troubleshooting steps:
- Voltage Test: Use a multimeter to check the alternator’s output voltage. It should typically be between 13.5 and 14.5 volts.
- Load Test: Perform a load test to assess the alternator’s ability to maintain voltage under load.
- Alternator Replacement: Replace the alternator if it fails the voltage or load test.
4.4. Steering Angle Sensor Calibration or Replacement
The steering angle sensor provides the ESP system with information about the driver’s steering input. If the sensor is miscalibrated or faulty, it can cause ESP malfunction.
Symptoms of a steering angle sensor issue:
- ESP Inoperative warning light
- Erratic steering behavior
- Difficulty maintaining lane position
Troubleshooting steps:
- Scan for Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to check for specific fault codes related to the steering angle sensor.
- Calibration: Perform a steering angle sensor calibration using a diagnostic tool.
- Sensor Replacement: Replace the sensor if calibration does not resolve the issue.
5. Step-by-Step Guide to Resetting the ESP Warning Light
In some cases, resetting the ESP system can resolve the issue. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Park your vehicle on a level surface.
- Turn off the engine.
- Locate the ESP button. This button may be labeled “ESP,” “TCS,” or have a similar symbol.
- Start the engine.
- Press and hold the ESP button for about 5-10 seconds.
- Release the button and observe the instrument cluster. The ESP warning light should turn off.
- Test drive your vehicle to confirm the ESP system is functioning correctly.
Note: This reset procedure may vary depending on the specific Mercedes-Benz model. If the warning light persists, further diagnosis is required.
6. Advanced Diagnostic Procedures
If the basic reset procedure does not resolve the ESP Inoperative warning, more advanced diagnostic procedures may be necessary. These procedures typically require specialized tools and expertise.
6.1. Using an OBD-II Scanner
An OBD-II scanner can retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from the vehicle’s computer, providing valuable information about the cause of the ESP issue.
Steps for using an OBD-II scanner:
- Locate the OBD-II port. This port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug the scanner into the port.
- Turn on the ignition.
- Follow the scanner’s instructions to read the DTCs.
- Record the DTCs and research their meaning.
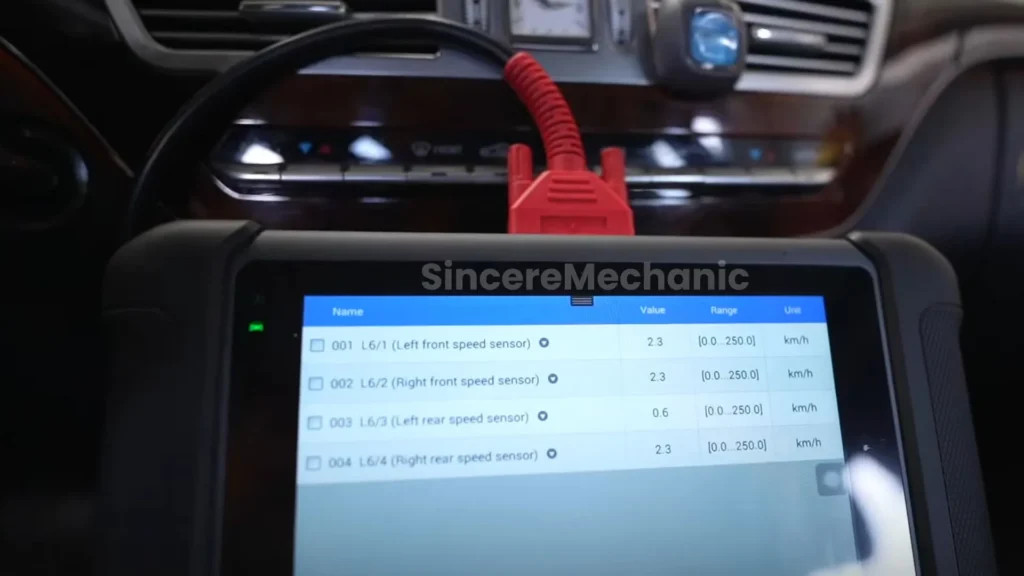
6.2. Live Data Analysis
Many advanced diagnostic tools can display live data from various sensors and systems, allowing you to monitor their performance in real-time. This can be helpful for identifying intermittent issues or sensor malfunctions.
Examples of useful live data parameters:
- Wheel speed sensor readings
- Steering angle sensor position
- Brake light switch status
- Battery voltage
- Alternator output voltage
By analyzing these data streams, you can gain valuable insights into the operation of the ESP system and identify potential problems.
7. The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET in Solving ESP Issues
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the complexities of modern vehicle systems like ESP. We offer a wide range of diagnostic tools, sensors, and replacement parts to help you resolve ESP Inoperative issues efficiently and effectively.
7.1. High-Quality Diagnostic Tools
We provide a comprehensive selection of OBD-II scanners and advanced diagnostic tools that are compatible with Mercedes-Benz vehicles. These tools can help you:
- Read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)
- Access live data streams
- Perform component testing
- Calibrate sensors
7.2. Premium Replacement Parts
We offer high-quality replacement parts for the ESP system, including:
- Wheel speed sensors
- Steering angle sensors
- Brake light switches
- ABS modules
- Batteries
- Alternators
All of our parts are sourced from reputable manufacturers and are designed to meet or exceed OEM specifications.
7.3. Expert Technical Support
Our team of experienced technicians is available to provide expert technical support and guidance to help you diagnose and resolve ESP issues. We can assist you with:
- Troubleshooting
- Diagnostic procedures
- Parts selection
- Installation advice
Don’t let ESP Inoperative warnings compromise your safety and driving experience. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today for expert assistance and high-quality solutions.
8. The Importance of Professional Assistance
While some ESP issues can be resolved with basic troubleshooting and DIY repairs, others may require the expertise of a qualified technician. If you are not comfortable working on your vehicle’s electrical or braking systems, it’s always best to seek professional assistance.
Benefits of professional service:
- Accurate diagnosis
- Proper repair procedures
- Use of specialized tools
- Warranty on parts and labor
- Peace of mind
Finding a reputable Mercedes-Benz mechanic:
- Ask for recommendations from friends or family
- Check online reviews
- Look for ASE certification (Automotive Service Excellence)
- Ensure the shop has experience working on Mercedes-Benz vehicles
9. Preventive Maintenance Tips to Avoid ESP Issues
Preventive maintenance is crucial for maintaining the proper functioning of your Mercedes-Benz ESP system and preventing future problems. Here are some essential maintenance tips:
- Regularly inspect your tires. Ensure they are properly inflated and have adequate tread depth. Uneven tire wear can affect the ESP system’s performance.
- Check your brakes. Inspect your brake pads, rotors, and calipers regularly. Replace worn brake components promptly.
- Maintain your battery. Keep your battery clean and properly charged. Replace the battery every 3-5 years, or as needed.
- Inspect wheel speed sensors. Check the sensors and wiring for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Perform regular wheel alignments. Proper wheel alignment is essential for optimal handling and ESP system performance.
- Address warning lights promptly. Don’t ignore warning lights on your dashboard. Have them diagnosed and repaired as soon as possible.
10. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are codes stored in your vehicle’s computer that indicate a specific problem. When the ESP Inoperative warning light appears, scanning for DTCs is essential for diagnosing the issue. Here are some common DTCs related to ESP problems in Mercedes-Benz vehicles:
| DTC Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| C1000 | Control Module N47-5 (ESP control unit) is defective | Faulty ESP control unit, wiring issues |
| C1100 | Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor – Circuit Malfunction | Faulty wheel speed sensor, wiring issues, damaged sensor ring |
| C1101 | Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor – Circuit Malfunction | Faulty wheel speed sensor, wiring issues, damaged sensor ring |
| C1102 | Left Rear Wheel Speed Sensor – Circuit Malfunction | Faulty wheel speed sensor, wiring issues, damaged sensor ring |
| C1103 | Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor – Circuit Malfunction | Faulty wheel speed sensor, wiring issues, damaged sensor ring |
| C1200 | Brake Light Switch – Circuit Malfunction | Faulty brake light switch, wiring issues |
| C1504 | Steering Angle Sensor – Internal Failure | Faulty steering angle sensor, calibration issues |
| C1510 | BAS (Brake Assist System) Control Module – Internal Failure | Faulty BAS control module, wiring issues |
| U0100 | Lost Communication With Engine Control Module (ECM) | Wiring issues, faulty ECM, CAN bus problems |
| U0121 | Lost Communication With Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) Control Module | Wiring issues, faulty ABS control module, CAN bus problems |
Note: This is not an exhaustive list, and the specific DTCs may vary depending on the Mercedes-Benz model and year.
11. ESP and Other Safety Systems
The ESP system works in conjunction with other safety systems in your Mercedes-Benz to provide comprehensive protection. Understanding these relationships can help you better appreciate the importance of maintaining your ESP system.
11.1. ESP and ABS (Anti-lock Braking System)
ESP and ABS are closely integrated systems that work together to enhance braking performance and stability. ABS prevents wheel lock-up during braking, while ESP uses individual wheel braking to correct skidding and maintain control.
11.2. ESP and Traction Control System (TCS)
TCS prevents wheel spin during acceleration, especially on slippery surfaces. ESP and TCS often share sensors and control modules, working together to optimize traction and stability.
11.3. ESP and Brake Assist System (BAS)
BAS detects emergency braking situations and applies maximum braking force to help reduce stopping distances. BAS relies on the ESP system to provide accurate information about the vehicle’s dynamics.
11.4. ESP and Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
ESC is a general term that encompasses various stability control systems, including ESP. In some cases, ESP may be referred to as ESC.
12. The Impact of Tire Condition on ESP Performance
The condition of your tires significantly affects the ESP system’s ability to maintain control. Here’s how:
- Tire Tread Depth: Adequate tread depth is essential for providing sufficient traction, especially in wet or snowy conditions. Worn tires with low tread depth can reduce the effectiveness of the ESP system. Aim for a tread depth of at least 4/32 of an inch.
- Tire Pressure: Maintaining the correct tire pressure is crucial for optimal handling and ESP performance. Check your tire pressure regularly and adjust it as needed. Refer to the sticker on your driver’s side doorjamb for the recommended tire pressure.
- Tire Wear: Uneven tire wear can indicate underlying suspension or alignment issues that can affect ESP performance. Have your tires inspected regularly and address any wear issues promptly.
- Tire Type: Using the correct type of tires for your vehicle and driving conditions is essential. Consult your owner’s manual or a tire professional for recommendations.
13. Real-World Scenarios Where ESP is Crucial
ESP plays a vital role in enhancing safety in various driving scenarios. Here are some examples:
- Emergency Maneuvers: ESP can help prevent loss of control during sudden lane changes or evasive maneuvers.
- Wet or Snowy Conditions: ESP can help maintain traction and stability on slippery surfaces.
- Cornering: ESP can help prevent oversteer or understeer when cornering at higher speeds.
- Skidding: ESP can quickly detect and correct skidding, helping the driver regain control.
14. ESP System Malfunctions and Safety Risks
Driving with a malfunctioning ESP system can significantly increase the risk of accidents, particularly in challenging driving conditions. Without ESP, the driver may lose control of the vehicle, leading to:
- Increased Stopping Distances: ABS and ESP work together to optimize braking performance. A malfunctioning ESP system can compromise braking effectiveness, increasing stopping distances.
- Loss of Steering Control: ESP helps maintain steering control during skidding and other challenging situations. Without ESP, the driver may struggle to steer the vehicle effectively.
- Increased Risk of Rollover: In severe cases, a malfunctioning ESP system can increase the risk of rollover, especially in SUVs and other high-center-of-gravity vehicles.
It is crucial to address ESP Inoperative warnings promptly to minimize these safety risks.
15. The Future of ESP Technology
ESP technology continues to evolve, with newer systems offering more advanced features and capabilities. Some of the trends in ESP technology include:
- Integration with Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS): ESP is increasingly integrated with ADAS features such as lane departure warning, adaptive cruise control, and automatic emergency braking.
- Predictive ESP: Some advanced ESP systems use sensors and algorithms to predict potential loss of control and intervene proactively.
- Individual Wheel Control: Newer ESP systems offer even more precise control over individual wheel braking, enhancing stability and handling.
- Over-the-Air Updates: Some manufacturers offer over-the-air software updates for ESP systems, allowing for continuous improvement and new feature additions.
16. ESP System and Legal Considerations
In some regions, ESP (or similar stability control systems) are mandatory on new vehicles. Additionally, disabling or tampering with the ESP system may be illegal or void your vehicle’s warranty.
Legal requirements:
- Many countries require new vehicles to be equipped with ESC (Electronic Stability Control), which includes ESP.
- Check your local regulations for specific requirements.
Warranty implications:
- Disabling or modifying the ESP system may void your vehicle’s warranty.
- Consult your warranty documentation or a dealership for more information.
17. Purchasing Guide for ESP Related Components at CARDIAGTECH.NET
Navigating the world of ESP components can be daunting. CARDIAGTECH.NET simplifies this process with a curated selection of top-quality parts and expert guidance. Here’s your go-to guide for purchasing ESP-related components:
- Identify the Issue: Begin by pinpointing the exact cause of your ESP Inoperative warning. Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). Common codes relate to wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, or the ESP control module.
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Ensure compatibility with your Mercedes-Benz A Class model and year. Consider factors like sensor type (magnetic or Hall effect) and connector style. A high-quality sensor ensures accurate speed readings for the ESP system.
- Steering Angle Sensors: A properly calibrated sensor is crucial for accurate steering input. Check for OEM-grade sensors that offer precise calibration and durability.
- Brake Light Switches: Inspect the switch for correct pin configuration and robust construction.
- ESP Control Modules: Replacing the ESP control module may require professional programming to integrate it with your vehicle’s system.
- Consult CARDIAGTECH.NET Experts: Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET’s technical support team for expert advice. Our technicians can help you verify compatibility and suggest the best components for your needs.
18. Cost Analysis of ESP Repairs
Understanding the costs associated with ESP repairs can help you budget accordingly. Here’s a breakdown of typical expenses:
| Repair Type | Average Cost (USD) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Wheel Speed Sensor Replacement | $150 – $350 | Includes the cost of the sensor and labor. Prices vary based on the location and the need for wheel alignment. |
| Steering Angle Sensor Calibration | $80 – $200 | Labor costs for calibrating the sensor using diagnostic tools. |
| Steering Angle Sensor Replacement | $300 – $700 | Includes the cost of the sensor and labor. Prices vary depending on the complexity of the installation. |
| Brake Light Switch Replacement | $80 – $200 | Includes the cost of the switch and labor. A straightforward repair, but prices can increase with diagnostic time. |
| ESP Control Module Replacement | $800 – $2000 | Includes the cost of the module, programming, and labor. This is a more complex repair that may require specialized tools and expertise. |
Note: These are estimated costs, and actual prices may vary depending on your location and the specific repair shop. Contact several repair shops for quotes.
19. Understanding Mercedes-Benz ESP Warning Messages
The ESP system communicates issues through various warning messages displayed on your dashboard. Each message indicates a specific problem that needs attention. Here’s a breakdown of common ESP warning messages:
- ESP Inoperative: This message indicates a general malfunction within the ESP system. It could be triggered by various issues, such as a faulty wheel speed sensor, steering angle sensor, or ESP control module.
- ESP Not Available: This message may appear when the ESP system is temporarily disabled, for example, during certain driving conditions or when another system is interfering.
- ESP Fault: This message indicates a specific fault within the ESP system. It may be accompanied by a diagnostic trouble code (DTC).
- ABS/ESP Warning Light: The ABS and ESP warning lights may illuminate together, indicating a problem with both systems.
Promptly addressing these messages is crucial for maintaining safety and stability.
20. ESP and Vehicle Modifications
Modifying your Mercedes-Benz A Class can affect the ESP system’s performance. Here’s what to consider:
- Suspension Modifications: Lowering or lifting your vehicle can alter the suspension geometry, affecting the ESP system’s ability to maintain control.
- Wheel and Tire Upgrades: Using different wheel and tire sizes can affect the ESP system’s calculations and performance.
- Engine Tuning: Increasing engine power without addressing other system components can overwhelm the ESP system’s capabilities.
21. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET for Expert Assistance
Maintaining the optimal performance of your Mercedes-Benz A Class ESP system requires quality tools and expert guidance. CARDIAGTECH.NET is your trusted partner, offering a comprehensive range of solutions to keep your vehicle running smoothly and safely.
Have questions or need expert advice? Contact us today!
- Address: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CARDIAGTECH.NET
Our expert technicians are ready to assist you with diagnostics, troubleshooting, and parts selection. Ensure your Mercedes-Benz A Class receives the best care, enhancing your driving experience and safety. Reach out now for immediate support and elevate your vehicle’s performance.
-
What does the ESP Inoperative warning mean on my Mercedes-Benz A Class?
This warning indicates a malfunction in the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) system, which helps prevent skidding and maintain control. It could be due to faulty sensors, low battery voltage, or other issues.
-
Can I drive my Mercedes-Benz A Class with the ESP Inoperative warning on?
While it’s possible to drive, it’s not recommended. The ESP system is crucial for safety, especially in challenging driving conditions. Have the issue diagnosed and repaired as soon as possible.
-
How do I reset the ESP warning light on my Mercedes-Benz A Class?
You can try resetting the system by parking on a level surface, turning off the engine, locating the ESP button, starting the engine, and pressing and holding the ESP button for 5-10 seconds. However, this may not resolve the underlying issue.
-
What are the common causes of the ESP Inoperative warning on a Mercedes-Benz A Class?
Common causes include faulty wheel speed sensors, low battery voltage, steering angle sensor issues, and brake light switch malfunctions.
-
How much does it cost to repair the ESP system on a Mercedes-Benz A Class?
Repair costs vary depending on the issue. Wheel speed sensor replacement can range from $150 to $350, while ESP control module replacement can cost $800 to $2000.
-
Can I replace the ESP components myself?
Some components, like wheel speed sensors and brake light switches, can be replaced with basic tools. However, more complex repairs, like ESP control module replacement, may require specialized tools and expertise.
-
Where can I buy high-quality ESP components for my Mercedes-Benz A Class?
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of high-quality ESP components for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
-
How does the ESP system work with other safety systems in my Mercedes-Benz A Class?
The ESP system works in conjunction with ABS, TCS, and BAS to provide comprehensive safety and stability.
-
What is the role of the steering angle sensor in the ESP system?
The steering angle sensor provides the ESP system with information about the driver’s steering input, which is crucial for maintaining control.
-
How can I prevent ESP issues in my Mercedes-Benz A Class?
Preventive maintenance, such as regular tire and brake inspections, battery maintenance, and wheel alignments, can help prevent ESP issues.
By following these guidelines and seeking expert assistance when needed, you can keep your Mercedes-Benz A Class ESP system functioning optimally, ensuring a safe and enjoyable driving experience.



