Esp Inactive Mercedes issues can be frustrating. This article, brought to you by CARDIAGTECH.NET, dives into the causes, solutions, and preventative measures for an inactive Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in your Mercedes-Benz. Understanding the ESP system, common faults, and repair strategies will keep you safe. We also cover related systems and tools for fixing ESP issues in Mercedes vehicles.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Mercedes-Benz ESP and Its Importance
- 2. Decoding the “ESP Inoperative” Warning Message
- 3. Common Causes of ESP Inactive in Mercedes Vehicles
- 4. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing ESP Inactive Issues
- 5. Repairing ESP Inactive: Practical Solutions and Procedures
- 6. The Role of Diagnostic Tools in ESP System Maintenance
- 7. Understanding ABS and Its Connection to ESP
- 8. How to Reset the ESP Warning Light on Your Mercedes-Benz
- 9. Preventative Maintenance to Avoid ESP System Issues
- 10. The Impact of ESP on Overall Vehicle Safety and Performance
- 11. What to Do When You Can’t Fix the ESP Issue Yourself
- 12. Exploring Other Safety Systems Related to ESP in Mercedes-Benz
- 13. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) Related to ESP
- 14. The Importance of Proper Tire Maintenance for ESP Functionality
- 15. How Aftermarket Modifications Can Affect Your ESP System
- 16. Case Studies: Real-World Examples of ESP Repairs
- 17. Tips for Finding a Reputable Mercedes-Benz Repair Shop
- 18. The Future of ESP Technology in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 19. Addressing Common Myths and Misconceptions About ESP
- 20. CARDIAGTECH.NET: Your Partner in Mercedes-Benz Diagnostics and Repairs
- 21. The Financial Implications of Ignoring an ESP Warning
- 22. The Legal and Ethical Considerations of Driving with ESP Inactive
- 23. Advanced Techniques for Troubleshooting Intermittent ESP Issues
- 24. How to Use a Multimeter for ESP System Diagnostics
- 25. Understanding Yaw Rate Sensors and Their Role in ESP
- 26. Exploring the Connection Between ESP and Air Suspension Systems
- 27. The Benefits of Professional ESP System Programming and Coding
- 28. Understanding the Relationship Between ESP and Transmission Control
- 29. How to Inspect and Maintain Your ESP System’s Wiring Harness
- 30. ESP System Calibration: Why It Matters and How to Do It
- 31. The Role of Wheel Alignment in ESP System Performance
- 32. Understanding the Different Types of ESP Systems in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
- 33. The Importance of Regular Brake System Maintenance for ESP Functionality
- 34. How to Perform a Road Test to Verify ESP System Repairs
- 35. Understanding the Role of the CAN Bus System in ESP Communication
- 36. How to Use Oscilloscope for Advanced ESP System Diagnostics
- 37. Tips for Avoiding ESP System Damage During Vehicle Storage
- 38. The Advantages of Upgrading Your ESP System Components
- 39. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About ESP Inactive Mercedes
1. Understanding Mercedes-Benz ESP and Its Importance
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in your Mercedes-Benz is a critical safety feature designed to prevent skidding and maintain control during challenging driving conditions. This system utilizes sensors to monitor wheel speed, steering angle, and yaw rate, intervening by applying individual brakes or adjusting engine power when it detects a loss of control. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), ESP systems can reduce single-vehicle crashes by as much as 35%. Keeping your ESP active helps ensure optimal vehicle handling and prevents accidents.
2. Decoding the “ESP Inoperative” Warning Message
Seeing an “ESP Inoperative” message on your Mercedes-Benz dashboard signals that the ESP system has been deactivated or is malfunctioning. This warning could indicate various issues, ranging from a simple sensor problem to a more complex system failure. Ignoring this warning is not advisable, as it compromises your vehicle’s stability and safety. Proper diagnosis and timely repairs are vital to reinstate the ESP system.
3. Common Causes of ESP Inactive in Mercedes Vehicles
Several factors can trigger an “ESP Inoperative” warning in Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Here are some of the most common culprits:
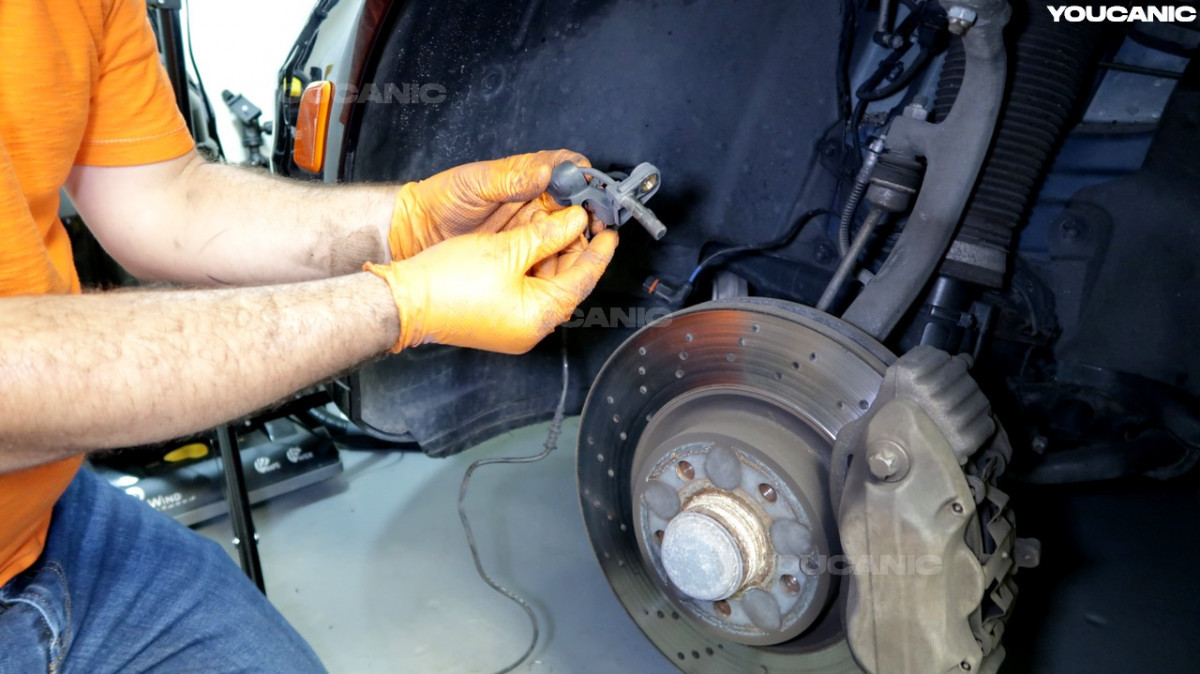
- Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors: These sensors are critical for monitoring wheel rotation and sending data to the ESP system. Damage or contamination can disrupt the signal, causing the ESP to deactivate.
- Steering Angle Sensor Malfunctions: The steering angle sensor provides information about the driver’s intended direction. If this sensor is misaligned or faulty, the ESP system may not function correctly.
- Low Battery Voltage: Mercedes-Benz vehicles rely on stable voltage for their electronic systems. A weak or failing battery can cause voltage drops that affect the ESP module, leading to its deactivation.
- Brake Light Switch Issues: The brake light switch signals when the brakes are applied. A faulty switch can send incorrect signals to the ESP system, causing it to shut down.
- ESP Control Module Problems: Although less common, the ESP control module itself can fail. This requires professional diagnostics and possibly module replacement.
- Tire Pressure Imbalance: The ESP system relies on accurate tire pressure readings. Significant pressure differences between tires can trigger the warning.
 Mercedes-Benz ESP reset & fix
Mercedes-Benz ESP reset & fix
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing ESP Inactive Issues
Diagnosing an inactive ESP system requires a systematic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Visual Inspection: Begin by inspecting the wheel speed sensors for any visible damage or loose connections.
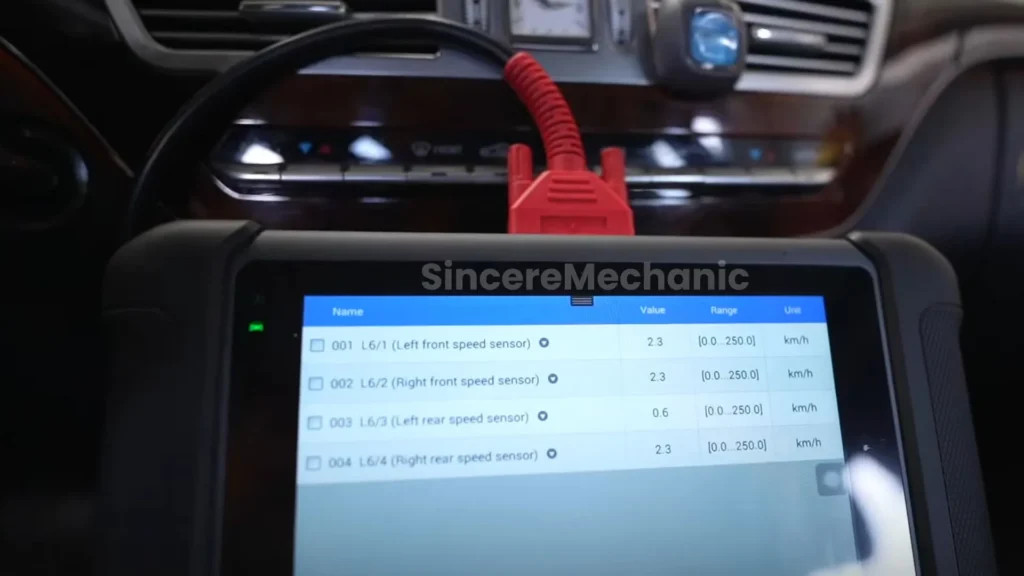
- OBD-II Scanning: Use an OBD-II scanner to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the ESP control module. Common codes related to ESP issues include C0031 (Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction), C0034 (Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction), and C0196 (Yaw Rate Sensor Malfunction).
- Battery Voltage Check: Check the battery voltage using a multimeter. A healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts when the engine is off and 13.7 to 14.7 volts when the engine is running.
- Steering Angle Sensor Calibration: Use a diagnostic tool to check the steering angle sensor readings. If the readings are inaccurate, perform a steering angle sensor calibration.
- Brake Light Switch Test: Test the brake light switch using a multimeter. Ensure it sends the correct signal when the brake pedal is pressed.
- Live Data Monitoring: Monitor live data from the wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor, and yaw rate sensor while driving. Look for any discrepancies or unusual readings.
- Component Testing: If necessary, use a multimeter or oscilloscope to test the individual components of the ESP system, such as the wheel speed sensors and the ESP control module.
5. Repairing ESP Inactive: Practical Solutions and Procedures
Once you’ve identified the cause of the ESP inactive issue, it’s time to implement the appropriate repair. Here are some practical solutions and procedures:
- Replacing Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors:
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Locate the faulty wheel speed sensor.
- Remove the wheel and brake caliper.
- Disconnect the sensor wiring.
- Remove the old sensor and install the new one.
- Reconnect the wiring, brake caliper, and wheel.
- Reconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Clear any stored DTCs.
- Calibrating the Steering Angle Sensor:
- Connect a diagnostic tool to the vehicle.
- Navigate to the ESP control module.
- Select the steering angle sensor calibration function.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to calibrate the sensor.
- Clear any stored DTCs.
- Replacing a Weak Battery:
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Remove the battery hold-down clamp.
- Disconnect the positive battery terminal.
- Remove the old battery.
- Install the new battery.
- Reconnect the positive and negative battery terminals.
- Secure the battery hold-down clamp.
- Replacing a Faulty Brake Light Switch:
- Locate the brake light switch near the brake pedal.
- Disconnect the wiring harness from the switch.
- Remove the old switch and install the new one.
- Reconnect the wiring harness.
- Replacing the ESP Control Module:
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Locate the ESP control module (usually under the dashboard or in the engine compartment).
- Disconnect the wiring harness from the module.
- Remove the old module and install the new one.
- Reconnect the wiring harness.
- Reconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Program the new module using a diagnostic tool.
6. The Role of Diagnostic Tools in ESP System Maintenance
Diagnostic tools are indispensable for ESP system maintenance. These tools can read diagnostic trouble codes, monitor live data, perform component testing, and calibrate sensors. Investing in a high-quality diagnostic tool like those offered by CARDIAGTECH.NET can save time and money by enabling accurate diagnostics and efficient repairs. Examples of useful tools include the Autel MaxiSYS MS906BT, the Launch X431 V+, and the Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis system.
7. Understanding ABS and Its Connection to ESP
The Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) is an integral part of the ESP system. ABS prevents the wheels from locking up during hard braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control. When the ESP system detects a loss of control, it works in conjunction with ABS to apply individual brakes and stabilize the vehicle. Malfunctions in the ABS system can also trigger the “ESP Inoperative” warning.
8. How to Reset the ESP Warning Light on Your Mercedes-Benz
After addressing the underlying issue, you may need to reset the ESP warning light. Here are a few methods:
- Manual Reset: Some Mercedes-Benz models have an “ESP Off” button. Press and hold this button for five seconds to reset the system.
- Steering Wheel Reset: Turn the steering wheel lock-to-lock (full left to full right) several times, then turn off the ignition and restart the vehicle.
- Diagnostic Tool Reset: Use a diagnostic tool to clear the stored DTCs in the ESP control module. This will usually reset the warning light.
If the warning light persists after these steps, there may be an unresolved issue, and further diagnostics are needed.
9. Preventative Maintenance to Avoid ESP System Issues
Preventative maintenance is key to avoiding ESP system issues. Here are some steps you can take:
- Regularly Inspect Wheel Speed Sensors: Check the wheel speed sensors for damage or contamination during routine maintenance.
- Maintain Proper Tire Pressure: Ensure that all tires are inflated to the recommended pressure levels.
- Keep Your Battery in Good Condition: Have your battery tested regularly and replace it when necessary.
- Check Brake Light Switch Function: Verify the brake light switch is functioning correctly to ensure proper ESP operation.
- Perform Routine Diagnostics: Use a diagnostic tool to check for any stored DTCs in the ESP control module.
10. The Impact of ESP on Overall Vehicle Safety and Performance
The ESP system significantly enhances vehicle safety and performance. By preventing skidding and maintaining control, ESP reduces the risk of accidents, particularly in adverse weather conditions. According to the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS), ESP can reduce the risk of fatal single-vehicle crashes by approximately 50%. Additionally, ESP improves vehicle handling and stability, providing a smoother and more confident driving experience.
11. What to Do When You Can’t Fix the ESP Issue Yourself
If you’re unable to diagnose or repair the ESP issue yourself, it’s best to seek professional assistance. A qualified Mercedes-Benz technician has the expertise, tools, and diagnostic equipment necessary to accurately identify and resolve complex ESP system problems. Attempting to fix the issue without proper knowledge can lead to further damage and compromise your safety.
12. Exploring Other Safety Systems Related to ESP in Mercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz vehicles are equipped with several safety systems that work in conjunction with ESP. These include:
- Brake Assist (BAS): BAS detects emergency braking situations and applies maximum braking force to reduce stopping distance.
- Acceleration Skid Control (ASR): ASR prevents wheel spin during acceleration, improving traction and stability.
- Electronic Brakeforce Distribution (EBD): EBD optimizes brake force distribution between the front and rear wheels, enhancing braking performance.
- Adaptive Brake Technology: This technology includes features like brake drying, hill start assist, and pre-filling the brake system in anticipation of emergency stops.
13. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) Related to ESP
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are crucial for identifying specific issues within the ESP system. Here are some common DTCs related to ESP:
| DTC Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| C0031 | Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty sensor, wiring issue, ABS module problem |
| C0034 | Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty sensor, wiring issue, ABS module problem |
| C0037 | Left Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty sensor, wiring issue, ABS module problem |
| C0040 | Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty sensor, wiring issue, ABS module problem |
| C0196 | Yaw Rate Sensor Malfunction | Faulty sensor, wiring issue, ESP module problem |
| C1100 | ESP Control Module – Internal Failure | Faulty module, programming issue |
| C1140 | Steering Angle Sensor – Implausible Signal | Misalignment, faulty sensor, wiring issue |
| C1175 | Brake Light Switch – Plausibility Error | Faulty switch, wiring issue |
| C1200 | ABS Hydraulic Pump Motor – Circuit Failure | Faulty motor, wiring issue, ABS module problem |
| C1444 | Supply Voltage – Too Low | Weak battery, alternator problem, wiring issue |
14. The Importance of Proper Tire Maintenance for ESP Functionality
Proper tire maintenance is crucial for ESP functionality. Uneven tire wear, incorrect tire pressure, or mismatched tires can negatively affect the ESP system. Ensure that your tires are properly inflated, have adequate tread depth, and are of the same type and size. Regular tire rotations can also help maintain even wear and extend tire life.
15. How Aftermarket Modifications Can Affect Your ESP System
Aftermarket modifications can sometimes interfere with the ESP system. Modifications such as suspension upgrades, larger wheels and tires, or performance chips can alter the vehicle’s handling characteristics and compromise the ESP system’s ability to function correctly. Always consult with a qualified technician before making any modifications that could affect the ESP system.
16. Case Studies: Real-World Examples of ESP Repairs
Here are a few real-world case studies illustrating common ESP repairs:
- Case Study 1: A Mercedes-Benz C-Class exhibited an “ESP Inoperative” warning due to a faulty left front wheel speed sensor. The technician replaced the sensor, cleared the DTCs, and performed a road test to verify the repair.
- Case Study 2: A Mercedes-Benz E-Class had an inactive ESP system caused by a misaligned steering angle sensor. The technician calibrated the sensor using a diagnostic tool, which resolved the issue.
- Case Study 3: A Mercedes-Benz S-Class displayed an “ESP Inoperative” warning due to a weak battery. The technician replaced the battery, and the ESP system returned to normal operation.
17. Tips for Finding a Reputable Mercedes-Benz Repair Shop
Finding a reputable Mercedes-Benz repair shop is essential for ensuring quality service and accurate repairs. Here are some tips:
- Look for ASE-Certified Technicians: ASE certification indicates that the technicians have met industry standards for knowledge and competence.
- Check Online Reviews: Read online reviews to get an idea of the shop’s reputation and customer satisfaction.
- Ask for Recommendations: Ask friends, family, or other Mercedes-Benz owners for recommendations.
- Verify Experience with ESP Systems: Ensure that the shop has experience diagnosing and repairing ESP systems on Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Inquire About Diagnostic Equipment: A reputable shop will have advanced diagnostic equipment, such as the Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis system.
18. The Future of ESP Technology in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
ESP technology continues to evolve in Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Future ESP systems may incorporate advanced features such as predictive stability control, which uses sensors and algorithms to anticipate potential loss-of-control situations and intervene proactively. Additionally, ESP systems may become more integrated with other vehicle systems, such as autonomous driving technologies, to enhance overall safety and performance.
19. Addressing Common Myths and Misconceptions About ESP
There are several myths and misconceptions surrounding ESP systems. Here are a few examples:
- Myth: ESP is only useful in winter weather. Fact: ESP is beneficial in all driving conditions, including dry pavement, rain, and snow.
- Myth: ESP can prevent all accidents. Fact: ESP can significantly reduce the risk of accidents, but it cannot overcome the laws of physics or compensate for reckless driving.
- Myth: Turning off ESP improves performance. Fact: In most situations, leaving ESP on is the safest option. Turning off ESP may be desirable in specific circumstances, such as when trying to free a vehicle stuck in snow.
20. CARDIAGTECH.NET: Your Partner in Mercedes-Benz Diagnostics and Repairs
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the complexities of Mercedes-Benz vehicles and the importance of maintaining their advanced safety systems. We offer a wide range of diagnostic tools and equipment to help you accurately diagnose and repair ESP inactive issues. Our products are designed to meet the needs of both professional technicians and DIY enthusiasts.
Don’t let an “ESP Inoperative” warning compromise your safety. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today to learn more about our diagnostic solutions and how we can help you keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly.
Navigating car repairs can be daunting, especially with complex systems like ESP. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we not only offer top-tier diagnostic tools but also empower you with the knowledge to tackle these issues confidently. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, our resources and equipment ensure you’re well-equipped to handle Mercedes-Benz ESP challenges.
21. The Financial Implications of Ignoring an ESP Warning
Ignoring an ESP warning can lead to significant financial consequences. Driving with an inactive ESP system increases the risk of accidents, which can result in costly repairs, insurance claims, and potential legal liabilities. Additionally, neglecting ESP system issues can lead to further damage to other vehicle components, increasing overall repair costs.
22. The Legal and Ethical Considerations of Driving with ESP Inactive
Driving with an inactive ESP system raises legal and ethical concerns. In some jurisdictions, it may be illegal to operate a vehicle with a known safety system malfunction. Moreover, driving with ESP inactive puts yourself and others at risk, which is ethically questionable. Prioritizing safety and addressing ESP system issues promptly is crucial.
23. Advanced Techniques for Troubleshooting Intermittent ESP Issues
Intermittent ESP issues can be particularly challenging to diagnose. Here are some advanced techniques for troubleshooting these problems:
- Data Logging: Use a diagnostic tool to log data from the ESP system while driving. This can help identify patterns or triggers that cause the ESP to deactivate.
- Stress Testing: Perform stress tests on the ESP system by simulating various driving conditions, such as hard braking, sharp turns, and acceleration.
- Wiring Harness Inspection: Carefully inspect the wiring harness for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Component Isolation: Isolate individual components of the ESP system to determine if one is causing the intermittent issue.
24. How to Use a Multimeter for ESP System Diagnostics
A multimeter is an essential tool for diagnosing ESP system issues. Here’s how to use a multimeter to test various components:
- Testing Wheel Speed Sensors: Measure the resistance of the wheel speed sensor. A typical resistance value is around 1,000 to 2,000 ohms.
- Testing Brake Light Switch: Check the continuity of the brake light switch. The switch should have continuity when the brake pedal is pressed.
- Testing Voltage at the ESP Control Module: Measure the voltage at the ESP control module. Ensure that the module is receiving the correct voltage (typically 12 volts).
- Testing Wiring Continuity: Check the continuity of the wiring harness between the sensors and the ESP control module.
25. Understanding Yaw Rate Sensors and Their Role in ESP
Yaw rate sensors are essential components of the ESP system. These sensors measure the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis, providing critical data for determining if the vehicle is skidding or losing control. A faulty yaw rate sensor can cause the ESP system to deactivate or function improperly.
26. Exploring the Connection Between ESP and Air Suspension Systems
In some Mercedes-Benz vehicles, the ESP system is integrated with the air suspension system. The air suspension system adjusts the vehicle’s ride height and stiffness to improve handling and stability. When the ESP system detects a loss of control, it can communicate with the air suspension system to adjust the suspension settings and enhance stability.
27. The Benefits of Professional ESP System Programming and Coding
In some cases, ESP system repairs may require programming or coding. This involves using a diagnostic tool to program the ESP control module with the correct software and parameters. Professional programming and coding ensure that the ESP system functions correctly and is properly integrated with the vehicle’s other systems.
28. Understanding the Relationship Between ESP and Transmission Control
The ESP system can also interact with the transmission control system. When the ESP system detects a loss of control, it can communicate with the transmission control system to adjust the gear selection and engine power output to improve stability.
29. How to Inspect and Maintain Your ESP System’s Wiring Harness
The wiring harness is a critical component of the ESP system. Inspect the wiring harness regularly for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the wires and ensure that there are no shorts or opens.
30. ESP System Calibration: Why It Matters and How to Do It
ESP system calibration is essential for ensuring accurate readings from the sensors. Calibration involves using a diagnostic tool to reset the sensor values and teach the ESP system the correct parameters. Proper calibration ensures that the ESP system functions correctly and responds appropriately to changing driving conditions.
31. The Role of Wheel Alignment in ESP System Performance
Proper wheel alignment is crucial for ESP system performance. Misaligned wheels can cause the ESP system to work harder to maintain control, leading to premature wear and tear on the system components. Ensure that your wheels are properly aligned to optimize ESP system performance.
32. Understanding the Different Types of ESP Systems in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
Mercedes-Benz vehicles may be equipped with different types of ESP systems, depending on the model and year. Some ESP systems may have advanced features such as torque vectoring or brake-based limited-slip differentials. Understanding the specific type of ESP system in your vehicle is essential for proper diagnosis and repair.
33. The Importance of Regular Brake System Maintenance for ESP Functionality
Regular brake system maintenance is crucial for ESP functionality. Worn brake pads, rotors, or calipers can negatively affect the ESP system’s ability to function correctly. Ensure that your brake system is properly maintained to optimize ESP system performance.
34. How to Perform a Road Test to Verify ESP System Repairs
After performing ESP system repairs, it’s essential to conduct a road test to verify that the system is functioning correctly. During the road test, simulate various driving conditions, such as hard braking, sharp turns, and acceleration, to ensure that the ESP system is intervening appropriately.
35. Understanding the Role of the CAN Bus System in ESP Communication
The CAN (Controller Area Network) bus system is used for communication between the various electronic control units in the vehicle, including the ESP control module. Problems with the CAN bus system can disrupt ESP communication and cause the system to malfunction.
36. How to Use Oscilloscope for Advanced ESP System Diagnostics
An oscilloscope is a powerful tool for advanced ESP system diagnostics. An oscilloscope can be used to analyze the waveforms of the sensor signals and identify any abnormalities or glitches.
37. Tips for Avoiding ESP System Damage During Vehicle Storage
Vehicle storage can sometimes lead to ESP system damage. To avoid this, disconnect the battery, store the vehicle in a dry environment, and avoid placing any heavy objects on the vehicle.
38. The Advantages of Upgrading Your ESP System Components
Upgrading your ESP system components can improve vehicle safety and performance. Upgrades may include installing high-performance wheel speed sensors, brake pads, or rotors.
39. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About ESP Inactive Mercedes
- What does “ESP Inoperative” mean on my Mercedes-Benz? It means the Electronic Stability Program is disabled or malfunctioning, reducing your vehicle’s stability control.
- Can I drive with the ESP light on? It’s not recommended. ESP helps prevent skidding, so driving with it off increases accident risk.
- How do I reset the ESP light on my Mercedes? Try turning the steering wheel lock-to-lock or pressing the “ESP Off” button for five seconds.
- What are common causes of ESP failure in Mercedes vehicles? Faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor issues, low battery voltage, or a bad brake light switch are common.
- Is it safe to disable ESP in my Mercedes? Generally, no. ESP enhances safety. Only disable it in specific situations like freeing a stuck vehicle.
- How often should I have my ESP system checked? During routine maintenance, ask your mechanic to check the ESP system for any stored error codes.
- Can aftermarket modifications affect my ESP system? Yes, modifications like suspension changes or larger tires can interfere with ESP.
- What diagnostic tools are best for Mercedes ESP issues? Tools like Autel MaxiSYS MS906BT or Launch X431 V+ are effective. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of suitable diagnostic tools.
- How does tire pressure affect ESP? Incorrect tire pressure can cause ESP to miscalculate stability, so maintain proper inflation.
- Where can I find a reliable Mercedes-Benz repair shop? Look for ASE-certified technicians, check online reviews, and ask for recommendations.
Is your Mercedes-Benz displaying an “ESP Inoperative” warning? Don’t compromise your safety. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today for expert advice and high-quality diagnostic tools. Our team of experienced professionals can help you diagnose and resolve ESP system issues quickly and efficiently. Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET. We are located at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States. Let us help you keep your Mercedes-Benz running smoothly and safely.



