Esp Faulty Visit Workshop Mercedes issues can be frustrating. CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to provide comprehensive guidance on diagnosing and resolving ESP (Electronic Stability Program) problems in your Mercedes. This guide covers common causes, troubleshooting steps, and solutions to help you get back on the road safely. We’ll explore vehicle dynamics, anti-lock braking system (ABS), and electronic control unit (ECU) functionalities.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the ESP “Visit Workshop” Message in Mercedes
- 2. Common Causes of ESP Malfunctions in Mercedes Vehicles
- 2.1. Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
- 2.2. Steering Angle Sensor Issues
- 2.3. Brake Light Switch Problems
- 2.4. ESP Control Unit Malfunctions
- 2.5. Low Battery Voltage
- 2.6. Wiring and Connection Problems
- 3. Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide for ESP Faults
- 3.1. Initial Inspection
- 3.2. Diagnostic Scan
- 3.3. Testing Individual Components
- 3.4. Calibration and Reset Procedures
- 4. Tools and Equipment Needed for ESP Repairs
- 5. DIY vs. Professional Repair: Making the Right Choice
- 5.1. When to Consider DIY Repair
- 5.2. When to Seek Professional Help
- 5.3. Cost Comparison
- 6. Preventing ESP Problems in Your Mercedes
- 6.1. Regular Maintenance
- 6.2. Safe Driving Habits
- 7. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for ESP Issues
- 7.1. Using Oscilloscopes
- 7.2. Data Logging and Analysis
- 7.3. Advanced Coding and Programming
- 8. Mercedes ESP System: A Deep Dive
- 8.1. Core Components of the ESP System
- 8.2. How the ESP System Works in Real-Time
- 8.3. Interaction with Other Vehicle Systems
- 9. Real-World Case Studies of ESP Faults in Mercedes
- 9.1. Case Study 1: Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
- 9.2. Case Study 2: Steering Angle Sensor Miscalibration
- 9.3. Case Study 3: Brake Light Switch Failure
- 10. Tips and Tricks from Experienced Mercedes Technicians
- 10.1. Visual Inspection First
- 10.2. Check the Basics
- 10.3. Use a High-Quality Scan Tool
- 10.4. Consult the Service Manual
- 10.5. Test, Don’t Guess
- 11. The Future of ESP Technology in Mercedes Vehicles
- 11.1. Integration with Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
- 11.2. Over-the-Air Updates
- 11.3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
- 12. Maintaining Your Mercedes: A Comprehensive Guide
- 12.1. Regular Fluid Checks and Changes
- 12.2. Suspension and Steering System Maintenance
- 12.3. Electrical System Maintenance
- 13. Understanding Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Codes
- 13.1. Common ESP-Related Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 13.2. Interpreting Diagnostic Codes Effectively
- 13.3. Clearing Codes and Re-Testing
- 14. Leveraging Online Communities and Resources for Mercedes Owners
- 14.1. Online Forums and Communities
- 14.2. Online Parts and Service Resources
- 14.3. YouTube Channels and Video Tutorials
- 15. Warranty Considerations for ESP Repairs on Mercedes Vehicles
- 15.1. Factory Warranty Coverage
- 15.2. Extended Warranty Options
- 15.3. Documenting Repairs for Warranty Claims
1. Understanding the ESP “Visit Workshop” Message in Mercedes
The “ESP visit workshop” message on your Mercedes dashboard indicates a fault within the Electronic Stability Program (ESP). ESP is a crucial safety system that helps maintain control of your vehicle during challenging driving conditions. When this message appears, it means the ESP system is not functioning correctly, which can compromise your safety.
- What is ESP? ESP is designed to prevent skidding and loss of control by monitoring various sensors and intervening when it detects instability. It uses sensors to track wheel speed, steering angle, and yaw rate, adjusting braking force to individual wheels to keep the vehicle on its intended path.
- Why is it important? A malfunctioning ESP system can reduce your ability to control the vehicle in emergency situations, such as sudden swerving or slippery road conditions. It’s essential to address this issue promptly to ensure your safety and the safety of others.
- Common symptoms: Besides the “ESP visit workshop” message, you might also notice the ESP warning light illuminated on your dashboard. Other symptoms may include reduced traction control, ABS light illumination, or difficulty maintaining stability during turns.
2. Common Causes of ESP Malfunctions in Mercedes Vehicles
Several factors can trigger the “ESP visit workshop” message in your Mercedes. Understanding these common causes can help you narrow down the problem and find the right solution.
2.1. Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
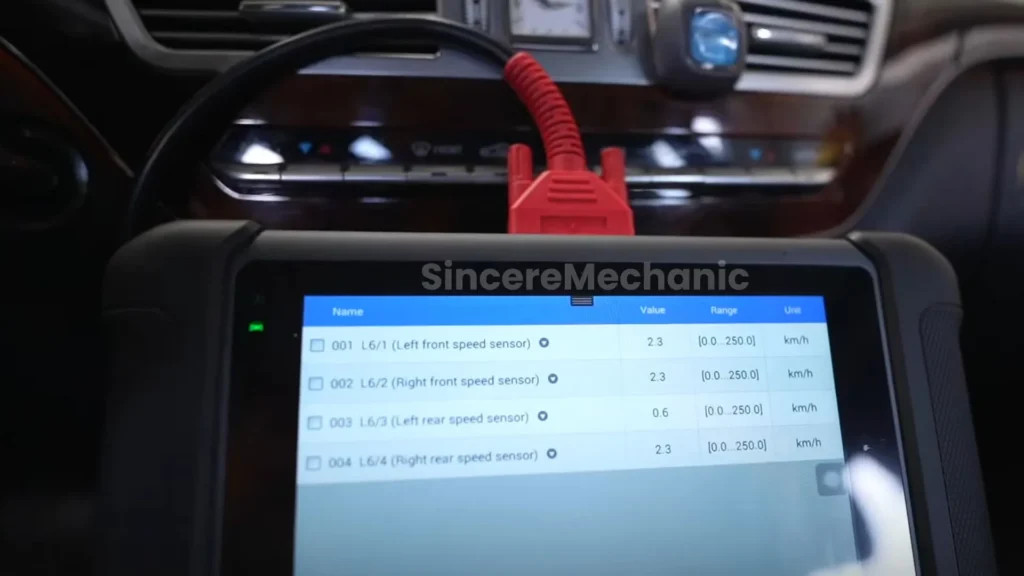
Wheel speed sensors are critical components of the ESP system. They monitor the rotational speed of each wheel and provide this data to the ESP control unit.
- How they fail: Wheel speed sensors can fail due to physical damage, corrosion, or electrical issues. Road debris, extreme temperatures, and general wear and tear can all contribute to their malfunction.
- Symptoms of failure: If a wheel speed sensor fails, the ESP system may receive incorrect data, leading to erratic behavior or complete system shutdown. Common symptoms include ABS and ESP warning lights, reduced traction control, and inaccurate speedometer readings.
- Testing and replacement: Testing wheel speed sensors typically involves using a multimeter to check for continuity and signal output. If a sensor is found to be faulty, it should be replaced immediately. At CARDIAGTECH.NET we have all the tools to help you to replace the faulty wheel speed sensor, you may contact us at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States or Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880.
2.2. Steering Angle Sensor Issues
The steering angle sensor measures the position of the steering wheel and provides this information to the ESP control unit. This data is crucial for determining the driver’s intended direction and making appropriate adjustments.
- How they fail: Steering angle sensors can fail due to misalignment, electrical faults, or internal component damage. These issues can arise from accidents, improper repairs, or normal wear and tear.
- Symptoms of failure: A faulty steering angle sensor can cause the ESP system to misinterpret the driver’s steering inputs, leading to incorrect interventions. Symptoms may include the ESP warning light, difficulty maintaining lane position, and erratic steering behavior.
- Calibration and repair: In many cases, a steering angle sensor can be recalibrated using a diagnostic tool. However, if the sensor is physically damaged or electrically faulty, it will need to be replaced.
2.3. Brake Light Switch Problems
The brake light switch is responsible for activating the brake lights when the brake pedal is pressed. It also sends a signal to the ESP control unit, indicating when the brakes are being applied.
- How they fail: Brake light switches can fail due to mechanical wear, electrical issues, or corrosion. Frequent use, exposure to moisture, and general aging can all contribute to their malfunction.
- Symptoms of failure: A faulty brake light switch can cause the ESP system to receive incorrect signals, leading to unintended interventions. Symptoms may include the ESP warning light, cruise control malfunction, and brake lights that stay on or don’t activate at all.
- Testing and replacement: Testing a brake light switch involves using a multimeter to check for proper continuity and signal output. If the switch is found to be faulty, it should be replaced.
2.4. ESP Control Unit Malfunctions
The ESP control unit is the brain of the ESP system, processing data from various sensors and making decisions about when and how to intervene.
- How they fail: ESP control units can fail due to electrical surges, internal component damage, or software glitches. These issues can arise from faulty wiring, battery problems, or exposure to extreme temperatures.
- Symptoms of failure: A malfunctioning ESP control unit can cause a wide range of issues, including the ESP warning light, ABS light, reduced traction control, and complete system failure. In some cases, the vehicle may also exhibit erratic braking behavior.
- Diagnosis and repair: Diagnosing ESP control unit problems often requires advanced diagnostic tools and expertise. In some cases, the control unit can be reprogrammed or repaired. However, in severe cases, it may need to be replaced.
2.5. Low Battery Voltage
Low battery voltage can cause a variety of electrical issues in modern vehicles, including problems with the ESP system.
- How it affects ESP: The ESP control unit requires a stable voltage supply to function correctly. If the battery voltage drops too low, the control unit may not be able to process data accurately or activate the necessary interventions.
- Symptoms of low voltage: Low battery voltage can manifest as the ESP warning light, ABS light, reduced traction control, and difficulty starting the vehicle. In some cases, the vehicle may also exhibit erratic electrical behavior.
- Testing and resolution: Testing the battery voltage is a simple process that can be done with a multimeter. If the voltage is below the recommended level, the battery should be charged or replaced.
2.6. Wiring and Connection Problems
Wiring and connection problems can disrupt the flow of data between the various components of the ESP system.
- How they occur: Wiring and connection problems can arise from corrosion, physical damage, or loose connections. Exposure to moisture, road salt, and vibrations can all contribute to these issues.
- Symptoms of wiring issues: Wiring and connection problems can cause intermittent ESP issues, such as the warning light appearing and disappearing. Other symptoms may include reduced traction control, ABS light, and erratic braking behavior.
- Inspection and repair: Inspecting the wiring and connections involves visually checking for damage, corrosion, and loose connections. Cleaning corroded connections and repairing damaged wires can often resolve these issues.
3. Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide for ESP Faults
Troubleshooting ESP faults in your Mercedes requires a systematic approach. Follow these steps to diagnose the problem effectively.
3.1. Initial Inspection
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of your vehicle.
- Check for visible damage: Look for any signs of physical damage to the wheels, tires, and suspension components.
- Inspect wiring and connections: Check the wiring and connections to the wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor, and ESP control unit. Look for any signs of corrosion, damage, or loose connections.
- Examine brake components: Inspect the brake pads, rotors, and calipers for wear and damage.
3.2. Diagnostic Scan
Use a diagnostic scan tool to retrieve fault codes from the ESP control unit.
- Connect the scan tool: Connect the scan tool to the OBD-II port, typically located under the dashboard.
- Read fault codes: Turn on the ignition and use the scan tool to read any stored fault codes from the ESP control unit.
- Interpret the codes: Research the fault codes to understand the potential causes of the ESP malfunction. Common codes include those related to wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor, and brake light switch.
3.3. Testing Individual Components
Test the individual components of the ESP system to identify any faults.
- Wheel Speed Sensors:
- Testing Procedure: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance and signal output of each wheel speed sensor.
- Expected Values: Consult the vehicle’s service manual for the correct resistance and signal output values.
- Common Issues: Look for open circuits, short circuits, or erratic signal patterns.
- Steering Angle Sensor:
- Testing Procedure: Use a diagnostic scan tool to monitor the steering angle sensor’s readings while turning the steering wheel.
- Expected Values: The readings should correspond accurately to the steering wheel’s position.
- Common Issues: Look for inaccurate readings, erratic fluctuations, or a complete lack of signal.
- Brake Light Switch:
- Testing Procedure: Use a multimeter to check for continuity when the brake pedal is pressed and released.
- Expected Values: The switch should show continuity when the brake pedal is pressed and no continuity when it’s released.
- Common Issues: Look for a switch that doesn’t activate or deactivate properly.
- Battery Voltage:
- Testing Procedure: Use a multimeter to measure the battery voltage with the engine off and running.
- Expected Values: The battery voltage should be around 12.6 volts with the engine off and between 13.7 and 14.7 volts with the engine running.
- Common Issues: Look for low voltage readings, which can indicate a weak or failing battery.
3.4. Calibration and Reset Procedures
After replacing or repairing any components, perform the necessary calibration and reset procedures.
- Steering Angle Sensor Calibration:
- Calibration Procedure: Use a diagnostic scan tool to recalibrate the steering angle sensor. Follow the tool’s instructions carefully to ensure proper calibration.
- Why it’s necessary: Calibration ensures that the ESP system accurately interprets the steering wheel’s position.
- ESP System Reset:
- Reset Procedure: Use a diagnostic scan tool to reset the ESP system and clear any stored fault codes.
- Why it’s necessary: Resetting the system allows it to relearn and adapt to the new or repaired components.
4. Tools and Equipment Needed for ESP Repairs
Having the right tools and equipment is essential for diagnosing and repairing ESP faults in your Mercedes.
- Diagnostic Scan Tool: A diagnostic scan tool is necessary for reading fault codes and monitoring sensor data.
- Multimeter: A multimeter is used for testing electrical components, such as wheel speed sensors and brake light switches.
- Socket Set and Wrenches: A socket set and wrenches are needed for removing and installing various components.
- Wire Strippers and Crimpers: Wire strippers and crimpers are used for repairing damaged wiring.
- OBD-II Connector: An OBD-II connector is used to connect the scan tool to the vehicle’s diagnostic port.
- Mercedes-Specific Diagnostic Software: For advanced diagnostics and programming, Mercedes-specific diagnostic software, such as XENTRY or DAS, may be required.
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we offer a wide range of diagnostic tools and equipment to help you with your ESP repairs. Contact us at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States or Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880 to learn more.
5. DIY vs. Professional Repair: Making the Right Choice
Deciding whether to tackle ESP repairs yourself or seek professional help depends on your skill level, experience, and the complexity of the problem.
5.1. When to Consider DIY Repair
- Simple Issues: If the problem is a simple one, such as a faulty brake light switch or a loose connection, you may be able to handle the repair yourself.
- Basic Mechanical Skills: If you have basic mechanical skills and experience working on cars, you may be comfortable performing some of the simpler ESP repairs.
- Access to Tools: If you have access to the necessary tools and equipment, you may be able to save money by doing the repair yourself.
5.2. When to Seek Professional Help
- Complex Issues: If the problem is more complex, such as a faulty ESP control unit or a steering angle sensor issue, it’s best to seek professional help.
- Limited Experience: If you have limited experience working on cars, you may not be able to diagnose and repair the problem correctly.
- Lack of Tools: If you don’t have access to the necessary tools and equipment, you may not be able to perform the repair safely or effectively.
5.3. Cost Comparison
- DIY Repair Costs: The cost of DIY ESP repairs can range from a few dollars for a simple brake light switch to several hundred dollars for a replacement wheel speed sensor.
- Professional Repair Costs: The cost of professional ESP repairs can range from a few hundred dollars for a simple diagnosis to several thousand dollars for a more complex repair involving the ESP control unit.
6. Preventing ESP Problems in Your Mercedes
Preventing ESP problems in your Mercedes involves regular maintenance and careful driving habits.
6.1. Regular Maintenance
- Wheel Speed Sensor Cleaning: Clean the wheel speed sensors regularly to remove dirt, debris, and corrosion.
- Brake System Inspection: Inspect the brake system regularly for wear and damage. Replace worn brake pads and rotors promptly.
- Tire Maintenance: Maintain proper tire pressure and alignment to ensure optimal traction and stability.
- Battery Maintenance: Keep the battery terminals clean and corrosion-free. Replace the battery when it reaches the end of its lifespan.
6.2. Safe Driving Habits
- Avoid Aggressive Driving: Avoid aggressive driving maneuvers, such as sudden acceleration, braking, and turning.
- Drive According to Conditions: Adjust your driving speed and style to match the road conditions.
- Maintain Safe Following Distance: Maintain a safe following distance to allow yourself plenty of time to react to sudden changes in traffic.
7. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for ESP Issues
For complex ESP issues, advanced diagnostic techniques may be necessary to pinpoint the problem.
7.1. Using Oscilloscopes
An oscilloscope can be used to analyze the waveforms of the signals from the wheel speed sensors and other components.
- How it works: An oscilloscope displays the voltage of a signal over time, allowing you to identify any irregularities or distortions.
- Benefits: Using an oscilloscope can help you identify subtle problems that may not be apparent with a multimeter or scan tool.
7.2. Data Logging and Analysis
Data logging involves recording the data from various sensors and components over time.
- How it works: Data logging can be done using a diagnostic scan tool or a dedicated data logger. The recorded data can then be analyzed to identify any patterns or anomalies.
- Benefits: Data logging can help you identify intermittent problems that may not be present during a static test.
7.3. Advanced Coding and Programming
In some cases, ESP problems may require advanced coding or programming to resolve.
- How it works: Advanced coding and programming involves modifying the software in the ESP control unit to correct errors or adapt to new components.
- Benefits: Advanced coding and programming can help you resolve complex ESP issues that cannot be fixed with simple repairs or calibrations.
8. Mercedes ESP System: A Deep Dive
To truly understand and tackle ESP issues, let’s delve deeper into the system itself.
8.1. Core Components of the ESP System
- Yaw Rate Sensor: Measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis.
- Lateral Acceleration Sensor: Measures the force acting on the vehicle sideways.
- Longitudinal Acceleration Sensor: Measures the force acting on the vehicle forward and backward.
- Hydraulic Unit: Contains valves that control brake pressure to individual wheels.
- Pump Motor: Provides pressure to the hydraulic unit.
8.2. How the ESP System Works in Real-Time
- Sensor Data Acquisition: The sensors continuously monitor vehicle dynamics.
- Data Processing: The ESP control unit processes the data and compares it to pre-programmed parameters.
- Intervention Decision: If the ESP detects a loss of control, it determines which wheels need braking.
- Actuation: The hydraulic unit applies brake pressure to the selected wheels, helping to stabilize the vehicle.
- Continuous Monitoring: The system continuously monitors and adjusts as needed.
8.3. Interaction with Other Vehicle Systems
- ABS (Anti-lock Braking System): ESP relies on ABS to prevent wheel lock-up during braking.
- ASR (Acceleration Skid Regulation): ASR works in conjunction with ESP to prevent wheel spin during acceleration.
- Engine Management System: ESP can communicate with the engine management system to reduce engine power in certain situations.
9. Real-World Case Studies of ESP Faults in Mercedes
Analyzing real-world case studies can provide valuable insights into diagnosing and resolving ESP faults.
9.1. Case Study 1: Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
- Vehicle: 2015 Mercedes-Benz C300
- Symptoms: ESP warning light, ABS light, reduced traction control.
- Diagnosis: Diagnostic scan revealed a fault code related to the right front wheel speed sensor. Testing with a multimeter confirmed that the sensor was faulty.
- Solution: The right front wheel speed sensor was replaced, and the ESP system was reset.
- Outcome: The ESP and ABS lights went off, and the vehicle’s traction control system was restored.
9.2. Case Study 2: Steering Angle Sensor Miscalibration
- Vehicle: 2018 Mercedes-Benz E300
- Symptoms: ESP warning light, difficulty maintaining lane position.
- Diagnosis: Diagnostic scan revealed a fault code related to the steering angle sensor. Live data showed that the sensor was not accurately reflecting the steering wheel’s position.
- Solution: The steering angle sensor was recalibrated using a diagnostic scan tool.
- Outcome: The ESP light went off, and the vehicle’s lane-keeping assist system was restored.
9.3. Case Study 3: Brake Light Switch Failure
- Vehicle: 2012 Mercedes-Benz C250
- Symptoms: ESP warning light, cruise control malfunction.
- Diagnosis: Testing with a multimeter revealed that the brake light switch was not functioning correctly.
- Solution: The brake light switch was replaced.
- Outcome: The ESP light went off, and the cruise control system was restored.
10. Tips and Tricks from Experienced Mercedes Technicians
Here are some valuable tips and tricks from experienced Mercedes technicians to help you diagnose and repair ESP faults more effectively.
10.1. Visual Inspection First
- Tip: Always start with a thorough visual inspection of the vehicle. Look for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Why: A visual inspection can often reveal obvious problems that may not be detected by a diagnostic scan tool.
10.2. Check the Basics
- Tip: Before diving into complex diagnostics, check the basics. Make sure the battery is fully charged, the tires are properly inflated, and the wheel alignment is correct.
- Why: Basic problems can often cause ESP faults.
10.3. Use a High-Quality Scan Tool
- Tip: Invest in a high-quality diagnostic scan tool that is specifically designed for Mercedes vehicles.
- Why: A high-quality scan tool can provide more accurate and detailed information than a generic scan tool.
10.4. Consult the Service Manual
- Tip: Consult the vehicle’s service manual for detailed information on the ESP system, including diagnostic procedures, wiring diagrams, and component specifications.
- Why: The service manual can provide valuable insights that may not be available elsewhere.
10.5. Test, Don’t Guess
- Tip: Always test the individual components of the ESP system before replacing them.
- Why: Replacing components without proper testing can be expensive and may not solve the problem.
11. The Future of ESP Technology in Mercedes Vehicles
ESP technology is constantly evolving, with new features and capabilities being added to Mercedes vehicles.
11.1. Integration with Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
- Trend: ESP is becoming increasingly integrated with ADAS, such as adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, and automatic emergency braking.
- Benefits: This integration allows for more precise and coordinated control of the vehicle, enhancing safety and convenience.
11.2. Over-the-Air Updates
- Trend: Mercedes is now offering over-the-air updates for its vehicles, including the ESP system.
- Benefits: Over-the-air updates allow for quick and easy software updates, ensuring that the ESP system is always up-to-date with the latest features and bug fixes.
11.3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
- Trend: Mercedes is exploring the use of AI to enhance the performance of the ESP system.
- Benefits: AI can be used to predict potential loss of control situations and intervene more quickly and effectively.
12. Maintaining Your Mercedes: A Comprehensive Guide
While addressing ESP faults is crucial, maintaining your Mercedes holistically is key to preventing future issues.
12.1. Regular Fluid Checks and Changes
- Engine Oil: Follow the recommended oil change intervals to keep your engine running smoothly.
- Transmission Fluid: Change the transmission fluid according to the manufacturer’s recommendations to prevent transmission problems.
- Brake Fluid: Flush the brake fluid every two years to remove moisture and contaminants.
- Coolant: Check the coolant level regularly and flush the system every few years to prevent corrosion and overheating.
12.2. Suspension and Steering System Maintenance
- Inspect Shocks and Struts: Check the shocks and struts for leaks and wear. Replace them as needed to maintain proper handling.
- Check Ball Joints and Tie Rods: Inspect the ball joints and tie rods for wear and play. Replace them as needed to prevent steering problems.
- Align the Wheels: Have the wheels aligned regularly to ensure even tire wear and optimal handling.
12.3. Electrical System Maintenance
- Check the Battery: Have the battery tested regularly to ensure it is in good condition. Replace it as needed to prevent electrical problems.
- Inspect Wiring and Connections: Check the wiring and connections for corrosion and damage. Repair or replace them as needed to prevent electrical faults.
- Check Fuses and Relays: Inspect the fuses and relays for damage. Replace them as needed to prevent electrical problems.
13. Understanding Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Codes
Navigating Mercedes-Benz diagnostic codes can be daunting. Here’s a breakdown to help you understand them better.
13.1. Common ESP-Related Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- C1000: ESP control unit malfunction.
- C1101: Fault in the wheel speed sensor circuit.
- C1120: Steering angle sensor fault.
- C1140: BAS (Brake Assist System) fault.
- C1170: Yaw rate sensor fault.
13.2. Interpreting Diagnostic Codes Effectively
- Use a Reliable Scan Tool: Invest in a Mercedes-specific scan tool for accurate code reading.
- Research the Code: Look up the code in a Mercedes-Benz service manual or online database.
- Consider Symptoms: Combine the code with the vehicle’s symptoms for a clearer picture.
- Verify the Fault: Perform additional tests to confirm the fault before replacing parts.
13.3. Clearing Codes and Re-Testing
- Clear Codes: After addressing the issue, clear the diagnostic codes using the scan tool.
- Re-Test: Drive the vehicle and re-scan for codes to ensure the problem is resolved.
14. Leveraging Online Communities and Resources for Mercedes Owners
Connecting with other Mercedes owners and accessing online resources can be invaluable for troubleshooting ESP issues.
14.1. Online Forums and Communities
- Mercedes-Benz Forums: Engage in discussions and seek advice from experienced Mercedes owners and technicians.
- Social Media Groups: Join Facebook groups and other social media communities dedicated to Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
14.2. Online Parts and Service Resources
- CARDIAGTECH.NET: Explore our website for a wide range of diagnostic tools and equipment.
- Mercedes-Benz Parts Websites: Find genuine Mercedes-Benz parts and accessories online.
- Online Service Manuals: Access online service manuals for detailed information on Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
14.3. YouTube Channels and Video Tutorials
- Mercedes-Benz Repair Channels: Watch video tutorials on YouTube for step-by-step instructions on diagnosing and repairing ESP faults.
- Automotive Diagnostic Channels: Follow channels that provide general automotive diagnostic tips and techniques.
15. Warranty Considerations for ESP Repairs on Mercedes Vehicles
Understanding your warranty coverage is essential when dealing with ESP repairs.
15.1. Factory Warranty Coverage
- New Vehicles: New Mercedes-Benz vehicles typically come with a factory warranty that covers ESP repairs for a certain period or mileage.
- Coverage Details: Review your warranty documentation to understand the specific coverage terms and conditions.
15.2. Extended Warranty Options
- Extended Warranties: Consider purchasing an extended warranty to cover ESP repairs beyond the factory warranty period.
- Coverage Options: Compare different extended warranty options to find the best coverage for your needs.
15.3. Documenting Repairs for Warranty Claims
- Keep Records: Keep detailed records of all ESP repairs, including the date, mileage, and description of the work performed.
- Use Authorized Repair Shops: Use authorized Mercedes-Benz repair shops for warranty repairs to ensure proper documentation and claim processing.
Experiencing an “ESP visit workshop Mercedes” message can be unsettling, but with the right knowledge and tools, you can diagnose and address the issue effectively. Whether you choose to tackle the repair yourself or seek professional help, CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to support you.
Are you facing challenges with your Mercedes ESP system? Do you need reliable diagnostic tools or expert advice? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, or Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880. Let us help you get back on the road with confidence.
1. What does the “ESP visit workshop” message mean on my Mercedes?
This message indicates a fault in the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) system, which helps maintain control during challenging driving conditions.
2. What are the common causes of ESP malfunctions in Mercedes vehicles?
Common causes include faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor issues, brake light switch problems, ESP control unit malfunctions, low battery voltage, and wiring issues.
3. How can I diagnose an ESP fault in my Mercedes?
Start with a visual inspection, use a diagnostic scan tool to retrieve fault codes, and test individual components like wheel speed sensors and the brake light switch.
4. Can I fix an ESP fault myself, or should I take it to a professional?
For simple issues like a faulty brake light switch, DIY is possible. Complex issues like a faulty ESP control unit require professional help.
5. What tools do I need for ESP repairs?
You’ll need a diagnostic scan tool, multimeter, socket set, wrenches, wire strippers, and possibly Mercedes-specific diagnostic software.
6. How can I prevent ESP problems in my Mercedes?
Regular maintenance, including cleaning wheel speed sensors, inspecting the brake system, maintaining proper tire pressure, and practicing safe driving habits, can help.
7. What is the role of wheel speed sensors in the ESP system?
Wheel speed sensors monitor the rotational speed of each wheel, providing data to the ESP control unit to prevent skidding.
8. How does the steering angle sensor affect the ESP system?
The steering angle sensor measures the position of the steering wheel, helping the ESP system determine the driver’s intended direction.
9. Can low battery voltage cause ESP problems?
Yes, low battery voltage can disrupt the ESP control unit’s function, leading to the ESP warning light and other issues.
10. What are some advanced diagnostic techniques for complex ESP issues?
Advanced techniques include using oscilloscopes to analyze signal waveforms, data logging, and advanced coding or programming of the ESP control unit.