Navigating the roads with confidence is paramount, and the ESP in Mercedes Benz plays a vital role in achieving just that, offering advanced safety and control. The Electronic Stability Program, a cornerstone of Mercedes-Benz engineering, enhances vehicle stability, reduces skidding, and improves overall driving safety, making every journey secure. Explore how CARDIAGTECH.NET can further optimize your vehicle’s performance with our specialized tools for diagnostics and maintenance, ensuring your Mercedes-Benz remains in peak condition. Vehicle dynamics, driver assistance, active safety are crucial elements for secure travels.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in Mercedes-Benz
- 1.1 The Core Functionality of ESP
- 1.2 How ESP Works: A Detailed Overview
- 1.3 Integration with Other Safety Systems
- 1.4 Historical Context and Development
- 1.5 The Importance of ESP in Modern Vehicles
- 2. Key Benefits of ESP in Mercedes-Benz
- 2.1 Preventing Skidding and Loss of Control
- 2.2 Enhancing Vehicle Stability
- 2.3 Reducing Understeer and Oversteer
- 2.4 Improving Handling in Adverse Conditions
- 2.5 Minimizing Rollover Risk
- 2.6 Enhancing Driver Confidence
- 2.7 Contributing to Overall Safety
- 3. Mercedes-Benz Models Equipped with ESP
- 3.1 Sedans and Coupes
- 3.2 SUVs
- 3.3 Roadsters and Convertibles
- 3.4 Other Models
- 3.5 Ensuring Safety Across the Lineup
- 4. How to Check if Your Mercedes-Benz Has ESP
- 4.1 Check the Dashboard for ESP Indicator Light
- 4.2 Consult the Vehicle’s Owner’s Manual
- 4.3 Inspect the Center Console Buttons
- 4.4 Review the Vehicle’s Specifications
- 4.5 Contact a Mercedes-Benz Dealership
- 4.6 Use a Diagnostic Tool
- 4.7 Check the Vehicle’s Window Sticker
- 5. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz ESP System
- 5.1 Regular Inspections and Diagnostics
- 5.2 Checking and Replacing Sensors
- 5.3 Monitoring Brake System Components
- 5.4 Ensuring Proper Tire Condition
- 5.5 Keeping the ESP System Software Updated
- 5.6 Addressing ESP Warning Lights
- 5.7 Avoiding Modifications That Affect ESP
- 5.8 Seeking Professional Maintenance
- 6. Common Issues and Troubleshooting ESP in Mercedes-Benz
- 6.1 ESP Warning Light On
- 6.2 Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
- 6.3 Steering Angle Sensor Problems
- 6.4 Yaw Rate Sensor Issues
- 6.5 Brake System Problems
- 6.6 Low Battery Voltage
- 6.7 Wiring and Connector Issues
- 6.8 Software Glitches
- 6.9 Seeking Professional Help
- 7. Optimizing Your Mercedes-Benz with CARDIAGTECH.NET
- 7.1 Diagnostic Tools for ESP Maintenance
- 7.2 Benefits of Using CARDIAGTECH.NET Tools
- 7.3 Featured Products for Mercedes-Benz ESP Maintenance
- 7.4 How to Use CARDIAGTECH.NET Tools for ESP Maintenance
- 7.5 Expert Support and Resources
- 7.6 Ensuring Optimal Performance
- 8. Real-World Benefits: ESP in Action
- 8.1 Preventing Accidents on Slippery Roads
- 8.2 Enhancing Control During Emergency Maneuvers
- 8.3 Improving Stability in Windy Conditions
- 8.4 Reducing Rollover Risk in SUVs
- 8.5 Enhancing Confidence in Challenging Situations
- 8.6 Real-Life Testimonials
- 8.7 Statistics and Studies
- 9. The Future of ESP and Automotive Safety
- 9.1 Integration with Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
- 9.2 Enhanced Sensor Technology
- 9.3 Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
- 9.4 Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
- 9.5 Enhanced Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication
- 9.6 Focus on Cybersecurity
- 9.7 Collaborative Development
1. Understanding the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in Mercedes-Benz
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in Mercedes-Benz is a crucial safety system designed to prevent skidding and maintain control in adverse driving conditions. Often referred to as electronic stability control (ESC) or dynamic stability control, ESP is engineered to provide stability and prevent accidents by monitoring and intervening when a loss of control is detected.
1.1 The Core Functionality of ESP
At its core, ESP enhances vehicle stability by detecting and mitigating skids. According to Bosch, a key partner in developing ESP, the system reduces accidents by up to 80% in critical situations. By monitoring the vehicle’s direction and driver’s intended path, ESP can selectively apply brakes to individual wheels to correct oversteer or understeer, thus helping the driver maintain control.
1.2 How ESP Works: A Detailed Overview
ESP operates through a network of sensors that continuously monitor the vehicle’s behavior. These sensors include:
- Steering Angle Sensor: Determines the direction the driver intends to go.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: Measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis.
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Monitor the speed of each wheel to detect potential skidding.
When these sensors detect a discrepancy between the driver’s intended direction and the vehicle’s actual movement, ESP intervenes. For instance, if the system detects oversteer (where the rear of the car slides out), it might apply the brake to the outer front wheel to create a counteracting force, bringing the vehicle back in line.
1.3 Integration with Other Safety Systems
ESP works in conjunction with other safety systems like the anti-lock braking system (ABS) and traction control system (TCS) to provide comprehensive safety. ABS prevents wheel lock-up during braking, while TCS limits wheel spin during acceleration. Together, these systems ensure maximum grip and control in various driving conditions.
1.4 Historical Context and Development
Mercedes-Benz, in collaboration with Bosch, introduced ESP in 1995, setting a new standard for automotive safety. This innovation has since become a standard feature in most modern vehicles, significantly reducing accident rates.
1.5 The Importance of ESP in Modern Vehicles
ESP is particularly vital in challenging driving conditions such as wet, icy, or gravel roads. It helps drivers maintain control and reduces the risk of accidents, enhancing overall safety. As stated by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), ESC systems like ESP have been proven to significantly reduce the risk of single-vehicle crashes, especially on slippery surfaces.
2. Key Benefits of ESP in Mercedes-Benz
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) offers numerous advantages that enhance driving safety and vehicle performance. These benefits range from preventing skidding to improving overall vehicle stability.
2.1 Preventing Skidding and Loss of Control
One of the primary benefits of ESP is its ability to prevent skidding, especially on slippery surfaces. By selectively applying brakes to individual wheels, ESP helps the driver maintain control and avoid accidents.
2.2 Enhancing Vehicle Stability
ESP enhances vehicle stability, particularly in challenging conditions such as cornering. By monitoring the vehicle’s movement and making necessary corrections, ESP ensures the car remains stable and predictable.
2.3 Reducing Understeer and Oversteer
ESP is effective in reducing both understeer and oversteer, two common types of skidding that can lead to loss of control. Understeer occurs when the front wheels lose traction, causing the car to go straight instead of turning. Oversteer happens when the rear wheels lose traction, causing the car to spin. ESP corrects these conditions, keeping the vehicle on its intended path.
2.4 Improving Handling in Adverse Conditions
ESP significantly improves handling in adverse conditions such as rain, snow, or ice. By providing additional stability and control, ESP reduces the risk of accidents and makes driving safer.
2.5 Minimizing Rollover Risk
ESP helps minimize the risk of rollover, especially in vehicles with a high center of gravity such as SUVs. By maintaining stability during sudden maneuvers, ESP reduces the likelihood of a rollover accident.
2.6 Enhancing Driver Confidence
ESP enhances driver confidence by providing an added layer of safety and control. Knowing that the vehicle is equipped with ESP allows drivers to feel more secure, especially in challenging driving conditions.
2.7 Contributing to Overall Safety
ESP contributes to overall safety by reducing the likelihood of accidents. Studies have shown that vehicles equipped with ESP have a significantly lower accident rate compared to those without the system. According to the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS), ESC systems like ESP have saved thousands of lives by preventing crashes.
3. Mercedes-Benz Models Equipped with ESP
Since the early 2000s, the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) has become a standard feature in most Mercedes-Benz models. This widespread adoption highlights Mercedes-Benz’s commitment to safety and innovation. Here are some notable models equipped with ESP:
3.1 Sedans and Coupes
- C-Class: Known for its blend of luxury and performance, the C-Class offers ESP as a standard feature, ensuring stability and control in various driving conditions.
- E-Class: As a mid-size luxury sedan, the E-Class combines comfort with advanced safety features, including ESP, to provide a smooth and secure driving experience.
- S-Class: The flagship sedan of Mercedes-Benz, the S-Class, includes ESP as part of its comprehensive suite of safety technologies, offering top-tier stability and control.
- CLA Coupe: A stylish and sporty coupe, the CLA comes standard with ESP, providing enhanced stability and handling for a dynamic driving experience.
- CLS Coupe: Combining elegance with performance, the CLS includes ESP to ensure stability and control, enhancing its appeal as a luxury coupe.
3.2 SUVs
- GLA SUV: As a compact SUV, the GLA is equipped with ESP to enhance stability and control, making it a safe and reliable choice for urban and highway driving.
- GLC SUV: The GLC offers a balance of luxury and versatility, with ESP as a standard feature to provide enhanced safety and stability in various driving conditions.
- GLE SUV: Known for its spacious interior and robust performance, the GLE includes ESP to ensure stability and control, enhancing its appeal as a family-friendly SUV.
- GLS SUV: The largest SUV in the Mercedes-Benz lineup, the GLS, comes standard with ESP, providing enhanced stability and control for a safe and comfortable ride.
- G-Class SUV: An iconic SUV known for its off-road capabilities, the G-Class includes ESP to enhance stability and control, ensuring safety both on and off the road.
3.3 Roadsters and Convertibles
- SLC Roadster: A sporty and stylish roadster, the SLC comes equipped with ESP, providing enhanced stability and control for an exhilarating driving experience.
- SL Roadster: As a luxury roadster, the SL includes ESP as part of its suite of advanced safety technologies, ensuring stability and control for a smooth and secure ride.
3.4 Other Models
- Mercedes-AMG® GT: A high-performance sports car, the AMG® GT includes ESP to enhance stability and control, ensuring a thrilling yet safe driving experience.
- V-Class: As a versatile van, the V-Class comes standard with ESP, providing enhanced stability and control for passenger safety and comfort.
3.5 Ensuring Safety Across the Lineup
By including ESP as a standard feature in most models, Mercedes-Benz demonstrates its commitment to providing a safe and secure driving experience for all customers. Whether you are driving a sedan, SUV, roadster, or van, ESP helps maintain control and prevent accidents.
4. How to Check if Your Mercedes-Benz Has ESP
Determining whether your Mercedes-Benz is equipped with the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is straightforward. Here are several methods to verify if your vehicle has this safety feature.
4.1 Check the Dashboard for ESP Indicator Light
One of the easiest ways to check for ESP is by looking for the ESP indicator light on the dashboard. This light usually illuminates briefly when you start the engine as part of the system’s self-check. The ESP indicator light typically features a car symbol with skid marks behind it. If the light remains on or flashes while driving, it indicates that ESP is actively engaged, correcting a loss of traction.
4.2 Consult the Vehicle’s Owner’s Manual
The owner’s manual is a comprehensive resource for information about your vehicle’s features and systems. Look for the section on safety features or electronic stability control to confirm whether your Mercedes-Benz is equipped with ESP. The manual will also provide details on how the system works and any related warnings or precautions.
4.3 Inspect the Center Console Buttons
Some Mercedes-Benz models have a button on the center console that allows you to disable or adjust the ESP system. If you find a button labeled “ESP” or with the car symbol and skid marks, your vehicle is likely equipped with the system. Pressing the button may disable ESP or switch it to a different mode, depending on the model.
4.4 Review the Vehicle’s Specifications
You can review the vehicle’s specifications online or through Mercedes-Benz’s official website to determine if ESP is listed as a standard or optional feature. This method is particularly useful if you are purchasing a used Mercedes-Benz and want to confirm its features.
4.5 Contact a Mercedes-Benz Dealership
If you are unsure whether your Mercedes-Benz has ESP, contact a local Mercedes-Benz dealership. Provide them with your vehicle’s VIN (Vehicle Identification Number), and they can look up the vehicle’s original specifications and confirm whether it was equipped with ESP at the factory.
4.6 Use a Diagnostic Tool
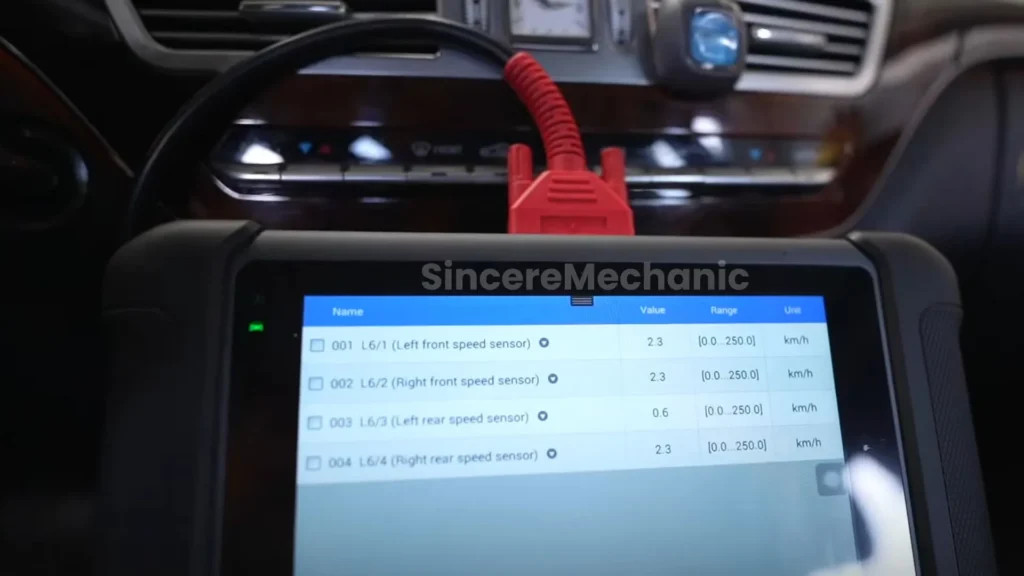
A diagnostic tool, such as those available at CARDIAGTECH.NET, can scan your vehicle’s computer system and provide detailed information about its features and systems. This can confirm whether ESP is present and functioning correctly. These tools are invaluable for mechanics and car enthusiasts who want to understand their vehicle’s systems in detail.
4.7 Check the Vehicle’s Window Sticker
If you have access to the vehicle’s original window sticker (Monroney sticker), it will list all the standard and optional features included on the vehicle when it was new. Look for “Electronic Stability Program” or “ESP” in the list of features.
5. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz ESP System
Maintaining the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in your Mercedes-Benz is crucial for ensuring its proper functioning and your safety. Regular checks and proper maintenance can help keep the ESP system in optimal condition.
5.1 Regular Inspections and Diagnostics
Regular inspections are vital for identifying potential issues early. Use diagnostic tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET to check the ESP system for error codes. These tools provide valuable insights into the system’s performance and can help detect problems before they escalate.
5.2 Checking and Replacing Sensors
The ESP system relies on several sensors, including steering angle sensors, yaw rate sensors, and wheel speed sensors. Ensure these sensors are functioning correctly. If a sensor fails, it can disrupt the ESP system’s operation. Replace faulty sensors promptly to maintain the system’s accuracy.
5.3 Monitoring Brake System Components
ESP relies on the braking system to function correctly. Regularly check brake pads, rotors, and brake lines for wear and tear. Ensure the brake fluid is at the correct level and is free from contamination. A well-maintained braking system is essential for the ESP to operate effectively.
5.4 Ensuring Proper Tire Condition
Tire condition plays a significant role in the ESP system’s effectiveness. Check tire pressure regularly and ensure tires have adequate tread depth. Uneven tire wear can affect the ESP system’s ability to maintain control. Rotate and balance tires as recommended by Mercedes-Benz.
5.5 Keeping the ESP System Software Updated
Keep the ESP system software updated to ensure it operates with the latest enhancements and bug fixes. Visit a Mercedes-Benz dealership or authorized service center to have the software updated.
5.6 Addressing ESP Warning Lights
If the ESP warning light illuminates on the dashboard, it indicates a potential issue with the system. Do not ignore this warning. Use a diagnostic tool to read the error codes and identify the problem. Address the issue promptly to restore the ESP system to proper working order.
5.7 Avoiding Modifications That Affect ESP
Avoid modifications that can affect the ESP system, such as altering the suspension or using non-approved tires. These modifications can interfere with the system’s calibration and reduce its effectiveness.
5.8 Seeking Professional Maintenance
For complex issues, seek professional maintenance from a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician. They have the expertise and specialized tools to diagnose and repair ESP system problems accurately.
6. Common Issues and Troubleshooting ESP in Mercedes-Benz
While the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is a robust safety feature, it can experience issues over time. Understanding common problems and troubleshooting steps can help you address these issues effectively.
6.1 ESP Warning Light On
One of the most common issues is the ESP warning light illuminating on the dashboard. This indicates a problem with the ESP system. Use a diagnostic tool from CARDIAGTECH.NET to read the error codes and identify the specific issue. Common causes include faulty sensors, wiring problems, or a malfunctioning control module.
6.2 Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
Wheel speed sensors are critical for the ESP system to function correctly. If a wheel speed sensor fails, it can trigger the ESP warning light and affect the system’s ability to detect and correct skidding. Use a diagnostic tool to check the wheel speed sensors and replace any faulty ones.
6.3 Steering Angle Sensor Problems
The steering angle sensor provides data on the driver’s intended direction. If this sensor malfunctions, it can disrupt the ESP system’s ability to determine the correct course of action. Use a diagnostic tool to check the steering angle sensor and recalibrate or replace it as needed.
6.4 Yaw Rate Sensor Issues
The yaw rate sensor measures the vehicle’s rotation. If this sensor fails, it can lead to inaccurate data and affect the ESP system’s performance. Use a diagnostic tool to check the yaw rate sensor and replace it if necessary.
6.5 Brake System Problems
ESP relies on the braking system to function correctly. Issues such as worn brake pads, rotors, or low brake fluid can affect the ESP system’s ability to apply brakes to individual wheels. Inspect the braking system and address any problems promptly.
6.6 Low Battery Voltage
Low battery voltage can sometimes cause the ESP system to malfunction. Ensure the battery is in good condition and properly charged. A weak battery can lead to various electrical issues, including ESP problems.
6.7 Wiring and Connector Issues
Check the wiring and connectors associated with the ESP system for damage or corrosion. Damaged wiring or corroded connectors can disrupt the flow of information and cause the ESP system to malfunction. Repair or replace any damaged wiring or connectors.
6.8 Software Glitches
Sometimes, software glitches can cause the ESP system to malfunction. Try resetting the system by disconnecting the battery for a few minutes and then reconnecting it. If the problem persists, have the software updated at a Mercedes-Benz dealership or authorized service center.
6.9 Seeking Professional Help
For complex issues, seek professional help from a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician. They have the expertise and specialized tools to diagnose and repair ESP system problems accurately.
7. Optimizing Your Mercedes-Benz with CARDIAGTECH.NET
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools and equipment designed to help you maintain and optimize your Mercedes-Benz, ensuring the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) and other critical systems function correctly.
7.1 Diagnostic Tools for ESP Maintenance
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides advanced diagnostic tools that allow you to read error codes, monitor sensor data, and perform system tests on your Mercedes-Benz ESP system. These tools are essential for identifying potential issues early and addressing them before they become major problems.
7.2 Benefits of Using CARDIAGTECH.NET Tools
- Accurate Diagnostics: Our tools provide precise and reliable diagnostic information, helping you pinpoint the exact cause of ESP-related issues.
- User-Friendly Interface: The tools feature an intuitive interface, making it easy for both experienced technicians and DIY enthusiasts to use.
- Comprehensive Coverage: CARDIAGTECH.NET tools support a wide range of Mercedes-Benz models, ensuring compatibility with your vehicle.
- Cost Savings: By diagnosing and addressing issues yourself, you can save money on expensive dealership repairs.
7.3 Featured Products for Mercedes-Benz ESP Maintenance
- OBD-II Scanners: These scanners allow you to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the ESP system.
- Sensor Testing Kits: These kits help you test the functionality of wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, and yaw rate sensors.
- Brake System Analyzers: These tools enable you to assess the condition of your brake system, ensuring it meets the requirements for proper ESP operation.
7.4 How to Use CARDIAGTECH.NET Tools for ESP Maintenance
- Connect the Tool: Plug the diagnostic tool into your Mercedes-Benz’s OBD-II port.
- Read Error Codes: Use the tool to read any error codes related to the ESP system.
- Interpret the Data: Consult the tool’s manual or online resources to understand the meaning of the error codes.
- Perform Tests: Use the tool to perform specific tests on sensors and other components.
- Address Issues: Based on the diagnostic results, address any identified issues by replacing faulty parts or performing necessary repairs.
7.5 Expert Support and Resources
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers expert support and resources to help you get the most out of your diagnostic tools. Our team of experienced technicians is available to answer your questions and provide guidance on troubleshooting ESP-related issues.
7.6 Ensuring Optimal Performance
By using CARDIAGTECH.NET diagnostic tools and following our maintenance guidelines, you can ensure that your Mercedes-Benz ESP system operates at its best, providing you with enhanced safety and control on the road.
8. Real-World Benefits: ESP in Action
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) provides numerous real-world benefits that enhance driving safety and vehicle performance in various situations. Here are some examples of how ESP can make a difference:
8.1 Preventing Accidents on Slippery Roads
One of the most significant benefits of ESP is its ability to prevent accidents on slippery roads. For instance, imagine driving your Mercedes-Benz on a rainy day when you suddenly encounter a patch of black ice. Without ESP, your car might lose traction and skid out of control. However, with ESP, the system detects the loss of traction and automatically applies the brakes to individual wheels, helping you regain control and avoid a potential collision.
8.2 Enhancing Control During Emergency Maneuvers
ESP can also enhance control during emergency maneuvers. Suppose you are driving on the highway and suddenly need to swerve to avoid an obstacle. Without ESP, your car might become unstable and difficult to control. However, with ESP, the system helps stabilize the vehicle and prevent it from spinning out, allowing you to safely navigate the obstacle and maintain control.
8.3 Improving Stability in Windy Conditions
Driving in windy conditions can be challenging, especially for high-profile vehicles such as SUVs. ESP helps improve stability by counteracting the effects of strong winds. For example, if a gust of wind pushes your Mercedes-Benz SUV to the side, ESP can automatically adjust the brakes and steering to keep the vehicle on its intended path, reducing the risk of an accident.
8.4 Reducing Rollover Risk in SUVs
SUVs have a higher center of gravity than sedans, making them more susceptible to rollovers. ESP helps reduce this risk by monitoring the vehicle’s stability and intervening when necessary. If the system detects that the vehicle is at risk of rolling over, it can apply the brakes to individual wheels to stabilize the vehicle and prevent a rollover accident.
8.5 Enhancing Confidence in Challenging Situations
ESP enhances driver confidence by providing an added layer of safety and control. Knowing that your Mercedes-Benz is equipped with ESP allows you to feel more secure and confident, especially in challenging driving conditions.
8.6 Real-Life Testimonials
Many drivers have shared their experiences of how ESP has helped them avoid accidents and maintain control in critical situations. These real-life testimonials highlight the effectiveness and importance of ESP as a safety feature.
8.7 Statistics and Studies
Studies have shown that vehicles equipped with ESP have a significantly lower accident rate compared to those without the system. These statistics provide further evidence of the real-world benefits of ESP and its contribution to overall safety.
9. The Future of ESP and Automotive Safety
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) has significantly advanced automotive safety, and its future promises even more innovations and enhancements. As technology evolves, ESP systems are becoming more sophisticated and integrated with other safety features.
9.1 Integration with Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
One of the key trends in automotive safety is the integration of ESP with Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS). ADAS technologies such as adaptive cruise control, lane departure warning, and automatic emergency braking work in conjunction with ESP to provide a comprehensive safety net.
9.2 Enhanced Sensor Technology
Future ESP systems will incorporate more advanced sensor technology to improve accuracy and responsiveness. For example, higher-resolution cameras and radar sensors will provide more detailed information about the vehicle’s surroundings, allowing the ESP system to make more informed decisions.
9.3 Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are playing an increasingly important role in automotive safety. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict potential hazards. By incorporating AI and ML into ESP systems, manufacturers can create more proactive and effective safety features.
9.4 Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
Over-the-air (OTA) updates allow manufacturers to remotely update vehicle software, including the ESP system. This means that vehicles can receive the latest safety enhancements and bug fixes without requiring a visit to a dealership.
9.5 Enhanced Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication
V2X communication allows vehicles to communicate with each other and with infrastructure such as traffic lights and road sensors. This technology can provide valuable information to the ESP system, allowing it to anticipate and respond to potential hazards more effectively.
9.6 Focus on Cybersecurity
As vehicles become more connected, cybersecurity is becoming an increasingly important concern. Manufacturers are investing in cybersecurity measures to protect ESP systems and other critical vehicle functions from cyberattacks.
9.7 Collaborative Development
The future of ESP and automotive safety will involve collaboration between automakers, technology companies, and regulatory agencies. By working together, these stakeholders can develop and implement the most effective safety solutions.
Here are some frequently asked questions about the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in Mercedes-Benz vehicles, providing you with a better understanding of this critical safety feature.
Q1: What is Electronic Stability Program (ESP)?
ESP, or Electronic Stability Program, is a safety feature designed to help prevent skidding and maintain control in adverse driving conditions by selectively applying brakes to individual wheels.
Q2: How does ESP work in a Mercedes-Benz?
ESP monitors the vehicle’s direction and compares it to the driver’s intended path. When a discrepancy is detected, ESP intervenes by applying brakes to specific wheels to correct oversteer or understeer.
Q3: What are the key benefits of ESP?
Key benefits include preventing skidding, enhancing vehicle stability, reducing understeer and oversteer, improving handling in adverse conditions, and minimizing rollover risk.
Q4: Is ESP standard on all Mercedes-Benz models?
Since the early 2000s, ESP has been a standard feature on most Mercedes-Benz models, demonstrating Mercedes-Benz’s commitment to safety.
Q5: How can I check if my Mercedes-Benz has ESP?
Check the dashboard for the ESP indicator light, consult the vehicle’s owner’s manual, inspect the center console buttons, or review the vehicle’s specifications online.
Q6: What should I do if the ESP warning light comes on?
If the ESP warning light illuminates, use a diagnostic tool to read the error codes and identify the problem. Address the issue promptly to restore the ESP system to proper working order.
Q7: Can I disable ESP in my Mercedes-Benz?
Some Mercedes-Benz models have a button to disable ESP, but it is generally recommended to keep ESP enabled for optimal safety, especially in challenging driving conditions.
Q8: How can CARDIAGTECH.NET help with ESP maintenance?
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers diagnostic tools that allow you to read error codes, monitor sensor data, and perform system tests on your Mercedes-Benz ESP system, ensuring it functions correctly.
Q9: What are some common issues with ESP in Mercedes-Benz vehicles?
Common issues include faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor problems, yaw rate sensor issues, brake system problems, and low battery voltage.
Q10: How often should I have my ESP system checked?
It is recommended to have your ESP system checked during regular vehicle maintenance, typically every 12 months or 12,000 miles, to ensure all components are functioning correctly.
By addressing these common questions, you can stay informed and take proactive steps to maintain the ESP system in your Mercedes-Benz, ensuring optimal safety and performance on the road.
Maintaining the ESP in your Mercedes-Benz is essential for your safety and the vehicle’s performance. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides the tools and resources you need to keep your ESP system in top condition. Contact us at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States or via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET for more information and expert support. Don’t compromise on safety – ensure your Mercedes-Benz ESP system is always ready to protect you.