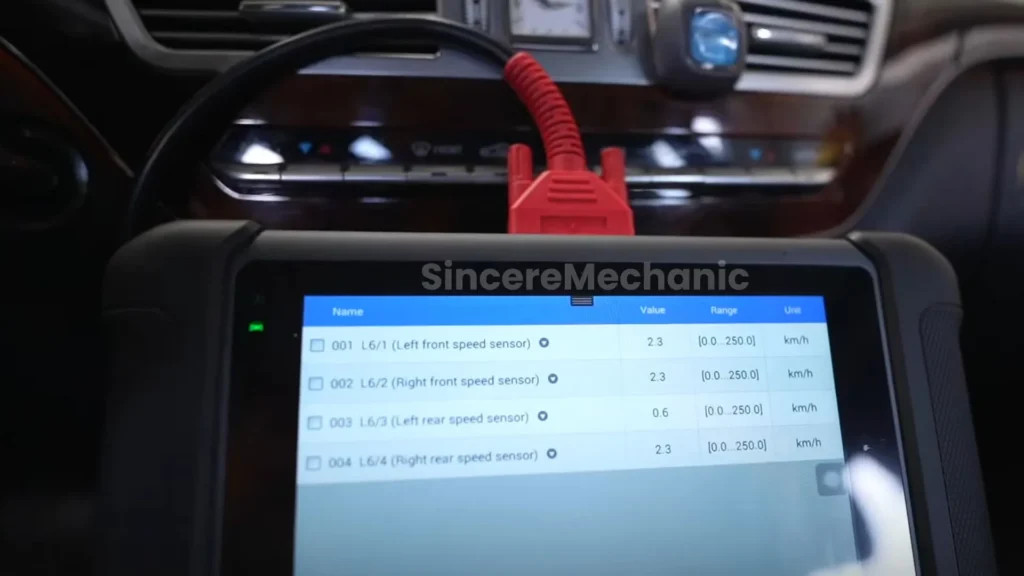
Is your Mercedes displaying an ESP fault? This article by CARDIAGTECH.NET, your trusted automotive resource, delves into the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) and what an ESP warning light might mean for your vehicle, providing guidance on when to seek expert assistance like a Mercedes repair shop. We’ll cover troubleshooting tips and solutions to ensure your vehicle’s stability control system is functioning optimally. Let’s explore the common causes and diagnostic steps to address Mercedes ESP issues, including stability control malfunctions and electronic stability program errors.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Electronic Stability Program (ESP)
- 1.1. How ESP Works
- 1.2. The Role of ESP in Preventing Accidents
- 2. Common Symptoms of an ESP Fault in Mercedes
- 2.1. ESP Warning Light Illumination
- 2.2. Reduced Engine Power
- 2.3. Difficulty Maintaining Stability
- 2.4. ABS Warning Light Illumination
- 2.5. Unusual Braking Behavior
- 2.6. Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3. Common Causes of ESP Faults in Mercedes
- 3.1. Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
- 3.2. Steering Angle Sensor Issues
- 3.3. Brake Light Switch Problems
- 3.4. ABS Module Malfunctions
- 3.5. Low Battery Voltage
- 3.6. Incorrect Tire Sizes
- 3.7. Wiring and Connection Issues
- 4. Diagnosing an ESP Fault in Your Mercedes
- 4.1. Visual Inspection
- 4.2. Diagnostic Scan Tool
- 4.3. Testing Wheel Speed Sensors
- 4.4. Testing the Steering Angle Sensor
- 4.5. Checking the Brake Light Switch
- 4.6. Inspecting Wiring and Connections
- 5. When to Seek Professional Assistance at a Mercedes Repair Shop
- 5.1. Complex Diagnostic Trouble Codes
- 5.2. Persistent ESP Faults
- 5.3. ABS Module Issues
- 5.4. Safety Concerns
- 5.5. Lack of Experience
- 6. Repairing ESP Faults in Mercedes
- 6.1. Replacing Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
- 6.2. Replacing the Steering Angle Sensor
- 6.3. Replacing the Brake Light Switch
- 6.4. Repairing or Replacing the ABS Module
- 6.5. Addressing Wiring and Connection Issues
- 7. Preventing ESP Faults in Your Mercedes
- 7.1. Regular Maintenance
- 7.2. Proper Tire Care
- 7.3. Avoiding Harsh Driving Conditions
- 7.4. Keeping the Vehicle Clean
- 7.5. Timely Repairs
- 8. The Importance of Using Quality Replacement Parts
- 8.1. OEM vs. Aftermarket Parts
- 8.2. Benefits of OEM Parts
- 8.3. Risks of Aftermarket Parts
- 9. Cost of Repairing ESP Faults in Mercedes
- 9.1. Wheel Speed Sensor Replacement
- 9.2. Steering Angle Sensor Replacement
- 9.3. Brake Light Switch Replacement
- 9.4. ABS Module Repair or Replacement
- 9.5. Wiring and Connection Repairs
- 10. ESP Fault Mercedes: Addressing Customer Challenges
- 10.1. Enhancing Efficiency
- 10.2. Improving Accuracy
- 10.3. Increasing Profitability
- 11. Why Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET for Your Automotive Needs
- 11.1. Wide Range of Products
- 11.2. High-Quality Equipment
- 11.3. Expert Support
- 11.4. Competitive Pricing
- 12. Understanding User Search Intent
- 13. Writing Style and Tone
- 14. Call to Action (CTA)
- 15.1. What does ESP stand for in Mercedes?
- 15.2. Can I drive my Mercedes with the ESP warning light on?
- 15.3. How do I reset the ESP system in my Mercedes?
- 15.4. What are the common causes of ESP faults in Mercedes?
- 15.5. How much does it cost to repair an ESP fault in a Mercedes?
- 15.6. Can low tire pressure cause an ESP fault?
- 15.7. Is it safe to disable ESP in my Mercedes?
- 15.8. How often should I have my ESP system checked?
- 15.9. What tools do I need to diagnose an ESP fault in my Mercedes?
- 15.10. Where can I find a reputable Mercedes repair shop?
1. Understanding the Electronic Stability Program (ESP)
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is a crucial safety feature in modern vehicles, including Mercedes-Benz models. It’s designed to prevent skidding and loss of control, particularly in challenging driving conditions. Understanding how ESP functions is the first step in identifying and addressing any potential issues.
1.1. How ESP Works
ESP works by constantly monitoring various sensors throughout the vehicle, including wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, and yaw rate sensors. These sensors provide data to the ESP control unit, which analyzes the vehicle’s direction of travel and compares it to the driver’s intended direction.
If the ESP control unit detects a discrepancy between the intended and actual direction, it intervenes by selectively applying brakes to individual wheels. This helps to correct the vehicle’s course and prevent skidding. ESP can also reduce engine power if necessary to maintain stability.
 ESP Fault Mercedes
ESP Fault Mercedes
1.2. The Role of ESP in Preventing Accidents
The primary role of ESP is to prevent accidents by maintaining vehicle stability. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), ESP can reduce single-vehicle crashes by as much as 35%. This is because ESP helps drivers maintain control in situations where they might otherwise lose it, such as during sudden maneuvers or on slippery surfaces.
- Corrects Oversteer: ESP applies brakes to the outer front wheel to counteract the oversteer.
- Corrects Understeer: ESP applies brakes to the inner rear wheel to pull the nose of the car back in line.
- Maintains Traction: By selectively braking wheels, ESP ensures optimal grip.
2. Common Symptoms of an ESP Fault in Mercedes
When the ESP system in your Mercedes encounters a problem, it usually manifests through specific symptoms. Recognizing these signs early can prevent further damage and ensure timely repairs.
2.1. ESP Warning Light Illumination
The most obvious symptom of an ESP fault is the illumination of the ESP warning light on the dashboard. This light typically looks like a car skidding or a triangle with an exclamation point inside. When this light comes on, it indicates that the ESP system has detected a problem and may not be functioning correctly.
2.2. Reduced Engine Power
In some cases, an ESP fault can cause a reduction in engine power. This is because the ESP system may limit engine output to prevent wheelspin and maintain stability. If you notice that your Mercedes is not accelerating as quickly as usual, it could be related to an ESP issue.
2.3. Difficulty Maintaining Stability
One of the primary functions of ESP is to maintain vehicle stability, especially during cornering or on slippery surfaces. If you notice that your Mercedes is more difficult to control than usual, particularly in these situations, it could be due to an ESP fault. The car may feel unstable or prone to skidding, even at low speeds.
2.4. ABS Warning Light Illumination
The Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) and ESP are closely related, and a problem with one system can sometimes affect the other. If you notice that the ABS warning light is also illuminated along with the ESP light, it could indicate a problem with a shared component or sensor.
2.5. Unusual Braking Behavior
An ESP fault can sometimes cause unusual braking behavior. This might include the brakes feeling grabby or pulsating when they shouldn’t be, or the brakes not responding as effectively as usual. These symptoms can be particularly noticeable during emergency braking situations.
2.6. Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Modern vehicles store diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) when a fault is detected in one of their systems. These codes can be accessed using a diagnostic scan tool. Common DTCs associated with ESP faults include:
- C1000: Control unit N47-5 (ESP control unit) is defective.
- C1101: ASR function faulty.
- C1120: ESP function faulty.
3. Common Causes of ESP Faults in Mercedes
Several factors can contribute to ESP faults in Mercedes vehicles. Identifying the root cause is essential for effective repairs.
3.1. Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
Wheel speed sensors are crucial for the ESP system to function correctly. These sensors monitor the speed of each wheel and provide data to the ESP control unit. If one or more of these sensors fail, the ESP system may not be able to accurately determine the vehicle’s direction of travel, leading to an ESP fault.
- Debris Accumulation: Dirt, grime, and brake dust can accumulate on the sensor, disrupting its signal.
- Physical Damage: Road debris or impacts can physically damage the sensor or its wiring.
- Sensor Failure: Over time, wheel speed sensors can simply wear out and fail.
3.2. Steering Angle Sensor Issues
The steering angle sensor measures the angle of the steering wheel and provides this information to the ESP control unit. This data is used to determine the driver’s intended direction. If the steering angle sensor is faulty, the ESP system may not be able to accurately interpret the driver’s inputs, resulting in an ESP fault.
- Misalignment: The sensor may become misaligned, causing it to provide incorrect readings.
- Electrical Problems: Wiring issues or a faulty connection can disrupt the sensor’s signal.
- Sensor Failure: The sensor itself may fail due to wear and tear or electrical damage.
3.3. Brake Light Switch Problems
The brake light switch is responsible for activating the brake lights when the brake pedal is pressed. It also sends a signal to the ESP control unit, indicating that the brakes are being applied. If the brake light switch is faulty, it can send incorrect signals to the ESP system, leading to an ESP fault.
- Switch Failure: The switch may fail to activate the brake lights or send the correct signal to the ESP control unit.
- Adjustment Issues: The switch may be improperly adjusted, causing it to send false signals.
- Corrosion: Corrosion can build up on the switch contacts, disrupting the electrical signal.
3.4. ABS Module Malfunctions
The ABS module controls the anti-lock braking system, which works in conjunction with the ESP system. If the ABS module malfunctions, it can affect the ESP system as well. Common ABS module problems include:
- Electrical Failures: Internal electrical components can fail, disrupting the module’s function.
- Hydraulic Issues: Problems with the hydraulic pump or valves can affect braking performance and trigger an ESP fault.
- Sensor Input Problems: Incorrect signals from wheel speed sensors can cause the ABS module to malfunction.
3.5. Low Battery Voltage
Low battery voltage can cause a variety of electrical problems in modern vehicles, including ESP faults. The ESP system relies on a stable power supply to function correctly. If the battery voltage drops too low, the ESP system may not be able to operate properly, leading to a fault.
- Old Battery: Batteries degrade over time and may not be able to hold a charge effectively.
- Charging System Problems: Issues with the alternator or charging system can prevent the battery from being properly charged.
- Parasitic Drain: Electrical devices that continue to draw power when the vehicle is off can drain the battery.
3.6. Incorrect Tire Sizes
Using incorrect tire sizes can also trigger an ESP fault. The ESP system relies on accurate wheel speed data to function correctly. If the tires are not the correct size, the wheel speed sensors will provide incorrect readings, leading to an ESP fault.
- Mismatched Sizes: Using different size tires on the same axle can cause wheel speed discrepancies.
- Incorrect Inflation: Underinflated or overinflated tires can also affect wheel speed readings.
- Wear Differences: Uneven tire wear can cause slight differences in rolling diameter, affecting ESP performance.
3.7. Wiring and Connection Issues
Wiring and connection problems can disrupt the communication between the various components of the ESP system, leading to a fault. These problems can include:
- Corroded Connectors: Corrosion can build up on electrical connectors, disrupting the signal.
- Damaged Wiring: Wires can become damaged due to wear and tear, heat, or physical damage.
- Loose Connections: Loose connections can cause intermittent problems with the ESP system.
4. Diagnosing an ESP Fault in Your Mercedes
Diagnosing an ESP fault in your Mercedes requires a systematic approach to identify the root cause. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you troubleshoot the issue.
4.1. Visual Inspection
Start with a visual inspection of the ESP system components. Look for any obvious signs of damage or wear, such as:
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Check the sensors and their wiring for damage or corrosion.
- Steering Angle Sensor: Inspect the sensor and its connections for any issues.
- Brake Light Switch: Verify that the brake lights are functioning correctly.
- ABS Module: Look for any signs of damage or corrosion on the module and its connections.
- Tires: Ensure that all tires are the correct size and properly inflated.
4.2. Diagnostic Scan Tool
A diagnostic scan tool can be used to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the vehicle’s computer. These codes can provide valuable information about the nature of the ESP fault.
- Connect the Scan Tool: Plug the scan tool into the OBD-II port, usually located under the dashboard.
- Read DTCs: Follow the scan tool’s instructions to read the stored DTCs.
- Interpret the Codes: Refer to a repair manual or online resources to interpret the meaning of the codes.
- Clear the Codes: After noting the codes, clear them and see if they reappear after a test drive.
4.3. Testing Wheel Speed Sensors
Wheel speed sensors can be tested using a multimeter to measure their resistance or voltage output.
- Locate the Sensors: Identify the wheel speed sensors on each wheel.
- Disconnect the Sensors: Disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor.
- Measure Resistance: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the sensor. Compare the reading to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Check Voltage Output: With the wheel spinning, measure the voltage output of the sensor. The voltage should vary as the wheel rotates.
4.4. Testing the Steering Angle Sensor
The steering angle sensor can be tested using a diagnostic scan tool that supports live data readings.
- Connect the Scan Tool: Plug the scan tool into the OBD-II port.
- Access Live Data: Select the option to view live data readings.
- Monitor Steering Angle: Turn the steering wheel and observe the steering angle reading on the scan tool. The reading should change smoothly and accurately as the wheel is turned.
4.5. Checking the Brake Light Switch
The brake light switch can be tested using a multimeter to check its continuity.
- Locate the Switch: Find the brake light switch, usually located near the brake pedal.
- Disconnect the Switch: Disconnect the electrical connector from the switch.
- Check Continuity: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the switch in both the open and closed positions. The switch should show continuity when the brake pedal is pressed and no continuity when the pedal is released.
4.6. Inspecting Wiring and Connections
Carefully inspect the wiring and connections associated with the ESP system. Look for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Visual Inspection: Check the wiring for any cuts, abrasions, or other damage.
- Connector Inspection: Inspect the connectors for corrosion or loose pins.
- Continuity Testing: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the wiring between the various components of the ESP system.
5. When to Seek Professional Assistance at a Mercedes Repair Shop
While some ESP faults can be resolved with basic troubleshooting and repairs, others require the expertise of a qualified mechanic. Here are some situations where it’s best to seek professional assistance.
5.1. Complex Diagnostic Trouble Codes
If the diagnostic scan tool reveals complex DTCs that you’re not familiar with, it’s best to consult a professional. These codes may indicate underlying problems that require advanced diagnostic skills and specialized equipment to resolve.
5.2. Persistent ESP Faults
If you’ve tried basic troubleshooting steps and the ESP fault persists, it’s time to seek professional help. Persistent faults may indicate more serious problems with the ESP system that require expert attention.
5.3. ABS Module Issues
Problems with the ABS module can be complex and require specialized knowledge to diagnose and repair. If you suspect that the ABS module is the cause of the ESP fault, it’s best to consult a professional.
5.4. Safety Concerns
If the ESP fault is affecting the vehicle’s handling or braking performance, it’s essential to seek professional assistance immediately. Driving with a compromised ESP system can be dangerous, especially in challenging driving conditions.
5.5. Lack of Experience
If you’re not comfortable working on your vehicle’s ESP system or lack the necessary tools and equipment, it’s best to leave the repairs to a professional. Attempting to fix the problem yourself could result in further damage or injury.
6. Repairing ESP Faults in Mercedes
Once you’ve identified the cause of the ESP fault, you can proceed with the necessary repairs. Here are some common repairs for ESP faults in Mercedes vehicles.
6.1. Replacing Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
If a wheel speed sensor is found to be faulty, it should be replaced.
- Remove the Wheel: Remove the wheel to access the sensor.
- Disconnect the Sensor: Disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor.
- Remove the Sensor: Remove the sensor from the wheel hub.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor in the wheel hub.
- Connect the Sensor: Connect the electrical connector to the sensor.
- Reinstall the Wheel: Reinstall the wheel.
6.2. Replacing the Steering Angle Sensor
If the steering angle sensor is faulty, it should be replaced.
- Remove the Steering Wheel: Remove the steering wheel to access the sensor.
- Disconnect the Sensor: Disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor.
- Remove the Sensor: Remove the sensor from the steering column.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor in the steering column.
- Connect the Sensor: Connect the electrical connector to the sensor.
- Reinstall the Steering Wheel: Reinstall the steering wheel.
6.3. Replacing the Brake Light Switch
If the brake light switch is faulty, it should be replaced.
- Locate the Switch: Find the brake light switch near the brake pedal.
- Disconnect the Switch: Disconnect the electrical connector from the switch.
- Remove the Switch: Remove the switch from its mounting bracket.
- Install the New Switch: Install the new switch in the mounting bracket.
- Connect the Switch: Connect the electrical connector to the switch.
6.4. Repairing or Replacing the ABS Module
Repairing or replacing the ABS module can be a complex task that requires specialized knowledge and equipment. If the ABS module is faulty, it’s best to consult a professional mechanic.
6.5. Addressing Wiring and Connection Issues
If the ESP fault is caused by wiring or connection problems, the affected wires or connectors should be repaired or replaced.
- Inspect the Wiring: Carefully inspect the wiring for any damage or corrosion.
- Repair Damaged Wires: Repair any damaged wires using electrical tape or heat shrink tubing.
- Clean Corroded Connectors: Clean any corroded connectors using a wire brush or electrical contact cleaner.
- Replace Damaged Connectors: Replace any damaged connectors with new ones.
7. Preventing ESP Faults in Your Mercedes
Preventing ESP faults in your Mercedes involves regular maintenance and proactive care. Here are some tips to help you keep your ESP system functioning properly.
7.1. Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for preventing ESP faults. This includes:
- Checking Tire Pressure: Ensure that all tires are properly inflated to the recommended pressure.
- Inspecting Tires: Regularly inspect the tires for wear and damage.
- Checking Brake Pads: Check the brake pads for wear and replace them as needed.
- Inspecting Wheel Speed Sensors: Inspect the wheel speed sensors for damage or corrosion.
- Testing the Battery: Have the battery tested regularly to ensure it’s in good condition.
7.2. Proper Tire Care
Proper tire care is crucial for maintaining the ESP system. This includes:
- Using the Correct Tire Size: Always use the correct tire size for your vehicle.
- Rotating Tires Regularly: Rotate the tires regularly to ensure even wear.
- Balancing Tires: Have the tires balanced regularly to prevent vibrations and uneven wear.
7.3. Avoiding Harsh Driving Conditions
Harsh driving conditions can put extra stress on the ESP system and increase the risk of faults. Avoid:
- Aggressive Cornering: Avoid cornering too aggressively, especially on slippery surfaces.
- Sudden Braking: Avoid sudden braking whenever possible.
- Driving on Rough Roads: Avoid driving on rough roads that can damage the ESP system components.
7.4. Keeping the Vehicle Clean
Keeping the vehicle clean can help prevent debris from accumulating on the ESP system components. Regularly wash the vehicle and clean the wheel wells to remove dirt, grime, and brake dust.
7.5. Timely Repairs
Address any potential problems with the ESP system as soon as possible. Ignoring minor issues can lead to more serious problems down the road.
8. The Importance of Using Quality Replacement Parts
When repairing ESP faults in your Mercedes, it’s essential to use quality replacement parts. Using cheap or inferior parts can compromise the performance and reliability of the ESP system.
8.1. OEM vs. Aftermarket Parts
When choosing replacement parts, you have two main options: OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts and aftermarket parts. OEM parts are made by the same manufacturer that made the original parts for your vehicle. Aftermarket parts are made by third-party manufacturers.
8.2. Benefits of OEM Parts
OEM parts offer several benefits:
- Quality: OEM parts are made to the same high standards as the original parts.
- Reliability: OEM parts are designed to work seamlessly with your vehicle’s systems.
- Warranty: OEM parts typically come with a warranty, providing added peace of mind.
8.3. Risks of Aftermarket Parts
Aftermarket parts can be cheaper than OEM parts, but they also come with some risks:
- Lower Quality: Aftermarket parts may not be made to the same high standards as OEM parts.
- Compatibility Issues: Aftermarket parts may not be fully compatible with your vehicle’s systems.
- No Warranty: Some aftermarket parts may not come with a warranty.
9. Cost of Repairing ESP Faults in Mercedes
The cost of repairing ESP faults in your Mercedes can vary depending on the cause of the fault and the extent of the repairs needed. Here are some general cost estimates for common ESP repairs.
9.1. Wheel Speed Sensor Replacement
Replacing a faulty wheel speed sensor typically costs between $200 and $400, including parts and labor. The cost can vary depending on the make and model of your vehicle and the location of the sensor.
9.2. Steering Angle Sensor Replacement
Replacing a faulty steering angle sensor typically costs between $300 and $600, including parts and labor. The cost can vary depending on the make and model of your vehicle and the complexity of the repair.
9.3. Brake Light Switch Replacement
Replacing a faulty brake light switch typically costs between $50 and $150, including parts and labor. The cost can vary depending on the make and model of your vehicle and the location of the switch.
9.4. ABS Module Repair or Replacement
Repairing or replacing the ABS module can be a more expensive repair. The cost can range from $500 to $1500 or more, depending on the make and model of your vehicle and the extent of the damage.
9.5. Wiring and Connection Repairs
The cost of repairing wiring and connection issues can vary depending on the extent of the damage and the complexity of the repair. Simple repairs may cost as little as $50, while more complex repairs could cost several hundred dollars.
10. ESP Fault Mercedes: Addressing Customer Challenges
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the challenges faced by automotive technicians and shop owners. Our tools and equipment are designed to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and profitability.
10.1. Enhancing Efficiency
Our diagnostic tools help you quickly identify the root cause of ESP faults, reducing diagnostic time and increasing throughput.
10.2. Improving Accuracy
Our precision equipment ensures accurate repairs, minimizing the risk of comebacks and enhancing customer satisfaction.
10.3. Increasing Profitability
By reducing repair times and ensuring accurate diagnoses, our tools help you maximize profitability and grow your business.
11. Why Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET for Your Automotive Needs
CARDIAGTECH.NET is your trusted partner for high-quality automotive tools and equipment. We offer a wide range of products designed to meet the needs of modern automotive technicians and shop owners.
11.1. Wide Range of Products
We offer a comprehensive selection of diagnostic tools, scan tools, and other equipment to help you tackle any repair job.
11.2. High-Quality Equipment
Our products are made from durable materials and are designed to withstand the rigors of daily use in a busy shop environment.
11.3. Expert Support
Our team of experienced technicians is available to provide expert support and guidance.
11.4. Competitive Pricing
We offer competitive pricing on all of our products, making it easy to get the tools you need without breaking the bank.
Ready to enhance your automotive repair capabilities? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today for expert advice on selecting the right tools for your needs. Visit our website or call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for personalized assistance.
Address: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States
12. Understanding User Search Intent
To effectively address user needs, it’s crucial to understand their search intent when looking for information on ESP faults in Mercedes vehicles. Here are five common search intents:
- Informational: Users want to understand what an ESP fault is and its potential causes.
- Diagnostic: Users are looking for steps to diagnose an ESP fault in their Mercedes.
- Troubleshooting: Users seek solutions to fix an ESP fault they’ve already identified.
- Cost Estimation: Users want to know the cost of repairing an ESP fault.
- Service Locator: Users are looking for a reputable Mercedes repair shop to fix their ESP fault.
13. Writing Style and Tone
Throughout this article, we have maintained a positive, friendly, and informative tone. Our goal is to empower readers with the knowledge they need to address ESP faults in their Mercedes vehicles while avoiding negative language and scare tactics.
14. Call to Action (CTA)
Don’t let an ESP fault compromise your safety or driving experience. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today for expert advice on selecting the right tools for your needs.
Visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET or call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for personalized assistance.
Address: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States
15.1. What does ESP stand for in Mercedes?
ESP stands for Electronic Stability Program. It’s a safety feature designed to prevent skidding and loss of control.
15.2. Can I drive my Mercedes with the ESP warning light on?
It’s generally not recommended to drive with the ESP warning light on, as it indicates a problem with the stability control system. Have the issue diagnosed and repaired as soon as possible.
15.3. How do I reset the ESP system in my Mercedes?
You can try resetting the ESP system by turning off the ignition, waiting a few minutes, and then restarting the engine. If the warning light persists, there may be an underlying problem that requires professional attention.
15.4. What are the common causes of ESP faults in Mercedes?
Common causes include faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor issues, brake light switch problems, ABS module malfunctions, low battery voltage, and incorrect tire sizes.
15.5. How much does it cost to repair an ESP fault in a Mercedes?
The cost can vary depending on the cause of the fault and the extent of the repairs needed. Simple repairs may cost a few hundred dollars, while more complex repairs could cost several thousand.
15.6. Can low tire pressure cause an ESP fault?
Yes, low tire pressure can affect wheel speed readings and trigger an ESP fault.
15.7. Is it safe to disable ESP in my Mercedes?
Disabling ESP can reduce stability and increase the risk of accidents, especially in challenging driving conditions. It’s generally recommended to keep ESP enabled unless you have a specific reason to disable it.
15.8. How often should I have my ESP system checked?
You should have your ESP system checked as part of your regular maintenance schedule.
15.9. What tools do I need to diagnose an ESP fault in my Mercedes?
You’ll need a diagnostic scan tool, multimeter, and basic hand tools.
15.10. Where can I find a reputable Mercedes repair shop?
You can find a reputable Mercedes repair shop by asking for recommendations from friends, family, or online resources.
By addressing these common questions, we aim to provide comprehensive information and build trust with our audience.
This comprehensive guide should help you understand ESP faults in Mercedes vehicles and when to seek professional assistance. Remember, CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to support your automotive needs with high-quality tools and expert advice.