Experiencing an ABS ESP inoperative warning on your Mercedes Benz can be alarming, but it’s a sign that crucial safety systems need attention. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we provide the diagnostic tools and expertise to pinpoint the problem and restore your vehicle’s stability control. Don’t compromise on safety; explore our range of automotive diagnostic equipment for Mercedes Benz, including ABS sensors, ESP modules, and steering angle sensors, to get your car back on the road with confidence.
Contents
- 1. Understanding ABS, ESP, and Their Importance
- 2. Decoding the “ABS ESP Inoperative” Warning
- 3. Common Causes of ABS/ESP Malfunctions in Mercedes Benz
- 4. Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
- 5. Diagnostic Tools for Mercedes Benz ABS/ESP Issues
- 6. The Role of Wheel Speed Sensors
- 7. Steering Angle Sensor Calibration: Why It Matters
- 8. ABS Module and Hydraulic Unit: In-Depth Look
- 9. Diagnosing Low Battery Voltage Impact
- 10. The Impact of Damaged Wiring and Connectors
- 11. Software and Calibration Errors Explained
- 12. Aftermarket Modifications: Compatibility Considerations
- 13. Driving Safety: What to Do When the Warning Appears
- 14. Preventative Maintenance Tips
- 15. Case Studies: Real-World Examples
- Case Study 1: Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
- Case Study 2: Steering Angle Sensor Calibration
- Case Study 3: Low Battery Voltage
- 16. The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET in Solving ABS/ESP Problems
- 17. ABS/ESP System Components: A Detailed Table
- 18. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
- 19. The Future of ABS/ESP Technology
- 20. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 21. ABS/ESP System Reset Procedures
- 22. Navigating Mercedes Benz Forums and Communities
- 23. The Importance of Using Genuine Mercedes Benz Parts
- 24. Potential Costs of ABS/ESP Repairs
- 25. Exploring DIY Repair Options
- 26. When to Seek Professional Help
- 27. Understanding ABS/ESP Warning Light Colors
- 28. Mercedes Benz ABS/ESP Recall Information
- 29. Tips for Finding a Reputable Repair Shop
- 30. Long-Term Maintenance Strategies
- 31. Using Mercedes Diagnostic Software
- 32. Understanding Related Systems: BAS, ASR, and 4-ETS
- 33. Staying Informed: Mercedes Benz Technical Bulletins
- 34. Addressing Common Misconceptions
- 35. The Human Factor: Driver Skills and Training
- 36. Exploring Legal and Insurance Implications
- 37. Innovations in ABS/ESP Materials and Design
- 38. Maximizing Vehicle Resale Value
- 39. ABS/ESP and Vehicle Inspection Requirements
- 40. Get Expert Help from CARDIAGTECH.NET
1. Understanding ABS, ESP, and Their Importance
The Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) and Electronic Stability Program (ESP) are vital safety features in modern vehicles, particularly Mercedes Benz models. ABS prevents wheel lock-up during braking, allowing you to maintain steering control, while ESP helps prevent skidding and loss of control, especially on slippery surfaces or during sudden maneuvers. Understanding how these systems work is crucial to diagnosing and resolving any issues.
- ABS (Anti-lock Braking System): Prevents wheel lock-up during hard braking, enabling steering control.
- ESP (Electronic Stability Program): Detects and prevents skidding by selectively applying brakes to individual wheels.
- Interdependence: Both systems rely on sensors and electronic control units to function correctly.
- Safety Enhancement: They significantly enhance vehicle safety by maintaining stability and control in challenging driving conditions.
2. Decoding the “ABS ESP Inoperative” Warning
When your Mercedes Benz displays the “ABS ESP inoperative” warning message, it signifies that one or both of these systems are not functioning as intended. This warning should not be ignored, as it indicates a potential compromise in your vehicle’s safety and stability.
- Warning Indication: The message signals a malfunction in the ABS or ESP systems.
- Safety Implications: Reduced ability to control the vehicle during braking or in slippery conditions.
- Diagnostic Importance: Requires prompt diagnosis to identify the root cause and prevent further issues.
 Mercedes-Benz C-Class Dashboard with ABS ESP Warning
Mercedes-Benz C-Class Dashboard with ABS ESP Warning
3. Common Causes of ABS/ESP Malfunctions in Mercedes Benz
Several factors can trigger the “ABS ESP inoperative” warning in a Mercedes Benz. Identifying the specific cause is the first step toward resolving the issue.
- Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors:
- Function: These sensors monitor the rotational speed of each wheel.
- Malfunction Symptoms: Inaccurate readings, leading to ABS/ESP system deactivation.
- Impact: Reduced braking and stability control.
- Steering Angle Sensor Issues:
- Function: Measures the position and rate of steering wheel movement.
- Malfunction Symptoms: Incorrect data sent to the ESP module, disabling the system.
- Impact: Impaired ability of the ESP to determine the intended direction.
- Yaw Rate Sensor Malfunction:
- Function: Measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis.
- Malfunction Symptoms: Erroneous readings, disrupting ESP functionality.
- Impact: ESP system unable to accurately detect and correct skidding.
- Brake System Problems:
- Function: Critical for both ABS and ESP to operate correctly.
- Malfunction Symptoms: Faulty brake pressure sensors or issues with the ABS module.
- Impact: ABS and ESP systems may fail to engage during emergency braking or loss of traction.
- Low Battery Voltage:
- Function: Provides power to all electronic components, including ABS and ESP.
- Malfunction Symptoms: Insufficient voltage can cause electronic systems to malfunction.
- Impact: Intermittent or complete failure of ABS and ESP systems.
- Damaged Wiring or Connectors:
- Function: Facilitate communication between the sensors, control units, and actuators.
- Malfunction Symptoms: Corroded or damaged connections can interrupt signal transmission.
- Impact: Loss of communication between ABS/ESP components.
- Software or Calibration Errors:
- Function: Software ensures all components operate in sync.
- Malfunction Symptoms: Errors in the software or incorrect calibration can cause system failures.
- Impact: ABS and ESP systems may not function as programmed.
- Faulty Hydraulic Unit:
- Function: Controls the brake pressure to each wheel.
- Malfunction Symptoms: Issues with the hydraulic control unit can trigger the warning.
- Impact: Inability to modulate brake pressure during ABS/ESP activation.
- Aftermarket Modifications:
- Function: Compatibility with original vehicle systems.
- Malfunction Symptoms: Non-compatible wheels, tires, or suspension components can interfere with ESP.
- Impact: ABS and ESP systems may not function correctly due to altered vehicle dynamics.
4. Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
Before seeking professional help, you can perform some basic troubleshooting steps to identify the potential cause of the “ABS ESP inoperative” warning.
- Visual Inspection:
- Step: Check for any visible damage to wheel speed sensors, wiring, and connectors.
- Objective: Identify obvious physical issues.
- Battery Voltage Check:
- Step: Use a multimeter to measure the battery voltage. It should be around 12.6 volts when the engine is off.
- Objective: Rule out low voltage as a potential cause.
- OBD-II Scanner Diagnostics:
- Step: Use an OBD-II scanner to read the error codes.
- Objective: Identify the specific component or system causing the issue.
- Wheel Speed Sensor Test:
- Step: Use a multimeter to check the resistance of each wheel speed sensor.
- Objective: Determine if any sensor is faulty.
- Steering Angle Sensor Calibration:
- Step: Use a diagnostic tool to recalibrate the steering angle sensor.
- Objective: Correct any misalignment issues.
- Brake Fluid Level Check:
- Step: Ensure the brake fluid level is within the recommended range.
- Objective: Low brake fluid can affect the braking system’s performance.
5. Diagnostic Tools for Mercedes Benz ABS/ESP Issues
Accurate diagnosis of ABS/ESP problems in Mercedes Benz vehicles often requires specialized diagnostic tools. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of high-quality tools to assist technicians and DIY enthusiasts.
- Mercedes-Specific OBD-II Scanners: Designed to read and interpret Mercedes-specific error codes.
- ABS Sensor Testers: Devices that test the functionality of wheel speed sensors.
- Steering Angle Sensor Calibration Tools: Tools used to calibrate the steering angle sensor after replacement or adjustment.
- MultiMeters: For checking voltages and resistances in the electrical system.
- Hydraulic Pressure Testers: Tools used to measure the brake fluid pressure in the hydraulic system.
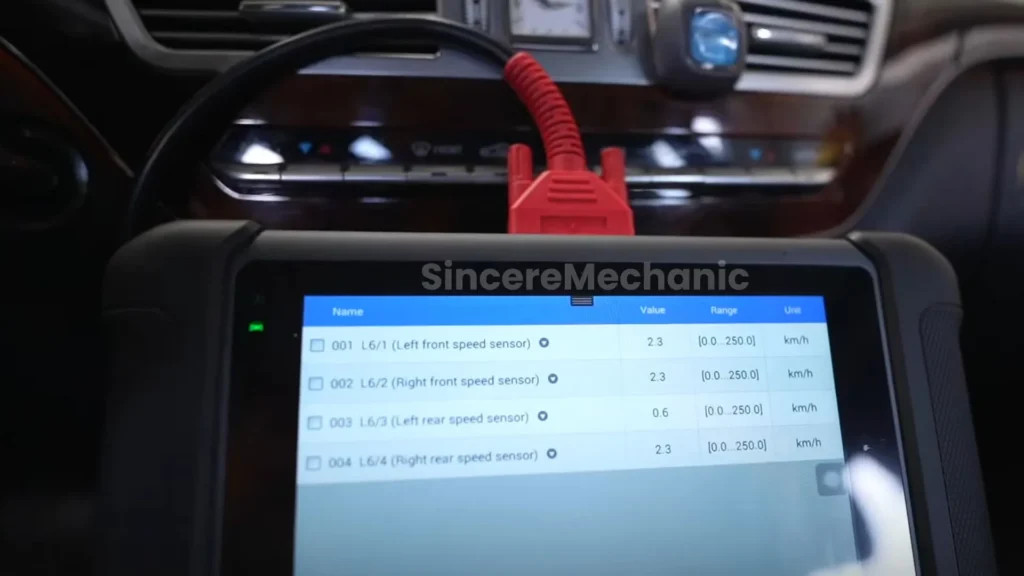
6. The Role of Wheel Speed Sensors
Wheel speed sensors are critical components of both the ABS and ESP systems. They provide real-time data on the rotational speed of each wheel, which is used to determine if a wheel is about to lock up or if the vehicle is skidding.
- Functionality: Measure the rotational speed of each wheel.
- Importance: Provide essential data for ABS and ESP systems to function correctly.
- Troubleshooting: Faulty sensors can cause inaccurate readings, leading to system deactivation.
 Wheel Speed Sensor
Wheel Speed Sensor
7. Steering Angle Sensor Calibration: Why It Matters
The steering angle sensor provides information about the steering wheel’s position to the ESP module. Proper calibration of this sensor is essential for the ESP system to function correctly.
- Functionality: Measures the steering wheel’s position.
- Importance: Essential for ESP to determine the intended direction of the vehicle.
- Calibration: Required after replacement or adjustment to ensure accurate readings.
8. ABS Module and Hydraulic Unit: In-Depth Look
The ABS module and hydraulic unit work together to control the brake pressure to each wheel during ABS activation. Problems with either of these components can lead to ABS/ESP malfunctions.
- ABS Module: Electronic control unit that processes data from sensors and controls the hydraulic unit.
- Hydraulic Unit: Modulates brake pressure to each wheel based on signals from the ABS module.
- Troubleshooting: Issues with either component can disrupt ABS and ESP functionality.
9. Diagnosing Low Battery Voltage Impact
Low battery voltage can cause a wide range of electrical issues in modern vehicles, including ABS/ESP malfunctions. Ensuring your battery is in good condition is vital for the proper functioning of these safety systems.
- Impact: Insufficient voltage can cause electronic systems to malfunction.
- Testing: Use a multimeter to check the battery voltage.
- Maintenance: Regular battery maintenance can prevent voltage-related issues.
10. The Impact of Damaged Wiring and Connectors
Damaged or corroded wiring and connectors can disrupt the communication between the various components of the ABS and ESP systems, leading to malfunctions.
- Importance: Wiring and connectors facilitate communication between sensors, control units, and actuators.
- Troubleshooting: Inspect for corrosion, damage, and loose connections.
- Maintenance: Regular inspection and maintenance can prevent communication issues.
11. Software and Calibration Errors Explained
Software and calibration errors can occur due to various reasons, such as software updates or incorrect programming. These errors can cause the ABS and ESP systems to malfunction.
- Causes: Software updates, incorrect programming.
- Troubleshooting: Requires specialized diagnostic tools to identify and correct.
- Solutions: Software updates, recalibration.
12. Aftermarket Modifications: Compatibility Considerations
Modifying your Mercedes Benz with aftermarket parts can sometimes interfere with the proper functioning of the ABS and ESP systems.
- Impact: Non-compatible wheels, tires, or suspension components can interfere with ESP.
- Considerations: Ensure all aftermarket parts are compatible with the vehicle’s safety systems.
- Recommendations: Consult with a professional before making modifications.
13. Driving Safety: What to Do When the Warning Appears
If the “ABS ESP inoperative” warning appears while driving, it is essential to take appropriate safety measures.
- Action: Reduce speed and drive cautiously.
- Recommendation: Avoid sudden braking or sharp turns.
- Next Steps: Have the vehicle inspected by a qualified technician as soon as possible.
14. Preventative Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance can help prevent ABS/ESP malfunctions and ensure the safety of your Mercedes Benz.
- Regular Inspections: Inspect wheel speed sensors, wiring, and connectors regularly.
- Battery Maintenance: Ensure the battery is in good condition.
- Brake Fluid Checks: Monitor brake fluid levels and replace as needed.
- Professional Servicing: Have the ABS and ESP systems serviced by a qualified technician.
15. Case Studies: Real-World Examples
Examining real-world case studies can provide valuable insights into diagnosing and resolving ABS/ESP issues.
Case Study 1: Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
- Vehicle: Mercedes-Benz C-Class
- Issue: “ABS ESP inoperative” warning.
- Diagnosis: Faulty wheel speed sensor.
- Solution: Replacement of the defective sensor.
Case Study 2: Steering Angle Sensor Calibration
- Vehicle: Mercedes-Benz E-Class
- Issue: “ABS ESP inoperative” warning after suspension work.
- Diagnosis: Steering angle sensor needed recalibration.
- Solution: Recalibration using a diagnostic tool.
Case Study 3: Low Battery Voltage
- Vehicle: Mercedes-Benz S-Class
- Issue: Intermittent “ABS ESP inoperative” warning.
- Diagnosis: Low battery voltage.
- Solution: Battery replacement.
16. The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET in Solving ABS/ESP Problems
CARDIAGTECH.NET is your trusted partner in diagnosing and resolving ABS/ESP issues in Mercedes Benz vehicles. We offer a wide range of diagnostic tools, replacement parts, and expert advice to help you get your vehicle back on the road safely.
- Diagnostic Tools: High-quality Mercedes-specific OBD-II scanners and sensor testers.
- Replacement Parts: Genuine and aftermarket wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, and ABS modules.
- Expert Advice: Experienced technicians available to provide guidance and support.
17. ABS/ESP System Components: A Detailed Table
| Component | Function | Common Issues |
|---|---|---|
| Wheel Speed Sensors | Monitor rotational speed of each wheel | Faulty readings, damage |
| Steering Angle Sensor | Measures steering wheel position | Miscalibration, failure |
| Yaw Rate Sensor | Measures vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis | Inaccurate readings, malfunction |
| ABS Module | Electronic control unit for ABS | Electrical failure, software errors |
| Hydraulic Unit | Controls brake pressure to each wheel during ABS activation | Leaks, valve failures |
| Wiring and Connectors | Facilitate communication between components | Corrosion, damage |
| Battery | Provides power to electronic components | Low voltage, failure |
| Brake Fluid | Transfers pressure in the braking system | Contamination, low level |
| Brake Pads and Rotors | Provide the friction needed to stop the vehicle | Wear and tear, damage |
| ESP Module | Electronic control unit for ESP | Electrical failure, software errors |
| Throttle Position Sensor | Monitors the position of the throttle | Incorrect data, corrosion |
| Crankshaft Position Sensor | Monitors the position and rotational speed of the crankshaft | Electrical failure, damage |
| Mass Airflow Sensor | Measures the mass of air entering the engine | Electrical failure, deposits, incorrect readings |
| Camshaft Position Sensor | Senses the position of the camshaft in an internal combustion engine | Electrical failure, oil contamination, incorrect readings |
18. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
For complex ABS/ESP issues, advanced diagnostic techniques may be required.
- Oscilloscope Testing: Analyzing sensor signals to identify anomalies.
- Data Logging: Recording sensor data during test drives to identify intermittent issues.
- Component Testing: Testing individual components to determine their functionality.
19. The Future of ABS/ESP Technology
ABS and ESP technologies are continuously evolving to improve vehicle safety and performance.
- Advancements: Integration with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
- Future Trends: Enhanced sensors, more sophisticated control algorithms.
- Benefits: Improved stability, reduced accident risk.
20. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are codes stored by the vehicle’s computer when a problem is detected. Understanding these codes can help you pinpoint the source of the ABS/ESP issue.
- Importance: DTCs provide valuable information about the nature of the problem.
- Reading DTCs: Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the codes.
- Interpreting DTCs: Refer to the vehicle’s service manual or online resources to understand the meaning of each code.
21. ABS/ESP System Reset Procedures
In some cases, resetting the ABS/ESP system can resolve certain issues.
- Battery Disconnect: Disconnecting the battery for a few minutes can reset the system.
- OBD-II Scanner Reset: Some OBD-II scanners have the capability to reset the ABS/ESP system.
- Professional Reset: A qualified technician can perform a system reset using specialized diagnostic equipment.
22. Navigating Mercedes Benz Forums and Communities
Online forums and communities can be valuable resources for troubleshooting ABS/ESP issues.
- Benefits: Sharing experiences, seeking advice from other owners, accessing technical information.
- Caution: Verify the accuracy of information from online sources.
- Recommendations: Participate in reputable Mercedes Benz forums and communities.
23. The Importance of Using Genuine Mercedes Benz Parts
When replacing ABS/ESP components, using genuine Mercedes Benz parts is highly recommended.
- Quality: Genuine parts are designed and manufactured to meet the vehicle’s specifications.
- Compatibility: Ensure proper fit and function.
- Warranty: Genuine parts typically come with a warranty.
24. Potential Costs of ABS/ESP Repairs
The cost of ABS/ESP repairs can vary depending on the nature of the problem and the parts required.
- Factors: Labor costs, parts prices, diagnostic fees.
- Estimates: Obtain estimates from multiple repair shops.
- Considerations: Factor in the cost of diagnostic tools if you plan to perform the repairs yourself.
25. Exploring DIY Repair Options
Depending on your mechanical skills and experience, you may be able to perform some ABS/ESP repairs yourself.
- Simple Repairs: Replacing wheel speed sensors, checking wiring and connectors.
- Complex Repairs: ABS module replacement, hydraulic unit repairs.
- Safety Precautions: Follow safety guidelines and use appropriate tools and equipment.
26. When to Seek Professional Help
While some ABS/ESP issues can be resolved through DIY efforts, it is essential to know when to seek professional help.
- Complex Issues: ABS module failures, hydraulic unit problems.
- Safety Concerns: If you are unsure about any aspect of the repair process.
- Specialized Tools: When specialized diagnostic equipment is required.
27. Understanding ABS/ESP Warning Light Colors
The color of the ABS/ESP warning light can provide additional information about the nature of the problem.
- Yellow: Indicates a potential issue that requires attention.
- Red: Indicates a serious problem that requires immediate attention.
- Flashing: Indicates an intermittent issue.
28. Mercedes Benz ABS/ESP Recall Information
Check for any recalls related to the ABS and ESP systems in your Mercedes Benz.
- Resources: Visit the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) website.
- Information: Enter your vehicle’s VIN to check for open recalls.
- Action: Follow the recall instructions provided by Mercedes Benz.
29. Tips for Finding a Reputable Repair Shop
Finding a qualified and reputable repair shop is essential for addressing ABS/ESP issues.
- Recommendations: Seek recommendations from friends, family, or online reviews.
- Certifications: Look for shops with ASE certifications or Mercedes Benz-specific training.
- Experience: Choose a shop with experience in working on Mercedes Benz vehicles.
- Estimates: Obtain estimates from multiple shops and compare prices.
30. Long-Term Maintenance Strategies
Implementing long-term maintenance strategies can help prevent ABS/ESP issues and ensure the longevity of your Mercedes Benz.
- Regular Servicing: Adhere to the recommended maintenance schedule.
- Preventive Maintenance: Perform regular inspections and maintenance of the ABS and ESP systems.
- Component Replacement: Replace worn or damaged components promptly.
- Driving Habits: Avoid harsh braking and aggressive driving.
31. Using Mercedes Diagnostic Software
Mercedes diagnostic software provides in-depth access to your vehicle’s systems, including ABS and ESP.
- Capabilities: Read and clear diagnostic trouble codes, perform component tests, and access real-time data.
- Popular Options: Mercedes XENTRY, iCarsoft MB II.
- Benefits: Accurate diagnostics and troubleshooting.
32. Understanding Related Systems: BAS, ASR, and 4-ETS
Mercedes Benz vehicles often include related systems such as Brake Assist (BAS), Acceleration Skid Control (ASR), and Electronic Traction System (4-ETS), which work in conjunction with ABS and ESP.
- BAS (Brake Assist): Detects emergency braking and applies maximum braking force.
- ASR (Acceleration Skid Control): Prevents wheel spin during acceleration.
- 4-ETS (Electronic Traction System): Applies brakes to individual wheels to improve traction on slippery surfaces.
- Interactions: Understanding how these systems interact can aid in diagnosing ABS/ESP issues.
33. Staying Informed: Mercedes Benz Technical Bulletins
Mercedes Benz issues technical service bulletins (TSBs) to address common problems and provide updated repair procedures.
- Importance: TSBs can provide valuable information about ABS/ESP issues.
- Accessing TSBs: Visit the NHTSA website or subscribe to a Mercedes Benz technical information service.
- Benefits: Stay informed about the latest repair techniques and solutions.
34. Addressing Common Misconceptions
There are several common misconceptions about ABS and ESP systems.
- Misconception: ABS shortens stopping distances in all situations.
- Fact: ABS is most effective on slippery surfaces.
- Misconception: ESP makes the vehicle immune to skidding.
- Fact: ESP helps prevent skidding but cannot overcome the laws of physics.
- Misconception: Once ABS or ESP activates, the vehicle is in danger.
- Fact: ABS and ESP are designed to help maintain control during emergency situations.
35. The Human Factor: Driver Skills and Training
Even with advanced safety systems like ABS and ESP, driver skills and training are essential for preventing accidents.
- Importance: Proper braking techniques, steering control, and awareness of road conditions.
- Training: Consider taking a defensive driving course.
- Benefits: Improved safety and reduced risk of accidents.
36. Exploring Legal and Insurance Implications
Malfunctioning ABS and ESP systems can have legal and insurance implications.
- Legal: Operating a vehicle with known safety defects may be illegal.
- Insurance: Failure to repair known safety defects may affect insurance coverage.
- Recommendations: Maintain your vehicle in good working order and address safety issues promptly.
37. Innovations in ABS/ESP Materials and Design
Manufacturers are continually innovating ABS/ESP materials and design to improve performance and reliability.
- Materials: Lightweight alloys, advanced composites.
- Design: Compact and efficient designs.
- Benefits: Improved performance, reduced weight, increased durability.
38. Maximizing Vehicle Resale Value
Maintaining the ABS and ESP systems in good working order can help maximize your vehicle’s resale value.
- Documentation: Keep records of all maintenance and repairs.
- Disclosure: Disclose any known issues to potential buyers.
- Benefits: Increased resale value and buyer confidence.
39. ABS/ESP and Vehicle Inspection Requirements
Many jurisdictions require vehicles to pass safety inspections, which may include checking the ABS and ESP systems.
- Requirements: Familiarize yourself with the inspection requirements in your area.
- Preparation: Ensure your vehicle is in good working order before the inspection.
- Benefits: Avoid failing the inspection and potential fines.
40. Get Expert Help from CARDIAGTECH.NET
Don’t let an “ABS ESP inoperative” warning compromise your safety. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today for expert advice, diagnostic tools, and replacement parts. Our team of experienced technicians is ready to help you diagnose and resolve any ABS/ESP issues in your Mercedes Benz. Visit us at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, or reach out via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Explore our website CARDIAGTECH.NET for more information and to view our product offerings. Act now and ensure your Mercedes Benz is safe and reliable!
-
What does “ABS ESP inoperative” mean on my Mercedes?
It indicates a malfunction in the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) or Electronic Stability Program (ESP), which are crucial for vehicle stability and safety. -
Can I drive with the ABS and ESP lights on?
It’s not recommended, as your vehicle’s stability and braking systems may be compromised. Drive cautiously and get it checked as soon as possible. -
What are the common causes of ABS/ESP failure in Mercedes Benz?
Common causes include faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor issues, low battery voltage, and damaged wiring. -
How can I diagnose the problem myself?
You can perform a visual inspection, check battery voltage, and use an OBD-II scanner to read error codes. -
What tools do I need for ABS/ESP diagnosis and repair?
You’ll need an OBD-II scanner, multimeter, ABS sensor tester, and possibly steering angle sensor calibration tools. Find these and more at CARDIAGTECH.NET. -
Are aftermarket modifications affecting my ABS/ESP system?
Non-compatible wheels, tires, or suspension components can interfere with ESP. Ensure all aftermarket parts are compatible with your vehicle. -
How much does it cost to repair ABS/ESP issues on a Mercedes Benz?
Costs vary depending on the problem and parts needed, but it’s best to get estimates from multiple repair shops. -
Can low battery voltage cause ABS/ESP problems?
Yes, insufficient voltage can cause electronic systems like ABS and ESP to malfunction. -
Where can I find genuine Mercedes Benz parts for ABS/ESP repairs?
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of genuine and high-quality aftermarket parts for Mercedes Benz vehicles. -
How often should I have my ABS/ESP system checked?
Include ABS/ESP system checks as part of your regular vehicle maintenance, typically during annual servicing.
Remember, when you encounter the “ABS ESP inoperative” warning on your Mercedes Benz, addressing the issue promptly is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s safety and performance. CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to provide the tools, parts, and expertise you need to keep your Mercedes running smoothly and safely. Don’t hesitate to reach out for assistance!