The 2006 Mercedes C230 Esp Malfunction can be a frustrating issue, but CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to help you understand and resolve it. Addressing issues related to your Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is crucial for maintaining safety and vehicle control; potential causes range from sensor issues to more complex system failures. Let’s explore the importance of ESP, delve into the causes and troubleshooting steps for a malfunctioning ESP system in your 2006 Mercedes C230, and learn about diagnostic tools, wheel speed sensors, and steering angle sensors.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the 2006 Mercedes C230 ESP System
- 1.1. How ESP Works in a Mercedes C230
- 1.2. Significance of ESP in Vehicle Safety
- 2. Identifying the ESP Malfunction in Your 2006 C230
- 2.1. Common Symptoms of ESP Issues
- 2.2. Understanding the ESP Warning Light
- 2.3. Initial Checks Before Seeking Professional Help
- 3. Diagnosing the 2006 Mercedes C230 ESP Malfunction
- 3.1. Using OBD-II Scanners for ESP Diagnostics
- 3.2. Common Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) Related to ESP
- 3.3. Advanced Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
- 4. Troubleshooting Common Causes of ESP Malfunctions
- 4.1. Wheel Speed Sensor Issues
- 4.2. Steering Angle Sensor Problems
- 4.3. Yaw Rate and Lateral Acceleration Sensor Faults
- 4.4. ESP Control Unit Malfunctions
- 5. Step-by-Step Guide to Repairing ESP Issues
- 5.1. Replacing a Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
- 5.2. Calibrating the Steering Angle Sensor
- 5.3. Addressing Wiring Issues
- 6. Maintaining Your Mercedes C230 ESP System
- 6.1. Regular Maintenance Tips
- 6.2. The Importance of Proper Wheel Alignment
- 6.3. When to Seek Professional Assistance
- 7. Choosing the Right Parts and Tools
- 7.1. Selecting Quality Replacement Parts
- 7.2. Essential Tools for ESP Repair
- 7.3. Where to Buy Reliable Parts and Tools
- 8. Cost Considerations for ESP Repair
- 8.1. Estimated Costs for Common Repairs
- 8.2. Factors Affecting Repair Costs
- 8.3. Balancing DIY vs. Professional Repair
- 9. Safety Precautions During ESP Repairs
- 9.1. Essential Safety Gear
- 9.2. Disconnecting the Battery Safely
- 9.3. Handling Electronic Components with Care
- 10. Real-World Case Studies
- 10.1. Case Study 1: Wheel Speed Sensor Failure
- 10.2. Case Study 2: Steering Angle Sensor Miscalibration
- 10.3. Case Study 3: ESP Control Unit Corrosion
- 11. Innovations in ESP Technology
- 11.1. Advancements in Sensor Technology
- 11.2. Integration with Other Safety Systems
- 11.3. Future Trends in ESP Systems
- 12. Resources and Further Reading
- 12.1. Online Forums and Communities
- 12.2. Repair Manuals and Technical Documentation
- 12.3. Expert Blogs and Articles
- 13. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 13.1. What does the ESP warning light mean in my 2006 Mercedes C230?
- 13.2. Can I drive my Mercedes C230 with the ESP light on?
- 13.3. How do I reset the ESP system in my Mercedes C230?
- 13.4. What are common causes of ESP malfunction in a 2006 C230?
- 13.5. How much does it cost to repair an ESP malfunction?
- 13.6. Can I replace a wheel speed sensor myself?
- 13.7. Do I need to calibrate the steering angle sensor after a wheel alignment?
- 13.8. Where can I buy replacement parts for my ESP system?
- 13.9. How often should I have my ESP system checked?
- 13.10. Is ESP covered under warranty?
1. Understanding the 2006 Mercedes C230 ESP System
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in your 2006 Mercedes C230 is a vital safety feature designed to prevent skidding and maintain control in challenging driving conditions. The ESP system enhances vehicle stability by detecting and reducing loss of traction, especially during cornering. By automatically applying brakes to individual wheels and adjusting engine power, ESP helps the driver maintain directional control and prevent accidents. The ESP integrates with other systems such as ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) and TCS (Traction Control System) to provide comprehensive stability management.
1.1. How ESP Works in a Mercedes C230
The ESP system in the 2006 Mercedes C230 utilizes a network of sensors to monitor the vehicle’s behavior. These sensors include:
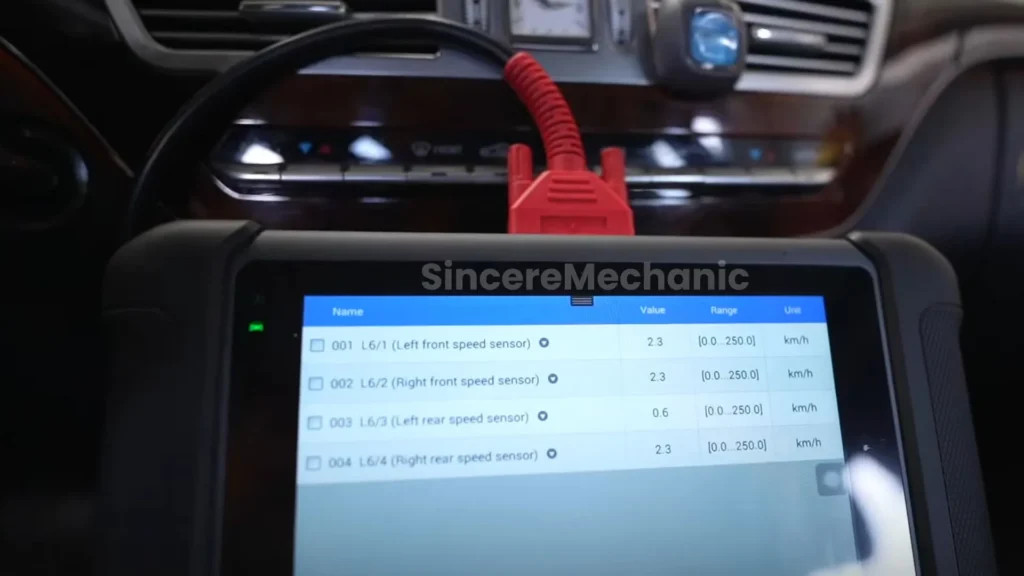
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Measure the rotational speed of each wheel.
- Steering Angle Sensor: Detects the angle of the steering wheel.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: Measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis.
- Lateral Acceleration Sensor: Detects sideways acceleration.
The ESP control unit processes this data and compares it to the driver’s intended path. If the system detects a deviation, such as oversteer (rear wheels losing traction) or understeer (front wheels losing traction), it intervenes by applying brakes to individual wheels and reducing engine power to bring the vehicle back under control.
1.2. Significance of ESP in Vehicle Safety
ESP is essential for vehicle safety, particularly in adverse conditions. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), ESP can reduce single-vehicle crashes by as much as 35%. For SUVs, the reduction is even higher, around 67%. This is because ESP helps drivers maintain control during emergency maneuvers, reducing the risk of rollovers and skidding. A properly functioning ESP system can be the difference between a safe drive and a collision.
2. Identifying the ESP Malfunction in Your 2006 C230
Recognizing the signs of an ESP malfunction is crucial for timely intervention. Here are common indicators that your 2006 Mercedes C230 may have an ESP issue.
2.1. Common Symptoms of ESP Issues
- ESP Warning Light: The most obvious sign is the ESP warning light illuminating on the dashboard. This light typically looks like a car skidding.
- Reduced Stability: The vehicle feels less stable, especially when cornering or driving on slippery surfaces.
- Erratic Braking: The brakes may apply unevenly or unexpectedly.
- Loss of Traction: The vehicle may lose traction more easily, even in normal driving conditions.
- ABS Light Illumination: Since ESP integrates with ABS, an ABS warning light may also appear.
2.2. Understanding the ESP Warning Light
The ESP warning light can indicate different states:
- Flashing: The ESP system is actively engaged, working to stabilize the vehicle. This is normal during slippery conditions or emergency maneuvers.
- Solid Illumination: The ESP system is disabled or malfunctioning. This requires investigation and repair.
- Intermittent Illumination: The ESP system may be experiencing intermittent issues, which can be harder to diagnose.
2.3. Initial Checks Before Seeking Professional Help
Before heading to a mechanic, perform these initial checks:
- Check Tire Pressure: Ensure all tires are properly inflated. Uneven tire pressure can affect ESP performance.
- Inspect Wheel Speed Sensors: Look for any visible damage or debris near the wheel speed sensors.
- Check the ESP Button: Ensure the ESP button (if equipped) has not been accidentally pressed, disabling the system.
- Restart the Vehicle: Sometimes, a simple restart can reset the system and clear the warning light.
- Scan for Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to check for any stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the ESP system.
3. Diagnosing the 2006 Mercedes C230 ESP Malfunction
Effective diagnosis is key to resolving ESP malfunctions. Here’s how to approach the diagnostic process.
3.1. Using OBD-II Scanners for ESP Diagnostics
An OBD-II scanner is essential for reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the vehicle’s computer. These codes provide valuable information about the nature and location of the problem.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD-II scanner into the diagnostic port, usually located under the dashboard.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Read the Codes: Follow the scanner’s instructions to read and record any stored DTCs.
- Interpret the Codes: Consult a reliable source or database to interpret the meaning of each code. Common ESP-related codes include those related to wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, and the ESP control unit.
3.2. Common Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) Related to ESP
- C1100, C1101, C1102, C1103: Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
- C1120: Steering Angle Sensor Malfunction.
- C1140: Yaw Rate Sensor Malfunction.
- C1175: BAS (Brake Assist System) Malfunction.
- C1200: ESP Control Unit Malfunction.
3.3. Advanced Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
For more in-depth diagnostics, consider using advanced tools such as:
- Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis: A dealer-level diagnostic system that provides comprehensive access to the vehicle’s control units and sensors.
- Multimeter: To check the continuity and voltage of sensor circuits.
- Oscilloscope: To analyze sensor signals and identify intermittent issues.
Step-by-Step Diagnostic Process:
- Verify the Code: Confirm that the DTC is valid and not a result of a temporary issue.
- Inspect Wiring and Connectors: Check for any damaged, corroded, or loose wiring and connectors related to the affected sensor or control unit.
- Test the Sensor: Use a multimeter or oscilloscope to test the sensor’s output signal. Compare the signal to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Check the Control Unit: If the sensor tests good, the problem may lie within the ESP control unit. Check for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Perform a System Test: Use a diagnostic tool to perform a system test of the ESP components. This can help identify any additional issues.
4. Troubleshooting Common Causes of ESP Malfunctions
Addressing the root causes of ESP malfunctions can restore your 2006 Mercedes C230’s stability.
4.1. Wheel Speed Sensor Issues
Wheel speed sensors are crucial for ESP operation. Common issues include:
- Damaged Sensors: Physical damage from road debris or accidents.
- Dirty Sensors: Accumulation of dirt and grime affecting sensor accuracy.
- Faulty Wiring: Damaged or corroded wiring causing signal interruption.
- Loose Connections: Loose connectors preventing proper signal transmission.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Visual Inspection: Check the sensor for any visible damage or debris.
- Cleaning: Clean the sensor and the surrounding area with a soft cloth.
- Wiring Check: Inspect the wiring for any damage or corrosion.
- Continuity Test: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the sensor circuit.
- Replacement: If the sensor is faulty, replace it with a new one.
4.2. Steering Angle Sensor Problems
The steering angle sensor provides essential data for ESP. Common issues include:
- Misalignment: Sensor not properly calibrated after wheel alignment.
- Contamination: Dirt or debris interfering with sensor accuracy.
- Electrical Faults: Damaged wiring or internal sensor failure.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Calibration: Recalibrate the steering angle sensor using a diagnostic tool.
- Inspection: Check the sensor for any visible damage or contamination.
- Wiring Check: Inspect the wiring for any damage or corrosion.
- Replacement: If the sensor is faulty, replace it with a new one.
4.3. Yaw Rate and Lateral Acceleration Sensor Faults
These sensors work together to provide information about the vehicle’s movement. Common issues include:
- Sensor Failure: Internal sensor malfunction due to age or damage.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged or corroded wiring causing signal interruption.
- Mounting Problems: Loose or improper sensor mounting affecting accuracy.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Visual Inspection: Check the sensor for any visible damage or loose mounting.
- Wiring Check: Inspect the wiring for any damage or corrosion.
- Signal Test: Use an oscilloscope to test the sensor’s output signal.
- Replacement: If the sensor is faulty, replace it with a new one.
4.4. ESP Control Unit Malfunctions
The ESP control unit processes sensor data and commands the system’s interventions. Common issues include:
- Software Glitches: Temporary software issues that can be resolved with a reset.
- Internal Failure: Permanent failure of the control unit due to age or damage.
- Corrosion: Corrosion on the control unit’s connectors.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Reset: Try resetting the control unit by disconnecting the battery for a few minutes.
- Inspection: Check the control unit and its connectors for any signs of corrosion.
- Software Update: Check for any available software updates for the control unit.
- Replacement: If the control unit is faulty, replace it with a new or refurbished unit.
5. Step-by-Step Guide to Repairing ESP Issues
Follow this guide to address ESP malfunctions in your 2006 Mercedes C230.
5.1. Replacing a Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
Tools Needed:
- New wheel speed sensor
- Wrench set
- Socket set
- Screwdriver
- OBD-II scanner
Steps:
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical accidents.
- Locate the Sensor: Locate the faulty wheel speed sensor on the affected wheel.
- Remove the Wheel: Remove the wheel to access the sensor.
- Disconnect the Sensor: Disconnect the sensor’s electrical connector.
- Remove the Sensor: Remove the sensor from its mounting location. This may require unscrewing or unclipping it.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor in the reverse order of removal.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Clear the Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear any stored DTCs.
- Test the System: Test drive the vehicle to ensure the ESP system is functioning properly.
5.2. Calibrating the Steering Angle Sensor
Tools Needed:
- Diagnostic tool capable of steering angle sensor calibration
Steps:
- Connect the Diagnostic Tool: Connect the diagnostic tool to the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Access the ESP System: Navigate to the ESP system menu in the diagnostic tool.
- Select Calibration Function: Select the steering angle sensor calibration function.
- Follow Instructions: Follow the diagnostic tool’s instructions to calibrate the sensor. This usually involves turning the steering wheel to specific angles.
- Verify Calibration: Verify that the calibration is successful by checking the sensor’s output in the diagnostic tool.
- Clear the Codes: Clear any stored DTCs related to the steering angle sensor.
- Test the System: Test drive the vehicle to ensure the ESP system is functioning properly.
5.3. Addressing Wiring Issues
Tools Needed:
- Multimeter
- Wiring diagram
- Electrical tape or heat shrink tubing
- Wire stripper
- Crimping tool
Steps:
- Identify the Faulty Wiring: Use a wiring diagram and a multimeter to identify the damaged or corroded wiring.
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Repair the Wiring: Repair the wiring by splicing in a new section of wire or cleaning and reconnecting corroded connectors.
- Insulate the Repair: Insulate the repair with electrical tape or heat shrink tubing.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Clear the Codes: Clear any stored DTCs related to the repaired circuit.
- Test the System: Test drive the vehicle to ensure the ESP system is functioning properly.
6. Maintaining Your Mercedes C230 ESP System
Regular maintenance can prevent ESP malfunctions and ensure optimal performance.
6.1. Regular Maintenance Tips
- Check Tire Pressure: Maintain proper tire pressure to ensure accurate ESP operation.
- Inspect Wheel Speed Sensors: Periodically inspect wheel speed sensors for damage or debris.
- Keep Sensors Clean: Clean sensors regularly to prevent build-up of dirt and grime.
- Check Wiring: Inspect wiring and connectors for damage or corrosion.
- Recalibrate Sensors: Recalibrate sensors after wheel alignments or suspension work.
6.2. The Importance of Proper Wheel Alignment
Proper wheel alignment is crucial for ESP performance. Misalignment can cause the steering angle sensor to provide inaccurate data, leading to ESP malfunctions. Ensure that your vehicle’s wheels are properly aligned according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
6.3. When to Seek Professional Assistance
While some ESP issues can be resolved with DIY repairs, others require professional assistance. Seek a qualified mechanic if:
- You are not comfortable working on your vehicle’s electrical system.
- You lack the necessary diagnostic tools.
- The problem persists after performing basic troubleshooting steps.
- The ESP control unit is suspected to be faulty.
7. Choosing the Right Parts and Tools
Using high-quality parts and tools is essential for reliable ESP repairs.
7.1. Selecting Quality Replacement Parts
- OEM Parts: Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) parts are designed to meet the exact specifications of your vehicle.
- Aftermarket Parts: Choose reputable brands with a proven track record of quality and reliability.
7.2. Essential Tools for ESP Repair
- OBD-II Scanner: A reliable OBD-II scanner for reading and clearing DTCs.
- Multimeter: For testing wiring and sensor circuits.
- Socket and Wrench Set: For removing and installing sensors and components.
- Wiring Repair Kit: For repairing damaged wiring.
- Diagnostic Software: Advanced diagnostic software for in-depth system analysis.
7.3. Where to Buy Reliable Parts and Tools
- Authorized Dealerships: Dealerships offer OEM parts and expert advice.
- Reputable Auto Parts Stores: Auto parts stores offer a wide selection of aftermarket parts and tools.
- Online Retailers: Online retailers offer competitive prices and a convenient shopping experience. CARDIAGTECH.NET can assist you with your needs; contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880.
8. Cost Considerations for ESP Repair
Understanding the costs associated with ESP repair can help you budget effectively.
8.1. Estimated Costs for Common Repairs
- Wheel Speed Sensor Replacement: $150 – $300 per sensor.
- Steering Angle Sensor Calibration: $80 – $150.
- Steering Angle Sensor Replacement: $200 – $400.
- Yaw Rate Sensor Replacement: $250 – $500.
- ESP Control Unit Replacement: $500 – $1500.
8.2. Factors Affecting Repair Costs
- Vehicle Model: Some models may have more complex ESP systems, increasing repair costs.
- Part Quality: OEM parts are generally more expensive than aftermarket parts.
- Labor Rates: Labor rates vary depending on the location and the mechanic’s expertise.
8.3. Balancing DIY vs. Professional Repair
Consider your skills, tools, and comfort level when deciding between DIY and professional repair. DIY repairs can save money, but professional repairs offer expertise and peace of mind.
9. Safety Precautions During ESP Repairs
Prioritize safety when working on your vehicle’s ESP system.
9.1. Essential Safety Gear
- Safety Glasses: Protect your eyes from debris and chemicals.
- Gloves: Protect your hands from dirt, grease, and chemicals.
- Work Clothes: Wear appropriate work clothes to protect your skin.
9.2. Disconnecting the Battery Safely
Always disconnect the negative terminal of the battery before working on the electrical system. This prevents electrical shocks and damage to the vehicle’s electronics.
9.3. Handling Electronic Components with Care
Handle electronic components with care to avoid damage. Avoid touching the pins or circuits on sensors and control units. Store electronic components in a safe place away from moisture and static electricity.
10. Real-World Case Studies
10.1. Case Study 1: Wheel Speed Sensor Failure
Scenario: A 2006 Mercedes C230 exhibited an ESP warning light and erratic braking.
Diagnosis: OBD-II scan revealed a fault code related to the left front wheel speed sensor.
Solution: The wheel speed sensor was replaced, and the fault code was cleared. The ESP system returned to normal operation.
10.2. Case Study 2: Steering Angle Sensor Miscalibration
Scenario: A 2006 Mercedes C230 exhibited an ESP warning light after a wheel alignment.
Diagnosis: Diagnostic tool indicated that the steering angle sensor was miscalibrated.
Solution: The steering angle sensor was recalibrated using a diagnostic tool. The ESP system returned to normal operation.
10.3. Case Study 3: ESP Control Unit Corrosion
Scenario: A 2006 Mercedes C230 exhibited an ESP warning light and multiple sensor fault codes.
Diagnosis: Inspection revealed corrosion on the ESP control unit connectors.
Solution: The corroded connectors were cleaned, and the ESP control unit was replaced. The ESP system returned to normal operation.
11. Innovations in ESP Technology
ESP technology continues to evolve, offering improved safety and performance.
11.1. Advancements in Sensor Technology
Newer ESP systems use more advanced sensors, such as:
- High-Resolution Wheel Speed Sensors: Provide more accurate data for precise ESP operation.
- Multi-Axis Yaw Rate Sensors: Offer improved measurement of vehicle rotation.
- Integrated Sensor Clusters: Combine multiple sensors into a single unit for enhanced reliability.
11.2. Integration with Other Safety Systems
ESP is increasingly integrated with other safety systems, such as:
- Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC): ACC uses ESP data to maintain a safe distance from other vehicles.
- Lane Departure Warning (LDW): LDW uses ESP data to detect unintentional lane departures.
- Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB): AEB uses ESP data to initiate emergency braking in critical situations.
11.3. Future Trends in ESP Systems
Future trends in ESP systems include:
- Predictive ESP: Systems that anticipate potential stability issues based on driver behavior and road conditions.
- Cloud-Based ESP: Systems that use cloud data to optimize ESP performance in real-time.
- AI-Enhanced ESP: Systems that use artificial intelligence to learn and adapt to different driving conditions.
12. Resources and Further Reading
Access additional resources to deepen your understanding of ESP systems.
12.1. Online Forums and Communities
- Mercedes-Benz Forums: Online forums where owners share information and experiences.
- Automotive Repair Forums: Online forums dedicated to automotive repair and maintenance.
12.2. Repair Manuals and Technical Documentation
- Mercedes-Benz Repair Manuals: Detailed repair manuals specific to your vehicle model.
- Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs): Information from the manufacturer about common issues and repairs.
12.3. Expert Blogs and Articles
- Automotive Blogs: Blogs written by automotive experts and enthusiasts.
- Technical Articles: Articles that provide in-depth information about automotive technology.
13. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
13.1. What does the ESP warning light mean in my 2006 Mercedes C230?
The ESP warning light indicates that the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is either actively engaged or malfunctioning. If the light is flashing, ESP is working to stabilize the vehicle. If the light is solid, ESP is disabled or has a fault.
13.2. Can I drive my Mercedes C230 with the ESP light on?
If the ESP light is flashing, it is generally safe to drive, but exercise caution. If the light is solid, it is best to avoid driving until the issue is resolved, as ESP is not functioning and stability could be compromised.
13.3. How do I reset the ESP system in my Mercedes C230?
Try turning the steering wheel lock to lock (full left to full right) while parked. If this doesn’t work, use an OBD-II scanner to clear any stored fault codes.
13.4. What are common causes of ESP malfunction in a 2006 C230?
Common causes include faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor issues, yaw rate sensor faults, and problems with the ESP control unit.
13.5. How much does it cost to repair an ESP malfunction?
Repair costs vary depending on the issue. Wheel speed sensor replacement can range from $150 to $300, while ESP control unit replacement can range from $500 to $1500.
13.6. Can I replace a wheel speed sensor myself?
Yes, if you have basic mechanical skills and the right tools. Follow the steps outlined in this guide.
13.7. Do I need to calibrate the steering angle sensor after a wheel alignment?
Yes, recalibration is often necessary to ensure accurate ESP operation.
13.8. Where can I buy replacement parts for my ESP system?
You can buy replacement parts from authorized dealerships, reputable auto parts stores, and online retailers. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET for assistance at +1 (641) 206-8880.
13.9. How often should I have my ESP system checked?
Have your ESP system checked during regular maintenance intervals, or if you notice any warning lights or stability issues.
13.10. Is ESP covered under warranty?
ESP may be covered under the vehicle’s warranty, depending on the terms and the age/mileage of the vehicle. Check your warranty documentation for details.
Facing ESP issues with your 2006 Mercedes C230 can be daunting, especially given the complexities of modern automotive systems. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the challenges you face and are dedicated to providing solutions that enhance your efficiency, precision, and safety.
Are you tired of spending countless hours diagnosing and repairing ESP malfunctions? Do you wish you had access to tools that could streamline your work, reduce errors, and boost customer satisfaction?
Here’s how CARDIAGTECH.NET can help:
- Advanced Diagnostic Tools: Our range of OBD-II scanners, multimeters, and diagnostic software ensures you can accurately identify and resolve ESP issues. These tools provide real-time data, fault code analysis, and system testing capabilities, allowing you to pinpoint problems quickly.
- High-Quality Replacement Parts: We offer a comprehensive selection of OEM and aftermarket parts, including wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, yaw rate sensors, and ESP control units. Sourcing reliable parts from CARDIAGTECH.NET ensures your repairs are durable and effective.
- Expert Support and Training: Our team of experienced technicians is available to provide support and guidance. Whether you need help diagnosing a complex issue or understanding how to use a particular tool, we’re here to assist you every step of the way. We also offer training programs to keep you updated with the latest automotive technologies and repair techniques.
- Cost-Effective Solutions: We understand the importance of managing your budget. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides competitive pricing on all our products and services, helping you reduce costs without compromising quality. Our goal is to offer solutions that increase your profitability and customer loyalty.
Don’t let ESP malfunctions slow you down. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today and discover how our tools and expertise can transform your approach to automotive repair.
- Address: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CARDIAGTECH.NET
Contact us now for a consultation and take the first step towards optimizing your automotive repair capabilities.