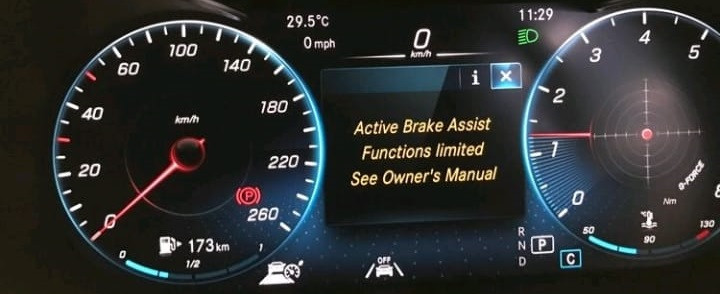
Mercedes-Benz Blind Spot Assist Inoperative? CARDIAGTECH.NET offers comprehensive solutions to diagnose and fix this issue, ensuring your safety systems function optimally. Our expertise extends to troubleshooting and resolving blind spot assist malfunctions, guaranteeing a safer driving experience. Trust CARDIAGTECH.NET for reliable blind spot assist repairs and advanced diagnostic tools.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Mercedes-Benz Blind Spot Assist
- 1.1. How the System Works
- 1.2. Benefits of Blind Spot Assist
- 2. Common Causes of “Blind Spot Assist Inoperative” Message
- 2.1. Dirty or Obstructed Sensors
- 2.2. Sensor Malfunction or Damage
- 2.3. Electrical Issues
- 2.4. Software Glitches
- 2.5. Misalignment of Sensors
- 3. Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
- 3.1. Initial Inspection
- 3.2. Advanced Diagnostics
- 3.3. Professional Assistance
- 4. Tools and Equipment for Diagnosing and Repairing Blind Spot Assist
- 4.1. Diagnostic Tools
- 4.2. Electrical Testing Equipment
- 4.3. Hand Tools
- 4.4. Calibration Equipment
- 5. Step-by-Step Repair Guide: Replacing a Radar Sensor
- 5.1. Preparation
- 5.2. Removal
- 5.3. Installation
- 5.4. Calibration
- 6. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Intermittent Issues
- 6.1. Data Logging
- 6.2. Freeze Frame Data Analysis
- 6.3. Component Testing
- 6.4. Visual Inspection
- 7. Software Updates and Recalibration Procedures
- 7.1. Software Updates
- 7.2. Recalibration Procedures
- 8. Case Studies: Real-World Diagnostic Scenarios
- 8.1. Case Study 1: Sensor Misalignment After Minor Collision
- 8.2. Case Study 2: Wiring Corrosion Due to Road Salt
- 8.3. Case Study 3: Software Bug Causing False Alarms
- 9. Preventive Maintenance Tips for Long-Term Reliability
- 9.1. Regular Cleaning
- 9.2. Visual Inspections
- 9.3. Software Updates
- 9.4. Professional Inspections
- 10. The Future of Blind Spot Assist Technology
- 10.1. Advanced Sensors
- 10.2. Sophisticated Algorithms
- 10.3. Tighter Integration
- Q1: What does “Blind Spot Assist Inoperative” mean on my Mercedes-Benz?
- Q2: What are the common causes of this message?
- Q3: Can I fix the “Blind Spot Assist Inoperative” issue myself?
- Q4: How do I clean the radar sensors?
- Q5: What tools are needed for diagnosing Blind Spot Assist issues?
- Q6: How often should I have my Blind Spot Assist system checked?
- Q7: Can software updates fix Blind Spot Assist problems?
- Q8: What happens if I ignore the “Blind Spot Assist Inoperative” message?
- Q9: Where are the blind spot sensors located on a Mercedes-Benz?
- Q10: How can CARDIAGTECH.NET help with this issue?
1. Understanding Mercedes-Benz Blind Spot Assist
Mercedes-Benz Blind Spot Assist is a crucial safety feature designed to alert drivers to vehicles in their blind spots. Using radar sensors, it monitors the areas alongside and behind the vehicle, providing visual and audible warnings when a vehicle is detected. This system significantly reduces the risk of accidents during lane changes and merges.
1.1. How the System Works
The Blind Spot Assist system uses radar sensors, typically located in the rear bumper, to detect vehicles in the adjacent lanes. When a vehicle enters the blind spot, a visual warning appears in the corresponding side mirror. If the driver activates the turn signal, an audible warning may also sound, further alerting the driver to the potential hazard.
- Radar Sensors: Continuously monitor the areas beside and behind the vehicle.
- Visual Warnings: Illuminated icons in the side mirrors.
- Audible Warnings: Sound when the turn signal is activated with a vehicle in the blind spot.
1.2. Benefits of Blind Spot Assist
- Enhanced Safety: Reduces the risk of accidents during lane changes.
- Increased Awareness: Provides drivers with critical information about their surroundings.
- Reduced Driver Fatigue: Helps drivers maintain awareness without constant visual checks.
- Improved Confidence: Offers peace of mind, especially in heavy traffic.
2. Common Causes of “Blind Spot Assist Inoperative” Message
When the “Blind Spot Assist Inoperative” message appears on your Mercedes-Benz dashboard, it indicates that the system is not functioning correctly. Several factors can trigger this message, ranging from simple sensor obstructions to more complex electrical issues. Identifying the root cause is essential for effective repair.
2.1. Dirty or Obstructed Sensors
One of the most common causes is dirt, mud, snow, or ice obstructing the radar sensors. These sensors need a clear field of vision to function correctly.
- Symptoms: Message appears intermittently, especially in bad weather.
- Solution: Clean the radar sensors located in the rear bumper. Use a soft cloth and mild detergent. Avoid using high-pressure washers, which can damage the sensors.
Image: Example of dirty radar sensors on a Mercedes-Benz bumper.
2.2. Sensor Malfunction or Damage
Physical damage to the radar sensors, such as cracks or disconnections, can cause the system to fail. This can occur due to minor collisions, road debris, or even wear and tear.
- Symptoms: Message appears consistently, regardless of weather conditions.
- Solution: Inspect the sensors for visible damage. If damaged, the sensor will need to be replaced. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET at +1 (641) 206-8880 for assistance in acquiring replacement sensors.
2.3. Electrical Issues
Wiring problems, such as loose connections, damaged wires, or corrosion, can disrupt the signal between the sensors and the vehicle’s control unit. Low battery voltage can also cause the system to malfunction.
- Symptoms: Intermittent or constant message, possibly accompanied by other electrical issues.
- Solution: Check the wiring connections to the sensors. Ensure they are secure and free from corrosion. Test the battery voltage to ensure it is within the proper range. A multimeter can be used for these tests.
2.4. Software Glitches
Software bugs or outdated software can sometimes cause the Blind Spot Assist system to malfunction. These glitches can disrupt the communication between the sensors and the vehicle’s computer.
- Symptoms: Message appears without any apparent physical cause.
- Solution: Try resetting the system by turning off the car, waiting a few minutes, and then restarting. If the problem persists, the software may need to be updated by a certified Mercedes-Benz technician.
2.5. Misalignment of Sensors
If the vehicle has been involved in a minor collision or the rear bumper has been removed and reinstalled, the radar sensors may become misaligned. Proper alignment is crucial for accurate detection.
- Symptoms: Message appears after a recent collision or bumper repair.
- Solution: Have the sensors realigned by a professional technician. This requires specialized equipment to ensure precise calibration.
3. Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
When faced with the “Blind Spot Assist Inoperative” message, following a systematic troubleshooting process can help identify and resolve the issue efficiently. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to diagnosing the problem.
3.1. Initial Inspection
- Step 1: Check the Sensors: Visually inspect the radar sensors in the rear bumper. Look for any signs of dirt, debris, or physical damage.
- Step 2: Clean the Sensors: If the sensors are dirty, gently clean them with a soft cloth and mild detergent. Ensure they are completely dry before proceeding.
- Step 3: Restart the Vehicle: Turn off the car, wait a few minutes, and then restart. This can sometimes reset the system and clear the message.
3.2. Advanced Diagnostics
If the initial inspection doesn’t resolve the issue, more advanced diagnostics may be necessary.
- Step 1: Use a Diagnostic Tool: Connect a diagnostic tool (such as the Xentry diagnostic pad) to the vehicle’s OBD-II port. Scan for any fault codes related to the Blind Spot Assist system.
- Step 2: Interpret Fault Codes: Refer to the vehicle’s service manual or a reliable online database to interpret the fault codes. This will provide more specific information about the nature of the problem.
- Step 3: Check Wiring Connections: Inspect the wiring connections to the radar sensors. Look for loose connections, damaged wires, or corrosion. Use a multimeter to test the continuity of the wires.
- Step 4: Test Sensor Functionality: If possible, use the diagnostic tool to test the functionality of each radar sensor. This can help determine if a sensor is malfunctioning and needs to be replaced.
3.3. Professional Assistance
If you are unable to diagnose or resolve the issue using the above steps, it is best to seek professional assistance.
- Step 1: Contact a Certified Technician: Contact a certified Mercedes-Benz technician or a reputable auto repair shop with experience in Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Step 2: Provide Detailed Information: Provide the technician with as much information as possible about the problem, including the symptoms, fault codes, and any troubleshooting steps you have already taken.
- Step 3: Follow Technician’s Recommendations: Follow the technician’s recommendations for repair. This may involve replacing a sensor, repairing wiring, or updating software.
4. Tools and Equipment for Diagnosing and Repairing Blind Spot Assist
Diagnosing and repairing a malfunctioning Blind Spot Assist system often requires specialized tools and equipment. Having the right tools on hand can streamline the troubleshooting process and ensure accurate repairs.
4.1. Diagnostic Tools
- OBD-II Scanner: An OBD-II scanner is essential for reading fault codes from the vehicle’s computer. This tool can provide valuable information about the nature of the problem.
- Xentry Diagnostic Pad: The Xentry diagnostic pad is a specialized tool designed specifically for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. It offers advanced diagnostic capabilities, including the ability to test sensor functionality and update software.
Image: Example of a Xentry diagnostic pad being used on a Mercedes-Benz.
4.2. Electrical Testing Equipment
- Multimeter: A multimeter is used to test the continuity of wires, measure voltage, and check for shorts in the electrical system.
- Wiring Diagram: A wiring diagram provides a detailed map of the electrical connections in the Blind Spot Assist system. This is essential for tracing wires and identifying potential problems.
4.3. Hand Tools
- Socket Set: A socket set is needed for removing and installing the radar sensors.
- Wrench Set: A wrench set is used for tightening and loosening bolts and nuts.
- Screwdriver Set: A screwdriver set is needed for removing and installing screws.
4.4. Calibration Equipment
- Radar Alignment Tool: A radar alignment tool is used to ensure the radar sensors are properly aligned after being removed or adjusted. This tool is essential for accurate detection.
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of diagnostic tools and equipment to assist in diagnosing and repairing Blind Spot Assist systems. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 to learn more about our products.
5. Step-by-Step Repair Guide: Replacing a Radar Sensor
If a radar sensor is found to be malfunctioning, it will need to be replaced. This step-by-step guide provides instructions on how to replace a radar sensor on a Mercedes-Benz vehicle.
5.1. Preparation
- Step 1: Gather Tools and Equipment: Gather the necessary tools and equipment, including a socket set, wrench set, screwdriver set, diagnostic tool, and the new radar sensor.
- Step 2: Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical shock.
- Step 3: Locate the Radar Sensor: Locate the radar sensor in the rear bumper. Refer to the vehicle’s service manual for the exact location.
5.2. Removal
- Step 1: Remove the Bumper Cover: Remove the bumper cover to access the radar sensor. This may involve removing screws, bolts, or clips.
- Step 2: Disconnect the Electrical Connector: Disconnect the electrical connector from the radar sensor.
- Step 3: Remove the Sensor: Remove the radar sensor from its mounting bracket. This may involve removing screws or bolts.
5.3. Installation
- Step 1: Install the New Sensor: Install the new radar sensor into the mounting bracket.
- Step 2: Connect the Electrical Connector: Connect the electrical connector to the radar sensor.
- Step 3: Reinstall the Bumper Cover: Reinstall the bumper cover.
- Step 4: Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
5.4. Calibration
- Step 1: Calibrate the Sensor: Use a radar alignment tool to calibrate the new radar sensor. This is essential for accurate detection.
- Step 2: Clear Fault Codes: Use a diagnostic tool to clear any fault codes related to the Blind Spot Assist system.
- Step 3: Test the System: Test the Blind Spot Assist system to ensure it is functioning correctly.
6. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Intermittent Issues
Intermittent issues with the Blind Spot Assist system can be particularly challenging to diagnose. These problems may occur sporadically and may not always trigger fault codes. Advanced diagnostic techniques can help identify the root cause of these elusive issues.
6.1. Data Logging
- Technique: Use a diagnostic tool to log data from the Blind Spot Assist system while driving. This can capture real-time information about sensor readings, communication signals, and other relevant parameters.
- Benefits: Data logging can help identify patterns or anomalies that may not be apparent during a static diagnostic test.
- Example: Log sensor readings while driving on different types of roads and in different weather conditions. Analyze the data to see if there are any correlations between sensor performance and external factors.
6.2. Freeze Frame Data Analysis
- Technique: When a fault code is triggered, the vehicle’s computer stores a snapshot of the system’s operating conditions at the time of the fault. This “freeze frame” data can provide valuable clues about the cause of the problem.
- Benefits: Freeze frame data can help identify specific conditions that may be contributing to the intermittent issue.
- Example: Analyze the freeze frame data to see if the fault occurred when the vehicle was traveling at a certain speed, in a certain gear, or under certain environmental conditions.
6.3. Component Testing
- Technique: Individually test the components of the Blind Spot Assist system to ensure they are functioning correctly. This may involve using a multimeter to test the continuity of wires, measuring voltage, and checking for shorts.
- Benefits: Component testing can help isolate a faulty component that may be causing the intermittent issue.
- Example: Test the radar sensors to ensure they are transmitting and receiving signals correctly. Test the wiring connections to ensure they are secure and free from corrosion.
6.4. Visual Inspection
- Technique: Conduct a thorough visual inspection of the Blind Spot Assist system, looking for any signs of damage, wear, or corrosion.
- Benefits: Visual inspection can help identify obvious problems that may be contributing to the intermittent issue.
- Example: Inspect the radar sensors for cracks or other damage. Inspect the wiring connections for loose connections or corrosion.
7. Software Updates and Recalibration Procedures
Software updates and recalibration procedures are essential for maintaining the proper functioning of the Blind Spot Assist system. These procedures ensure that the system is operating with the latest software and that the radar sensors are properly aligned.
7.1. Software Updates
- Purpose: Software updates address bugs, improve performance, and add new features to the Blind Spot Assist system.
- Procedure: Software updates are typically performed using a diagnostic tool, such as the Xentry diagnostic pad. The tool connects to the vehicle’s computer and downloads the latest software from Mercedes-Benz.
- Benefits: Software updates can resolve intermittent issues, improve sensor accuracy, and enhance the overall performance of the Blind Spot Assist system.
7.2. Recalibration Procedures
- Purpose: Recalibration ensures that the radar sensors are properly aligned and that the system is accurately detecting vehicles in the blind spots.
- Procedure: Recalibration is typically performed using a radar alignment tool. The tool is positioned in front of the vehicle, and the sensors are adjusted until they are properly aligned.
- Benefits: Recalibration ensures that the Blind Spot Assist system is accurately detecting vehicles in the blind spots, reducing the risk of accidents.
8. Case Studies: Real-World Diagnostic Scenarios
Examining real-world diagnostic scenarios can provide valuable insights into the complexities of troubleshooting Blind Spot Assist systems. These case studies illustrate common problems and effective solutions.
8.1. Case Study 1: Sensor Misalignment After Minor Collision
- Problem: A customer reported that the Blind Spot Assist system stopped working after a minor collision.
- Diagnosis: A diagnostic scan revealed a fault code indicating sensor misalignment.
- Solution: The radar sensors were realigned using a radar alignment tool. The fault code was cleared, and the system was tested to ensure it was functioning correctly.
8.2. Case Study 2: Wiring Corrosion Due to Road Salt
- Problem: A customer reported that the Blind Spot Assist system was intermittently failing during the winter months.
- Diagnosis: A visual inspection revealed corrosion on the wiring connections to the radar sensors.
- Solution: The corroded wiring connections were cleaned and repaired. The sensors were tested to ensure they were functioning correctly.
8.3. Case Study 3: Software Bug Causing False Alarms
- Problem: A customer reported that the Blind Spot Assist system was frequently issuing false alarms, even when there were no vehicles in the blind spots.
- Diagnosis: A diagnostic scan revealed no fault codes. However, a software update was available for the Blind Spot Assist system.
- Solution: The software was updated using a diagnostic tool. The false alarms stopped, and the system was functioning correctly.
9. Preventive Maintenance Tips for Long-Term Reliability
Preventive maintenance is key to ensuring the long-term reliability of the Blind Spot Assist system. Regular maintenance can help prevent problems from occurring in the first place and can extend the life of the system.
9.1. Regular Cleaning
- Tip: Regularly clean the radar sensors to remove dirt, debris, and other obstructions.
- Frequency: Clean the sensors every few months, or more often if you frequently drive in dirty or dusty conditions.
- Benefits: Regular cleaning can help prevent sensor malfunctions and can ensure accurate detection.
9.2. Visual Inspections
- Tip: Regularly inspect the radar sensors and wiring connections for any signs of damage, wear, or corrosion.
- Frequency: Inspect the sensors and wiring connections every time you wash your car or perform other maintenance tasks.
- Benefits: Visual inspections can help identify problems early, before they cause a system failure.
9.3. Software Updates
- Tip: Keep the Blind Spot Assist system’s software up-to-date.
- Frequency: Check for software updates every time you take your car in for service.
- Benefits: Software updates can address bugs, improve performance, and add new features to the Blind Spot Assist system.
9.4. Professional Inspections
- Tip: Have the Blind Spot Assist system professionally inspected every few years.
- Frequency: Schedule a professional inspection every two to three years, or more often if you frequently drive in harsh conditions.
- Benefits: Professional inspections can identify problems that may not be apparent during a visual inspection.
10. The Future of Blind Spot Assist Technology
Blind Spot Assist technology is constantly evolving, with new features and capabilities being developed all the time. The future of this technology is likely to include more advanced sensors, more sophisticated algorithms, and tighter integration with other safety systems.
10.1. Advanced Sensors
- Trend: Future Blind Spot Assist systems are likely to use more advanced sensors, such as lidar and radar, to provide more accurate and detailed information about the surrounding environment.
- Benefits: Advanced sensors can improve the accuracy of the system and can enable new features, such as pedestrian detection and cyclist detection.
10.2. Sophisticated Algorithms
- Trend: Future Blind Spot Assist systems are likely to use more sophisticated algorithms to analyze sensor data and make decisions about when to issue warnings.
- Benefits: Sophisticated algorithms can reduce the number of false alarms and can improve the overall performance of the system.
10.3. Tighter Integration
- Trend: Future Blind Spot Assist systems are likely to be more tightly integrated with other safety systems, such as lane departure warning and automatic emergency braking.
- Benefits: Tighter integration can create a more comprehensive safety net for drivers and can help prevent accidents.
Is your Mercedes-Benz Blind Spot Assist Inoperative? Don’t compromise on safety. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our location at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States for expert diagnostics and repair services. Let us help you restore your vehicle’s safety features and drive with confidence. Visit CARDIAGTECH.NET today!
Q1: What does “Blind Spot Assist Inoperative” mean on my Mercedes-Benz?
It means the Blind Spot Assist system isn’t functioning correctly, indicating a potential safety risk.
Q2: What are the common causes of this message?
Common causes include dirty sensors, sensor damage, electrical issues, software glitches, or sensor misalignment.
Q3: Can I fix the “Blind Spot Assist Inoperative” issue myself?
Simple issues like dirty sensors can be fixed by cleaning them. More complex problems require professional diagnosis and repair.
Q4: How do I clean the radar sensors?
Use a soft cloth and mild detergent to gently clean the sensors located in the rear bumper.
Q5: What tools are needed for diagnosing Blind Spot Assist issues?
Tools include an OBD-II scanner, multimeter, socket set, and possibly a Xentry diagnostic pad for advanced diagnostics.
Q6: How often should I have my Blind Spot Assist system checked?
Have it professionally inspected every two to three years, or more often if you frequently drive in harsh conditions.
Q7: Can software updates fix Blind Spot Assist problems?
Yes, software updates can address bugs, improve performance, and resolve certain issues.
Q8: What happens if I ignore the “Blind Spot Assist Inoperative” message?
Ignoring the message means driving without the safety benefits of the system, increasing the risk of accidents during lane changes.
Q9: Where are the blind spot sensors located on a Mercedes-Benz?
The sensors are typically located in the rear bumper, near the corners.
Q10: How can CARDIAGTECH.NET help with this issue?
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers expert diagnostics, repair services, and a range of diagnostic tools to help resolve Blind Spot Assist issues. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for assistance.